What Is Organizational Development?
Organization development is a structured, strategic approach to improving a company’s overall health, adaptability, and effectiveness. It focuses on refining processes, structures, and cultures to foster continuous growth, increase employee engagement, and strengthen an organization’s ability to handle change. Unlike short-term improvements, OD is an ongoing process that aligns business goals with people and operations to ensure long-term success.
OD is grounded in behavioral science and uses data-driven strategies to enhance workplace dynamics. Organizations that invest in OD create environments where employees thrive, teams collaborate efficiently, and businesses stay competitive in evolving industries.
Goals of Organizational Development
Organizational development (OD) is a strategic approach aimed at enhancing an organization’s overall health, adaptability, and effectiveness. The primary goals of OD include:
-
Improving Organizational Effectiveness: At its core, OD seeks to enhance an organization’s ability to achieve its strategic objectives and improve overall performance. This involves refining processes, optimizing structures, and fostering a culture that supports the organization’s mission and vision.
-
Enhancing Adaptability: In today’s fast-paced business environment, adaptability is crucial. OD helps organizations develop the capacity to swiftly respond to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and evolving workforce needs, ensuring long-term sustainability.
-
Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement: OD encourages a culture of continuous learning, innovation, and improvement. By promoting ongoing development and refinement, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge.
-
Developing Leadership and Talent: Building strong leadership and nurturing talent are essential for driving future growth and success. OD focuses on leadership development programs and talent management strategies to ensure that the organization has the right people in place to lead and innovate.
-
Improving Employee Engagement and Satisfaction: Engaged and satisfied employees are more productive and committed to the organization’s success. OD initiatives aim to enhance employee engagement, satisfaction, and well-being, which in turn drives productivity and retention.
How Organizational Development Works
The organizational development process follows a cycle of assessment, intervention, and evaluation to create lasting change. It involves understanding the current state of an organization, identifying areas for improvement, implementing targeted solutions, and ensuring those changes are sustainable. Companies that prioritize the organizational development process rely on a combination of leadership engagement, strategic planning, and employee feedback to refine their internal operations.
The organizational development process includes:
-
Assessing the current structure – Identifying inefficiencies and areas for growth.
-
Designing interventions – Developing targeted programs to improve collaboration, efficiency, and culture.
-
Implementing change – Executing initiatives with the support of leadership and employees.
-
Evaluating success – Measuring impact through key performance indicators (KPIs) and refining strategies accordingly.
Why Organizational Development Matters
A company’s ability to evolve directly impacts its success. OD is essential because it helps businesses:
-
Align employees with business goals – Ensuring that every team member understands their role in achieving company objectives.
-
Strengthen leadership capabilities – Equipping managers and executives with the skills needed to navigate organizational challenges.
-
Improve decision-making – Encouraging transparency and collaboration to enhance problem-solving.
-
Increase agility – Enabling organizations to quickly adapt to market shifts and technological advancements.
-
Enhance employee engagement – Creating a work environment that values personal growth and professional development.
Companies that neglect OD may experience stagnation, poor morale, and difficulty retaining top talent. By continuously refining processes and fostering a culture of growth, businesses remain adaptable and competitive during periods of organizational changes.
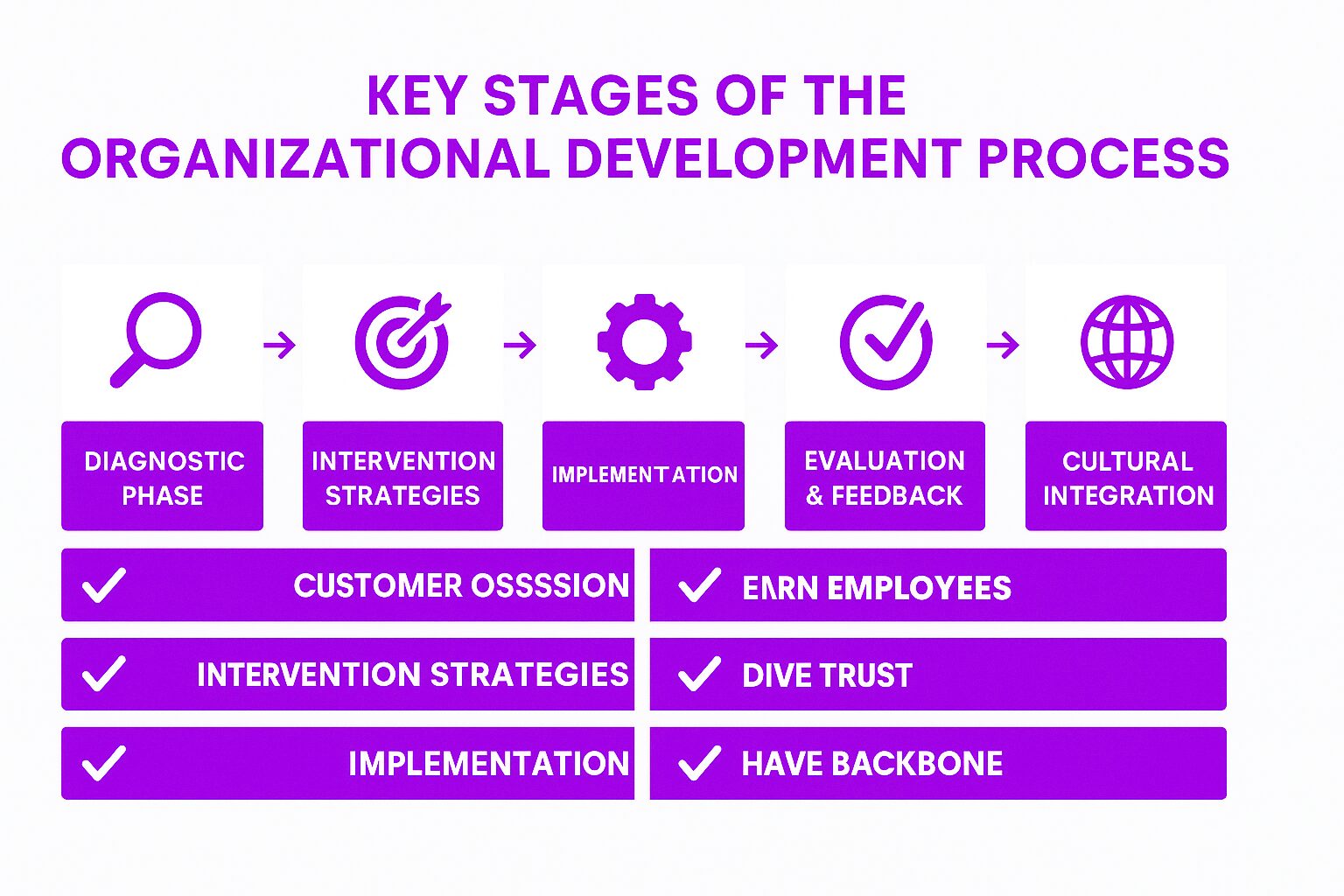
Key Stages of the Organizational Development Process
1. Diagnostic Phase
Organizations assess their internal health by gathering insights from employees, leadership, and performance data. Common diagnostic methods include:
-
Employee surveys
-
One-on-one interviews
-
Performance reviews
-
Business process audits
2. Intervention Strategies
Once challenges are identified, companies develop organizational development strategies. Interventions may include:
-
Restructuring teams or departments
-
Enhancing training and professional development programs
-
Improving communication channels
-
Implementing new technologies to streamline workflows
3. Implementation
Organizations roll out OD initiatives while ensuring that employees understand the purpose of the changes. Leadership involvement is key to ensuring smooth transitions and widespread adoption.
4. Evaluation and Feedback
Continuous assessment helps determine the effectiveness of OD initiatives. Companies measure:
-
Employee engagement levels
-
Productivity improvements
-
Operational efficiencies
-
Leadership effectiveness
5. Cultural Integration
To sustain OD efforts, companies must align new processes with their values and culture. Employees need clear expectations, ongoing training, and leadership support to ensure lasting success.
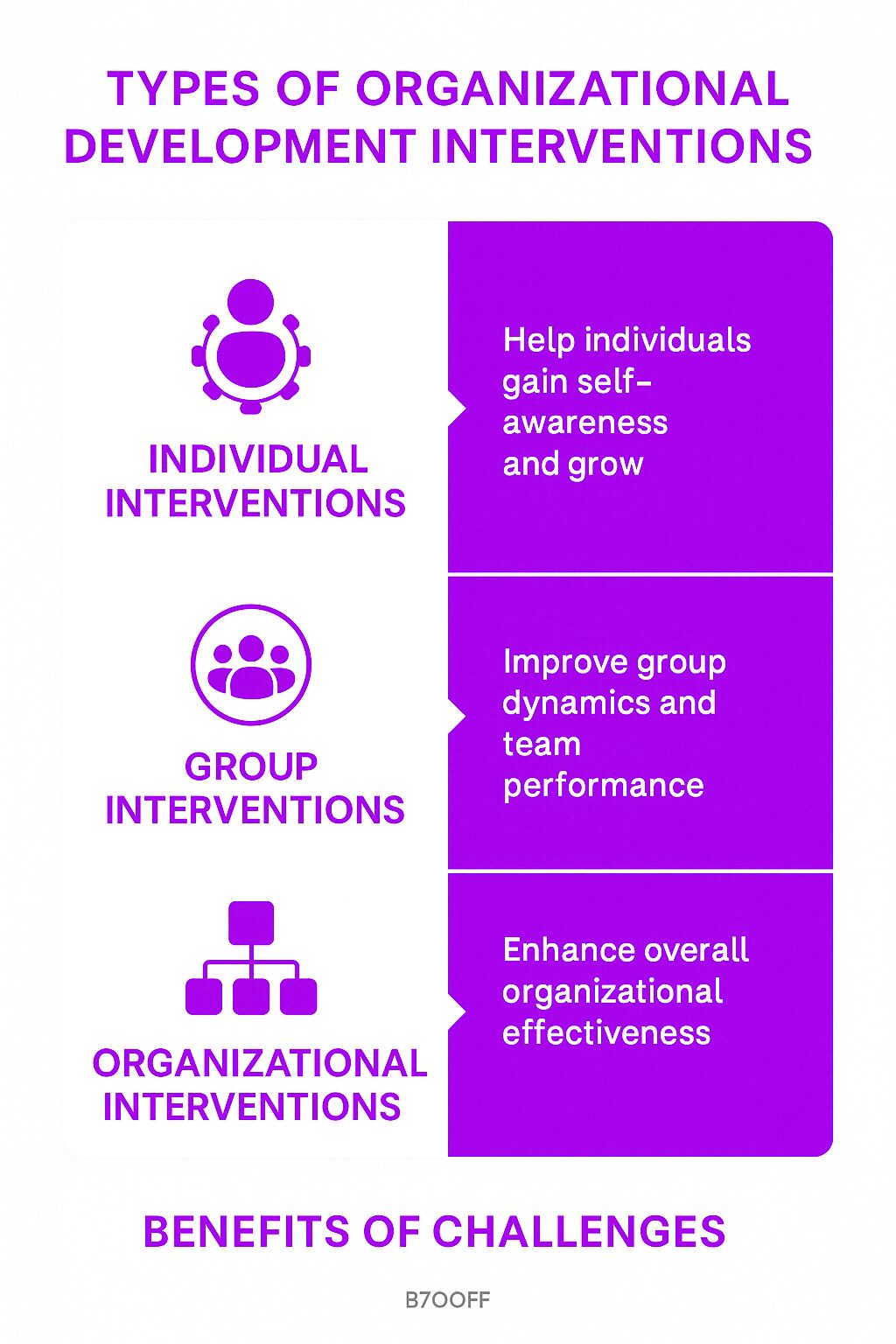
Organizational Development Interventions
Organizational development interventions are targeted programs and processes designed to address specific challenges and improve organizational effectiveness. These interventions can be categorized into three main types:
-
Individual Interventions: These focus on personal development and improving individual performance. Examples include leadership development programs, coaching, and personal workflow optimization. By enhancing individual capabilities, organizations can drive overall performance improvements.
-
Group Interventions: These are aimed at improving the dynamics and effectiveness of teams or departments. Team building activities, conflict resolution workshops, and group training sessions are common examples. Effective group interventions foster collaboration, innovation, and efficiency within teams.
-
Organizational Interventions: These involve large-scale changes that impact the entire organization. Examples include total quality management (TQM) initiatives, performance management systems, and transformational change programs. These interventions are designed to align the organization’s processes, structures, and culture with its strategic goals.
By implementing these interventions, organizations can address specific issues, enhance overall effectiveness, and create a culture of continuous improvement.
Organizational Development Models
Organizational development models provide structured frameworks for understanding and implementing change within an organization. Some of the most popular OD models include:
-
Lewin’s Three-Step Model: This model is a simple yet effective method for instituting change. It involves three steps: unfreezing (preparing the organization for change), changing (implementing the change), and refreezing (solidifying the new state). This model helps organizations manage the transition smoothly.
-
Action Research Model: This model involves a collaborative effort between researchers and practitioners to solve organizational problems. It is a systematic approach that includes diagnosing the issue, planning and implementing interventions, and evaluating the results. This iterative process ensures continuous improvement.
-
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) Model: BPR is a more radical approach to change, involving the complete reimagining of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in performance. This model is often used when incremental changes are insufficient to meet organizational goals.
-
McKinsey 7-S Framework: This framework helps organizations understand the interdependencies between seven key factors: shared values, strategy, structure, systems, style, skills, and staff. By analyzing and aligning these elements, organizations can achieve more effective and sustainable change.
These models provide valuable tools for guiding organizational change and development, helping organizations achieve their desired outcomes.
Benefits of Organizational Development
Stronger Leadership Development
OD fosters leadership development by equipping managers with the tools to guide teams effectively. Leadership programs improve communication, strategic thinking, and problem-solving skills.
Improved Employee Engagement
Employees who feel valued and supported are more motivated to contribute to company success. OD initiatives create environments where workers feel empowered and connected to their organization’s mission.
Increased Collaboration
OD strengthens teamwork by removing barriers between departments. Cross-functional collaboration leads to innovation, efficiency, and more aligned business operations.
Greater Adaptability
Companies that prioritize OD are better equipped to handle industry changes, economic fluctuations, and workforce shifts. They develop resilience by fostering a culture that embraces continuous improvement.
Better Decision-Making for Organizational Effectiveness
By focusing on data-driven strategies, OD helps leaders make informed choices that align with long-term business goals.
Challenges in Organizational Development
Resistance to Change
Employees may be hesitant to adopt new processes or strategies. Overcoming resistance requires clear communication, leadership support, and employee involvement in decision-making.
Measuring Success
OD initiatives can be difficult to quantify, especially cultural improvements. Companies need to track progress using both qualitative and quantitative metrics.
Leadership Buy-In
If executives do not fully commit to OD efforts, initiatives may fail. Leaders must champion change and actively participate in development programs.
Maintaining Consistency
Sustaining OD efforts requires ongoing reinforcement. Organizations need long-term strategies, rather than one-time interventions, to see lasting impact.
Best Practices for Organizational Development
1. Involve Employees at Every Stage
Employees should have a voice in OD initiatives. Encouraging participation in discussions and decision-making fosters greater acceptance and engagement.
2. Align Strategies with Business Goals
Every OD initiative should contribute to the broader mission of the company. Clearly defined goals help measure success and ensure that efforts drive meaningful change.
3. Foster Continuous Learning
Providing ongoing training and development opportunities ensures that employees stay informed and equipped for success. Companies should prioritize mentorship programs, leadership workshops, and cross-functional learning.
4. Emphasize Communication
Transparent communication helps employees understand why OD initiatives are necessary. Companies should use multiple channels—meetings, emails, internal platforms—to keep everyone informed.
5. Evaluate and Adjust Regularly
Organizations should continuously assess their OD efforts and make adjustments as needed. Using employee feedback and performance data ensures that strategies remain effective.
Human Resource Management and Organizational Development
Human Resource Management (HRM) and Organizational Development (OD) are closely related fields that complement each other in enhancing organizational effectiveness. While HRM focuses on managing and optimizing the organization’s human capital, OD takes a broader, strategic approach to drive overall improvement.
HRM involves activities such as recruitment, performance management, and employee relations, which are essential for maintaining a productive workforce. On the other hand, OD addresses broader aspects like workflows, organizational structures, and culture. By implementing effective organizational development interventions, organizations can create an environment that supports both individual and collective growth.
In essence, HRM provides the foundation for managing human resources, while OD builds on this foundation to drive strategic change and continuous improvement. Together, they ensure that the organization is well-equipped to achieve its goals and adapt to future challenges.
Data Collection and Organizational Development
Data collection is a critical component of organizational development, as it provides the insights needed to understand the current state of the organization and identify areas for improvement. OD practitioners use various data collection methods to gather comprehensive information:
-
Surveys: Surveys are used to collect data on employee attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors. They provide a broad overview of the organizational climate and help identify common issues and areas for improvement.
-
Interviews: One-on-one interviews offer in-depth insights into individual perspectives and experiences. They allow for a deeper understanding of specific issues and can uncover underlying causes of organizational challenges.
-
Observations: Observing organizational processes and behaviors in real-time provides valuable information about how work is actually performed. This method helps identify inefficiencies and areas where processes influence worker behavior.
-
Focus Groups: Focus groups gather information about group dynamics and collective perspectives. They are useful for exploring complex issues and generating ideas for potential solutions.
By analyzing the data collected through these methods, OD practitioners can develop targeted interventions that address specific challenges and drive organizational change. This data-driven approach ensures that OD efforts are aligned with the organization’s goals and lead to meaningful improvements.
Related Concepts
Change Management
OD and change management go hand in hand. Change management focuses on guiding employees through transitions, while OD ensures long-term improvement.
Employee Engagement
Engaged employees contribute more to organizational success. OD strengthens engagement by fostering a positive workplace culture and professional growth opportunities.
Performance Management
OD initiatives often include performance evaluation strategies that help align employee contributions with business goals.
Knowledge Sharing
Collaboration and knowledge exchange are key components of OD. Organizations that encourage knowledge-sharing build stronger teams and retain institutional knowledge.
Real-World Examples of Organizational Development
A Tech Company Enhancing Collaboration
A global technology firm used OD strategies to restructure its teams and improve communication between remote employees. By implementing collaboration tools and leadership training, productivity increased by 20%.
A Retailer Reducing Employee Turnover
A large retail chain introduced OD programs focused on employee engagement and training. After improving onboarding and career development opportunities, turnover rates decreased, and customer satisfaction improved.
A Healthcare Provider Improving Patient Care
A hospital system adopted OD strategies to streamline workflows and reduce burnout among medical staff. By implementing structured feedback loops and leadership training, patient outcomes improved, and employee satisfaction increased.
Final Thoughts
Organizational Development is a continuous journey that helps businesses refine their strategies, empower employees, and remain competitive. Companies that embrace OD create work environments where employees feel valued, leadership is effective, and business goals are achieved. By investing in data-driven strategies and fostering a culture of adaptability, organizations can build a future-ready workforce and drive long-term success.