What Is Knowledge Management?
Knowledge management is the process of collecting, organizing, storing, and sharing knowledge within an organization to enhance efficiency, decision-making, and collaboration. It ensures that valuable insights, expertise, and best practices are easily accessible to employees, preventing knowledge loss and duplication of effort. A knowledge base is just one component of a comprehensive approach to a broader knowledge management strategy.
Organizations rely on knowledge management to improve productivity, foster innovation, and create a culture of continuous learning. Knowledge management aims to enhance organizational efficiency and ensure that crucial information is readily accessible to users when needed. A well-structured knowledge management system helps businesses maintain a competitive edge by ensuring employees have the information they need to work effectively.
Definition
Knowledge management is the systematic process of creating, identifying, capturing, organizing, storing, sharing, and utilizing knowledge to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It involves the strategic management of knowledge resources, including data, information, and expertise, to enhance organizational efficiency, foster innovation, and maintain a competitive edge. By effectively managing knowledge, organizations can ensure that valuable insights and best practices are readily accessible, driving continuous improvement and informed decision-making.
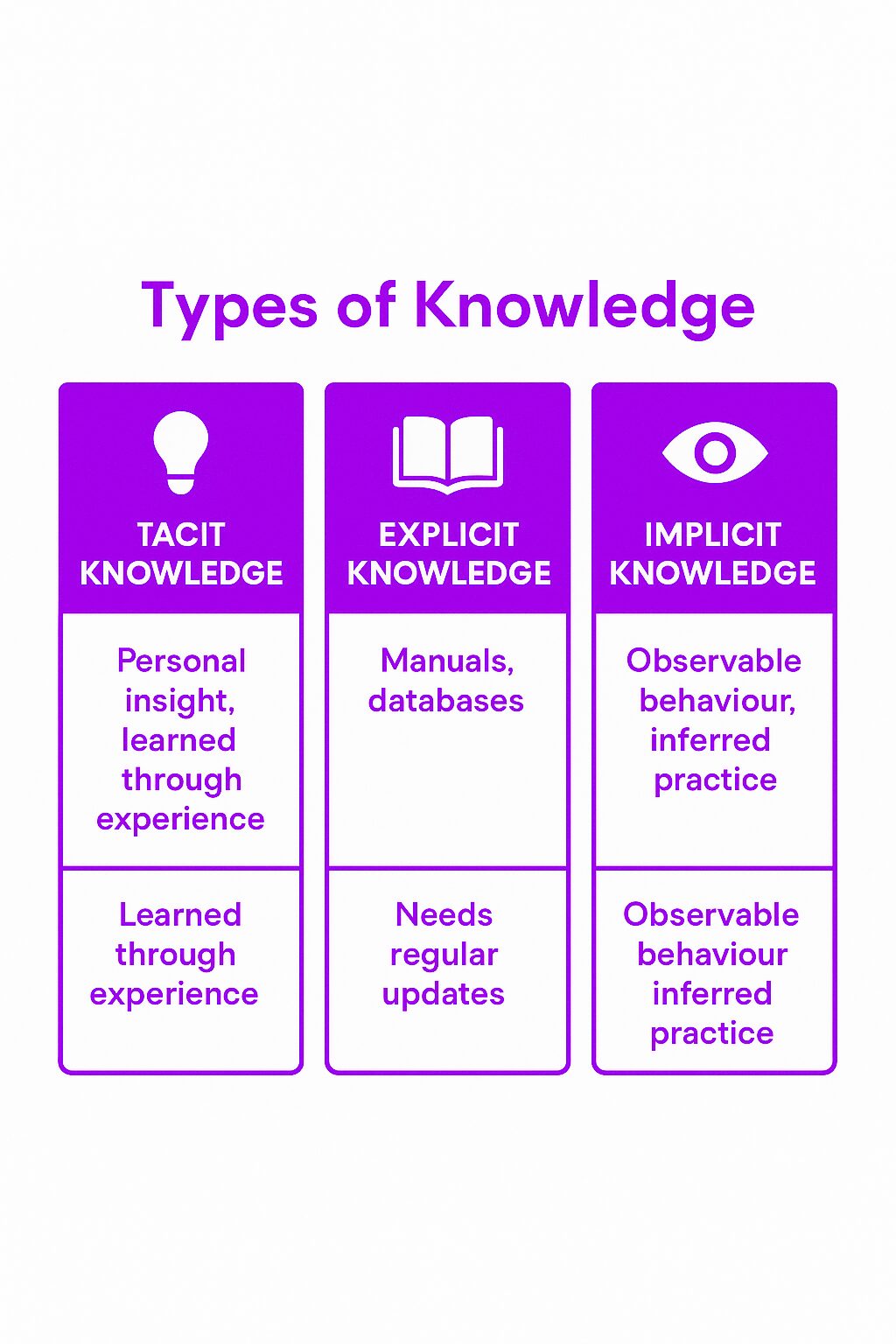
Types of Knowledge
Organizations need to manage various types of knowledge to ensure comprehensive knowledge management. These include:
-
Tacit Knowledge: Tacit knowledge is deeply personal and often gained through experience and practice. It includes insights, intuitions, and skills that are difficult to articulate and transfer to others. This type of knowledge is context-dependent and resides within individuals, making it challenging to capture and share.
-
Explicit Knowledge: Explicit knowledge is codified and can be easily articulated, documented, and transferred. It includes structured information such as manuals, reports, procedures, and databases. Explicit knowledge is often stored in digital repositories, making it accessible and easy to share across the organization.
-
Implicit Knowledge: Implicit knowledge is not explicitly stated but is implied through actions and behaviors. It is often gained through experience and practice, similar to tacit knowledge, but can be inferred from the way individuals and teams operate. Managing implicit knowledge involves observing and understanding these behaviors to capture and share valuable insights.
How Knowledge Management Works
Knowledge management includes capturing both explicit and tacit knowledge, encompassing several key components and structured methods for identifying, storing, and sharing knowledge. Explicit knowledge includes structured information such as manuals, policies, and databases. Tacit knowledge, on the other hand, consists of insights, experiences, and skills that employees develop over time.
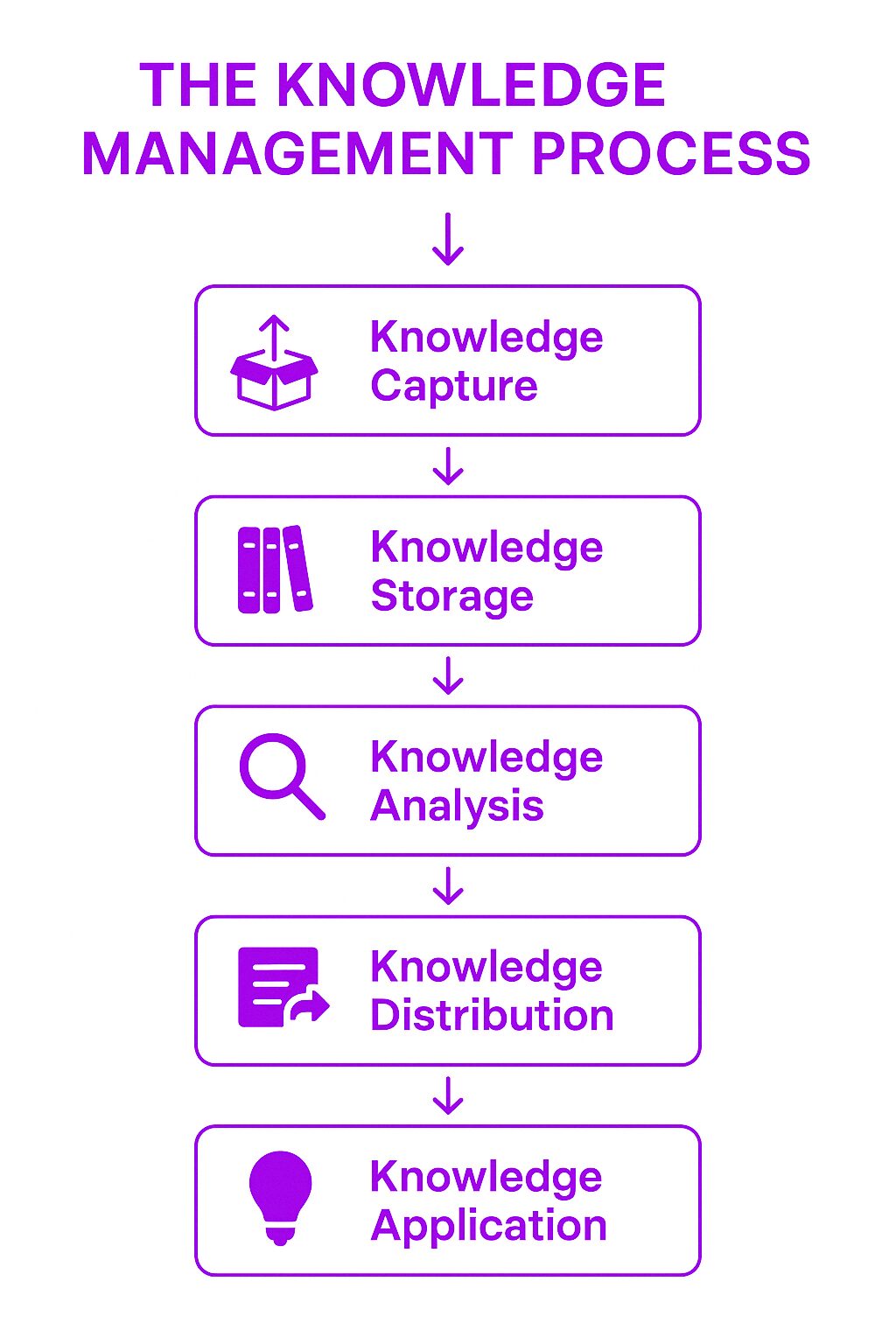
The knowledge management process typically follows these steps:
-
Knowledge Capture – Identifying and documenting valuable information from employees, processes, and systems.
-
Knowledge Storage – Organizing information in digital repositories, intranets, or cloud-based platforms.
-
Knowledge Analysis – Categorizing and refining knowledge to ensure relevance and accuracy.
-
Knowledge Distribution – Making knowledge easily accessible through search functions, wikis, and internal communication tools.
-
Knowledge Application – Encouraging employees to use available information to improve decision-making and workflows.
Key Components of Knowledge Management
Leadership Support
Successful knowledge management requires leadership involvement. Executives and managers should actively promote knowledge-sharing initiatives and set an example by contributing insights. A dedicated knowledge management team plays a crucial role in guiding the implementation and success of knowledge management systems within organizations.
Knowledge-Sharing Culture
Organizations should foster an organizational culture where employees feel encouraged to share expertise, as it is significant in driving knowledge management initiatives and fostering a knowledge-sharing environment. Incentives, collaboration tools, and open communication channels help create an environment where knowledge exchange thrives.
Knowledge Management System and Technology
A well-structured knowledge management system includes digital tools such as:
-
Intranet platforms for centralized information storage.
-
AI-powered search engines to improve knowledge retrieval.
-
Collaboration software for real-time information sharing.
-
Learning management systems (LMS) for training and skill development.
-
Knowledge management software to organize and protect information, enhancing security features to prevent data leaks.
Processes and Workflows
Clear workflows define how knowledge is captured, validated, and updated. Establishing procedures for content creation, verification, and maintenance ensures that employees have access to reliable and current information.
Why Knowledge Management Matters
Enhances Decision-Making
When employees have quick access to accurate and relevant knowledge, they make better-informed decisions. Knowledge management eliminates guesswork and reliance on outdated information.
Improves Productivity
Employees spend less time searching for information when knowledge is structured and accessible. A centralized knowledge base allows teams to retrieve answers quickly, reducing disruptions and improving efficiency.
Encourages Collaboration
Knowledge-sharing tools break down silos and allow employees across departments to collaborate effectively. Organizations with strong knowledge management systems promote cross-functional teamwork and innovation.
Supports Employee Onboarding and Training
New employees benefit from documented best practices, training materials, and process guidelines. Knowledge management accelerates onboarding and reduces the time required to become fully productive.
Preserves Institutional and Tacit Knowledge
When employees leave, their organizational knowledge often leaves with them. A well-maintained knowledge management system ensures that critical insights remain within the organization and are available for future employees.
Benefits and Challenges of Knowledge Management
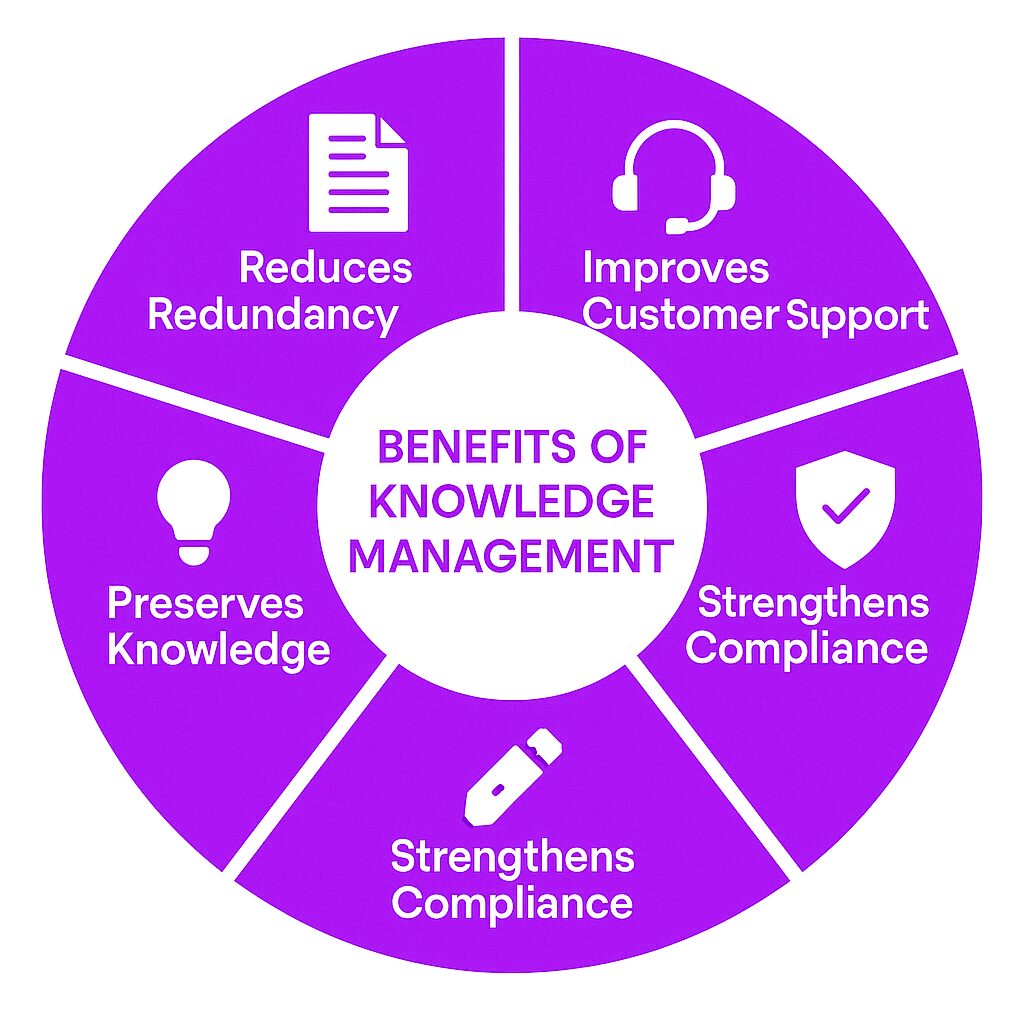
Benefits
Reduces Redundancy
By providing a central knowledge base, organizations avoid repeated efforts and unnecessary duplication of work.
Improves Customer Support
Knowledge creation helps customer service teams access accurate information quickly, leading to faster issue resolution and improved customer satisfaction, thereby enhancing customer experiences and operational efficiency.
Strengthens Compliance and Risk Management
Maintaining up-to-date policies and procedures ensures compliance with regulations and reduces organizational risk.
Boosts Employee Engagement
Employees feel more engaged when they can easily contribute and access valuable information. A culture of knowledge-sharing fosters professional growth.
Challenges
Resistance to Change
Employees may be hesitant to adopt new knowledge-sharing practices. Overcoming this resistance requires leadership support and user-friendly systems.
Information Overload
Without proper organization, excessive information can overwhelm employees. Categorization, search optimization, and AI-driven recommendations help streamline access to relevant knowledge.
Maintaining Content Relevance
Outdated or incorrect information can lead to mistakes. Organizations should establish regular review cycles to keep knowledge current.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Sensitive information must be protected. Organizations need clear access controls and cybersecurity measures to prevent unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Implementing Knowledge Management
Define Clear Objectives
Organizations should establish specific goals for their knowledge management initiatives, such as improving efficiency, reducing training time, or enhancing collaboration. Implementing effective knowledge management strategies is crucial as they serve as essential frameworks for organizing and leveraging content across various systems.
Choose the Right Technology
Selecting the right knowledge management tools ensures that information is easy to find and share. AI-powered search engines, content management systems, and collaboration platforms help facilitate knowledge access.
Encourage Employee Participation
A successful knowledge management system requires employee engagement. Organizations can encourage participation by recognizing contributions and creating user-friendly interfaces.
Provide Training and Support
Employees need training to use knowledge management tools effectively. Regular workshops and user guides help ensure adoption.
Continuously Update and Improve Knowledge Systems
Knowledge management is an ongoing process. Organizations should regularly review and update content to maintain accuracy and relevance.
Intellectual Property and Security
Protecting intellectual property and ensuring the security of knowledge resources are critical components of knowledge management. Organizations must implement robust security measures to safeguard their knowledge from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure. This includes establishing access controls to restrict who can view and edit information, using encryption to protect data in transit and at rest, and ensuring secure storage solutions. By prioritizing intellectual property and security, organizations can maintain the integrity and confidentiality of their valuable knowledge assets.
Related Concepts
Content Management
Knowledge management overlaps with content management, which focuses on creating, storing, and distributing digital content within an organization.
Enterprise Social Networks
These platforms allow employees to collaborate, share knowledge, and communicate in real-time.
Knowledge Retention Strategies
Organizations use knowledge retention strategies to capture valuable information from departing employees and ensure continuity.
Real-World Examples of Knowledge Management
Tech Companies
Software companies maintain knowledge bases with product documentation, coding best practices, and troubleshooting guides to support engineers and developers.
Healthcare Organizations
Hospitals store medical research, patient care protocols, and compliance guidelines in digital knowledge management systems to improve healthcare delivery.
Retail and Customer Support Teams
Retail businesses use knowledge management to train employees, optimize customer interactions, and maintain consistency across store locations.
Remote and Hybrid Workforces
Distributed teams rely on knowledge management tools to collaborate effectively, ensuring that employees can access necessary information from any location.
Measuring Knowledge Management Success
Evaluating the success of knowledge management initiatives is essential to ensure they meet their intended goals and objectives. Organizations can use various metrics and evaluation methods to measure the effectiveness of their knowledge management systems. Metrics such as the number of knowledge articles created, the frequency of searches conducted, and the number of users accessing the system provide quantitative insights. Additionally, evaluation methods like surveys, focus groups, and interviews can offer qualitative feedback, helping to identify strengths and areas for improvement in the knowledge management process.
Metrics and Evaluation
To comprehensively measure the success of knowledge management initiatives, organizations can use a range of metrics and evaluation methods:
-
Return on Investment (ROI): This metric assesses the financial return on investment in knowledge management initiatives, helping organizations understand the economic value generated.
-
Net Present Value (NPV): NPV measures the present value of future cash flows from knowledge management initiatives, providing a long-term financial perspective.
-
Customer Satisfaction: This metric evaluates the level of satisfaction among customers with the knowledge management system, indicating its impact on customer service and support.
-
Employee Engagement: Measuring employee engagement with the knowledge management system helps assess how effectively it is being utilized and its impact on employee productivity and morale.
-
Knowledge Sharing: This metric tracks the level of knowledge sharing among employees and teams, highlighting the effectiveness of knowledge dissemination practices.
-
Innovation: Evaluating the level of innovation and creativity generated through the knowledge management system provides insights into its role in fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
By using these metrics and evaluation methods, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact and effectiveness of their knowledge management initiatives, ensuring they continue to drive value and support organizational goals.
Final Thoughts
Knowledge management is essential for organizations looking to improve efficiency, collaboration, and innovation. By implementing a structured approach to capturing, organizing, and sharing knowledge, businesses can empower employees, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage. A well-executed knowledge management strategy ensures that valuable information remains accessible, helping organizations adapt to change and drive long-term success.