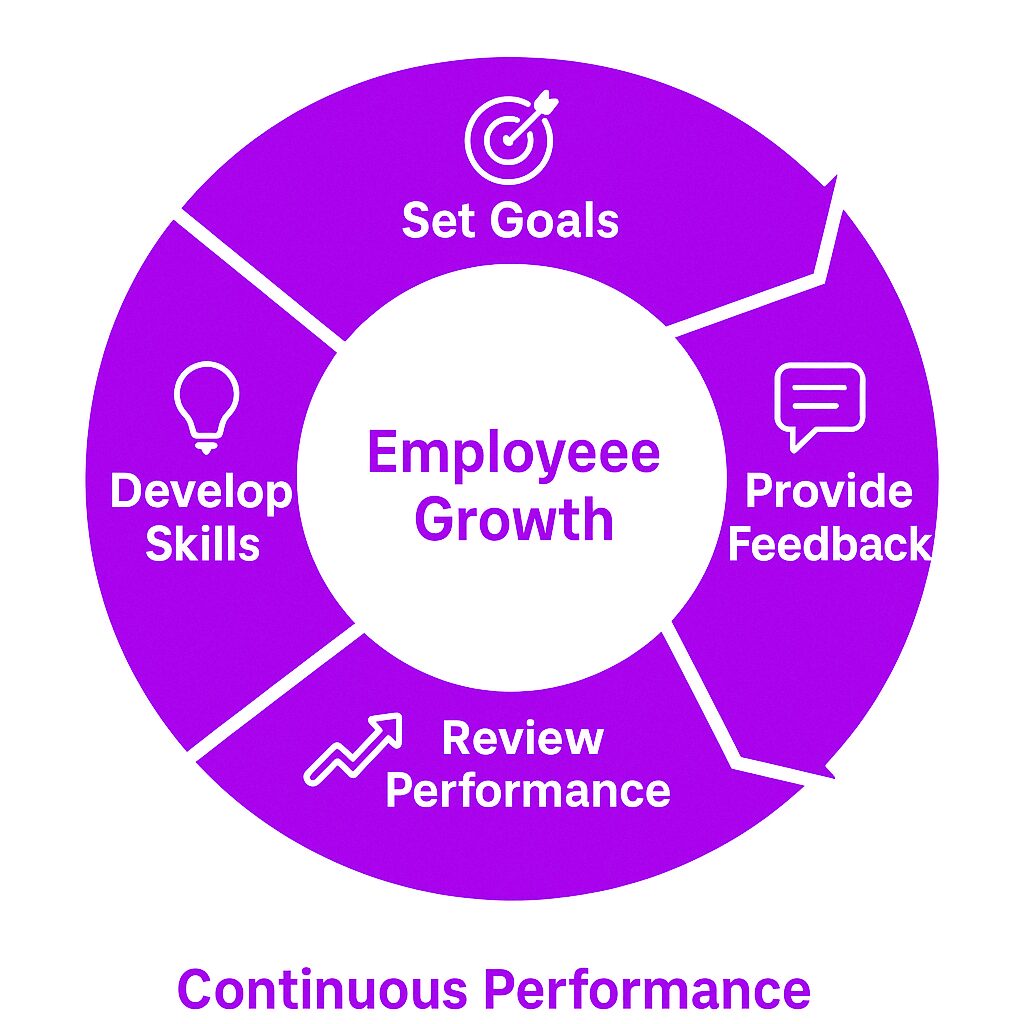
What is Performance Management?
Performance management is an ongoing process where managers and employees collaborate to set goals, track progress, provide feedback, and develop skills. Traditional methods like the annual performance appraisal occur once or twice a year. However, continuous performance management is a modern approach that involves ongoing dialogues between managers and employees about performance and goals. It helps employees understand what is expected of them while ensuring their work contributes to the company’s overall success. Unlike traditional performance appraisals, which happen once or twice a year, performance management is continuous. It focuses on improving performance in real time, making adjustments as needed, and recognizing achievements along the way.
Performance Management Goals
Performance management goals are the cornerstone of effective performance management. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure clarity and focus. Setting these goals collaboratively between employees and managers fosters commitment and ownership, making it more likely that employees will strive to achieve them.
Aligning performance management goals with the organization’s key performance indicators (KPIs) and strategic objectives ensures that individual efforts contribute to the broader business success. This alignment helps employees understand how their work impacts the organization, driving motivation and engagement.
Regularly reviewing and updating performance management goals is crucial to keep them relevant and achievable. This dynamic approach allows for adjustments based on changing business needs and employee progress. Providing ongoing feedback and coaching helps employees stay on track and continuously improve their performance.
Documenting the goal-setting process, including expectations and deadlines, ensures transparency and accountability. Utilizing performance management software can streamline and automate this process, making it easier to track progress and provide timely feedback. Regular progress reviews and coaching sessions are essential to help employees meet their performance management goals and contribute to the organization’s success.
How the Performance Management System Works
Performance management isn’t just about reviewing past performance. It’s about shaping future success. It involves goal-setting, regular feedback, performance reviews, training, and employee recognition. Done well, it keeps employees motivated, aligns their work with company goals, and helps businesses grow.
Many companies are moving away from outdated annual reviews to more dynamic, feedback-driven approaches. For example, Deloitte transformed its performance management process by replacing formal annual evaluations with real-time conversations. This change saved the company nearly 2 million hours and significantly boosted employee engagement.
Key Stages of Performance Management
1. Goal Setting and Planning
Clear performance expectations give employees direction. Without them, people can feel lost or unmotivated. Effective performance management starts with setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
Instead of vague targets like “improve customer service,” a SMART goal would be: “Reduce customer complaint resolution time from 48 hours to 24 hours by the end of Q2.”
Setting goals should be a two-way process. Employees should have a say in their objectives to ensure they’re realistic and meaningful. Goals should also align with company priorities so that individual success contributes to business success.
3.2 2. Continuous Performance Management, Feedback, and Communication
Gone are the days when feedback was only given once a year. Today, the best-performing companies provide ongoing feedback.
Regular check-ins help employees stay on track, understand what’s expected, and make necessary adjustments before small issues become big problems. These conversations should be open and honest, with a focus on learning and improvement rather than criticism.
Managers who check in with their employees weekly see 3x higher engagement levels compared to those who only do annual reviews.
3.3 3. Performance Appraisals, Reviews, and Evaluations
While ongoing feedback is essential, formal performance reviews still have their place. These structured discussions allow managers and employees to reflect on progress, discuss challenges, and adjust goals.
Modern performance reviews are:
-
More frequent (quarterly or monthly instead of annually)
-
Two-way conversations, not just manager-led
-
Focused on future development rather than just past performance
4. Employee Development and Training
Performance management isn’t just about evaluating employees—it’s about helping them grow. Training, mentorship, and upskilling opportunities ensure employees continue to develop their skills.
For example, a marketing manager struggling with data analytics might benefit from a course on Google Analytics or a mentorship with a senior data analyst. Providing these learning opportunities keeps employees engaged and prepares them for future leadership roles.
5. Recognition and Rewards
Recognizing achievements is crucial. Employees who feel appreciated are more likely to stay motivated and engaged.
Recognition doesn’t have to be expensive. A simple “thank you” from a manager, a shout-out in a team meeting, or an employee of the month award can go a long way.
Some companies use monetary incentives, bonuses, or promotions to reward top performers. Others use non-monetary rewards like extra vacation days, flexible work arrangements, or professional development opportunities.
Human Resources Role in Performance Management
Human Resources (HR) plays a pivotal role in the performance management process, providing essential guidance and support to both managers and employees. HR is responsible for developing and implementing the organization’s performance management framework, which includes defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that align with strategic objectives.
HR ensures that the performance management process is fair, transparent, and unbiased. This involves providing training and development programs to help employees improve their performance and achieve their goals. HR also offers feedback and coaching to managers, enhancing their performance management skills and ensuring they can effectively support their teams.
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the performance management process is another critical HR responsibility. This includes providing guidance and support to employees who are struggling to meet their performance management goals and ensuring that the process is continuously improved and updated.
HR’s role extends to aligning the performance management process with the organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring that individual and team performance contributes to overall business success. By developing and implementing effective performance management strategies, HR helps create a culture of continuous improvement and development.
Why Performance Management Matters
Creates a Culture of Accountability
When expectations are clear and employees receive regular feedback, they’re more likely to take ownership of their work. They understand what’s required and feel responsible for delivering results.
Drives Business Growth
Performance management ensures employees are working towards company goals. When everyone is aligned, productivity increases, customer satisfaction improves, and revenue grows.
Reduces Employee Turnover
Employees who feel valued and see opportunities for growth are less likely to leave. Companies with strong performance management systems have lower turnover rates and higher employee satisfaction.
Improves Employee Engagement
Engaged employees are more productive, motivated, and committed to their work. Performance management helps build engagement by providing clear goals, continuous support, and recognition.
Benefits and Challenges of Performance Management
Benefits
-
Higher Employee EngagementEmployees who receive regular feedback and recognition see improvements in employees’ performance, leading to higher engagement and productivity.
-
Stronger Manager-Employee RelationshipsFrequent conversations build trust and improve communication between managers and employees.
-
Better Decision-MakingData-driven performance management helps identify trends, strengths, and areas for improvement.
-
Increased ProductivityWhen employees know what’s expected and receive ongoing support, they perform better.
Challenges
-
Resistance to Change
Employees and managers accustomed to traditional annual reviews may resist adopting continuous feedback. -
Time-Consuming
Regular check-ins and performance discussions require commitment from both managers and employees. -
Potential for Bias
Subjective evaluations can lead to unfair assessments if managers don’t use objective data.
Technology in Performance Management
Technology has revolutionized the performance management process, providing powerful tools and systems to support and enhance employee performance. Performance management software can streamline and automate various aspects of the process, making it more efficient and effective.
One of the key benefits of technology in performance management is the ability to provide real-time feedback and coaching. This immediate support helps employees make necessary adjustments and improve their performance continuously. Data and analytics play a crucial role, offering insights into KPIs and metrics that inform decision-making and highlight areas for improvement.
Technology also provides platforms for employees to track their progress and achievements, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. Managers can use these platforms to monitor and evaluate employee performance, ensuring that everyone stays aligned with organizational objectives.
HR can leverage technology to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the performance management process, ensuring continuous improvement. By integrating performance management software with other HR systems, organizations can create a cohesive and comprehensive approach to managing employee performance.
Best Practices for Effective Performance Management
-
Make Feedback a Daily HabitA well-designed performance management strategy is crucial for enhancing both employee development and organizational performance. Waiting until a quarterly review to address issues is ineffective. Real-time feedback helps employees make adjustments immediately.
-
Use Data and MetricsPerformance should be measured using clear, objective criteria rather than relying on subjective opinions.
-
Encourage Open CommunicationEmployees should feel comfortable discussing challenges and asking for support.
-
Set Clear, Achievable GoalsOverly ambitious or vague goals lead to frustration and confusion. Goals should be realistic and specific.
-
Provide Development OpportunitiesOffer training programs, mentorship, and career growth paths to keep employees engaged.
-
Recognize and Reward AchievementsA culture of appreciation boosts morale and motivates employees to perform at their best.
Related Concepts
Employee Engagement
Engaged employees are more motivated, committed, and productive. Performance management helps drive engagement through goal-setting, feedback, and recognition.
Workplace Culture and Leadership Development
Leaders play a crucial role in fostering a positive workplace culture. Effective performance management ensures managers support and develop their teams.
Employee Recognition Programs
Performance management programs play a crucial role in employee recognition by facilitating continuous feedback, goal setting, and development. Recognition programs help reinforce positive behaviors and keep employees motivated. These can include peer recognition, manager shout-outs, and company-wide awards.
Real-World Examples of Performance Management in Action
Deloitte’s Shift to Continuous Feedback
Performance management tools have played a crucial role in Deloitte’s shift to continuous feedback, integrating advanced technologies to enhance performance tracking and engagement.
Deloitte replaced annual performance reviews with weekly check-ins. This move saved the company millions of hours and improved employee engagement by providing ongoing support.
Google’s OKR System
Google uses Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) to set clear, measurable goals for employees. This approach keeps employees focused on high-impact activities.
Netflix’s Radical Transparency Approach
Netflix has an open feedback culture where employees give and receive real-time feedback. This helps maintain high performance and accountability.
The Future of Performance Management
The future of performance management is evolving towards a more dynamic, continuous, and personalized approach. Moving away from traditional annual performance appraisals, the focus is now on providing real-time feedback and coaching to support ongoing development and improvement.
Technology will play a central role in this transformation, with performance management software and data analytics driving more informed and effective decision-making. These tools will enable a more personalized approach, tailoring performance management strategies to individual needs and preferences.
Collaboration and inclusivity will be key, involving employees, managers, and HR in the performance management process. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone is aligned and working towards common goals, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and development.
Agility and adaptability will also be crucial, allowing organizations to respond to changing business needs and priorities. A data-driven approach will provide the insights needed to make informed decisions and drive performance.
The future of performance management will prioritize employee development and growth, creating a more employee-centric approach. By integrating performance management with other HR processes and systems, organizations can create a more sustainable and long-term strategy that supports both individual and organizational success.
Final Thoughts
Performance management is about more than just evaluations. It’s a continuous process of setting goals, providing feedback, developing employees, and recognizing achievements. Companies that embrace modern performance management practices see higher engagement, better productivity, and stronger business results.
By shifting away from rigid annual reviews and focusing on ongoing communication, businesses create a culture of growth and accountability—one where employees feel valued and motivated to perform at their best.