What Is Leadership?
Leadership is the ability to guide, influence, and inspire others toward a shared goal. It is not limited to individuals in management roles; anyone who motivates and directs a group can be considered a leader. Effective leaders need to inspire and foster a sense of commitment among their team members, not only towards organizational goals but also towards personal success and mutual support within the leadership-follower relationship. Leadership is about making decisions, fostering collaboration, and driving progress.
Good leadership creates direction, builds trust, and encourages accountability. It involves clear communication, problem-solving, and the ability to navigate challenges effectively. Leadership is not a one-size-fits-all concept—it varies across industries, teams, and organizational cultures.
Leadership Principles
Leadership principles are the foundation of effective leadership. They provide a framework for leaders to make decisions, guide their actions, and inspire their teams. Some key leadership principles include:
-
Customer Obsession: Effective leaders prioritize the needs and satisfaction of their customers, ensuring that their teams are aligned with delivering exceptional service and value.
-
Ownership: The best leaders take full responsibility for their actions and decisions, fostering a culture of accountability within their teams.
-
Invent and Simplify: Leaders encourage innovation and simplicity, driving their teams to develop creative solutions and streamline processes.
-
Are Right, A Lot: Good leaders make informed decisions and are open to diverse perspectives, leveraging the collective intelligence of their teams.
-
Learn and Be Curious: Leaders prioritize continuous learning and development, both for themselves and their teams, to stay ahead in a rapidly changing environment.
-
Hire and Develop the Best: Effective leaders focus on hiring top talent and investing in their development to build high-performing teams.
-
Insist on the Highest Standards: Leaders set and maintain high standards for themselves and their teams, ensuring excellence in all aspects of their work.
-
Think Big: Visionary leaders think strategically and aim high, inspiring their teams to pursue ambitious goals.
-
Bias for Action: Leaders prioritize action and results, encouraging their teams to take initiative and drive progress.
-
Frugality: Efficient leaders prioritize cost-effectiveness and resourcefulness, ensuring that their teams operate within budget constraints.
-
Earn Trust: Leaders earn and maintain the trust of their customers and teams through integrity, transparency, and reliability.
-
Dive Deep: Leaders operate at all levels, staying connected to the details and understanding the intricacies of their teams’ work.
-
Have Backbone; Disagree and Commit: Courageous leaders challenge decisions when necessary and commit to their teams’ success.
-
Deliver Results: Leaders prioritize quality and timeliness, ensuring that their teams consistently achieve their objectives.
-
Strive to be Earth’s Best Employer: Leaders prioritize the growth and development of their employees, creating a supportive and enriching work environment.
How Leadership Works
Leadership functions by setting a vision, communicating goals, and ensuring teams work together toward a common objective. Leaders are responsible for making informed decisions, guiding team members, and fostering an environment where people feel motivated and supported.
Effective leadership requires self-awareness, adaptability, and emotional intelligence. Leaders must balance authority with empathy, knowing when to take charge and when to delegate. Whether leading a corporate team, a nonprofit organization, or a small business, the core principles remain the same: influence, accountability, and vision.
Key Components of Leadership
Vision
A leader provides a clear sense of purpose and direction. They set strategic goals and align team efforts with the organization’s mission.
Communication
Leaders must convey their expectations, listen to feedback, and ensure transparency in all interactions. Open communication builds trust and clarity.
Decision-Making
Good leaders make informed choices based on available data, experience, and intuition. Understanding and identifying the qualities of a good leader through extensive research and analysis is crucial. They assess risks, weigh alternatives, and take responsibility for outcomes.
Empowerment
Leaders act by encouraging team members to take initiative and responsibility, demonstrating qualities such as ownership and compassion. By delegating tasks and trusting employees with responsibilities, they foster confidence and skill development.
Adaptability
The best leaders adjust to change, whether in market trends, team dynamics, or industry shifts. Individuals aspiring to leadership positions should possess traits like adaptability, honesty, hope, and teamwork to navigate these changes effectively. They remain flexible and guide others through uncertainty.
Integrity
Ethical leadership is non-negotiable. Leadership qualities such as honesty, accountability, and fairness can be developed over time through experience, education, and ongoing personal growth. Leaders must demonstrate these traits in all their decisions and actions.
Leadership Theories
Leadership theories provide a framework for understanding the complexities of leadership. Some key leadership theories include:
-
Trait Theory: This theory suggests that leadership is based on the inherent characteristics and personality traits of the leader. It posits that certain qualities, such as confidence and charisma, are essential for effective leadership.
-
Behavioral Theory: According to this theory, leadership is defined by the behaviors and actions of the leader. It emphasizes that effective leaders can be developed through learning and practice, focusing on specific behaviors that lead to success.
-
Situational Theory: This theory proposes that leadership is contingent on the situation and context in which the leader operates. It highlights the importance of adaptability, suggesting that different situations require different leadership styles.
-
Contingency Theory: Similar to situational theory, contingency theory asserts that the effectiveness of a leader depends on their ability to adapt to changing circumstances. It emphasizes the need for leaders to be flexible and responsive to their environment.
-
Transformational Theory: This theory focuses on the leader’s ability to inspire and motivate their teams. Transformational leaders are characterized by their vision, passion, and ability to create significant change within their organizations.
-
Servant Leadership Theory: This theory emphasizes the leader’s role in serving and prioritizing the needs of their teams. Servant leaders focus on the well-being and development of their team members, fostering a supportive and collaborative environment.
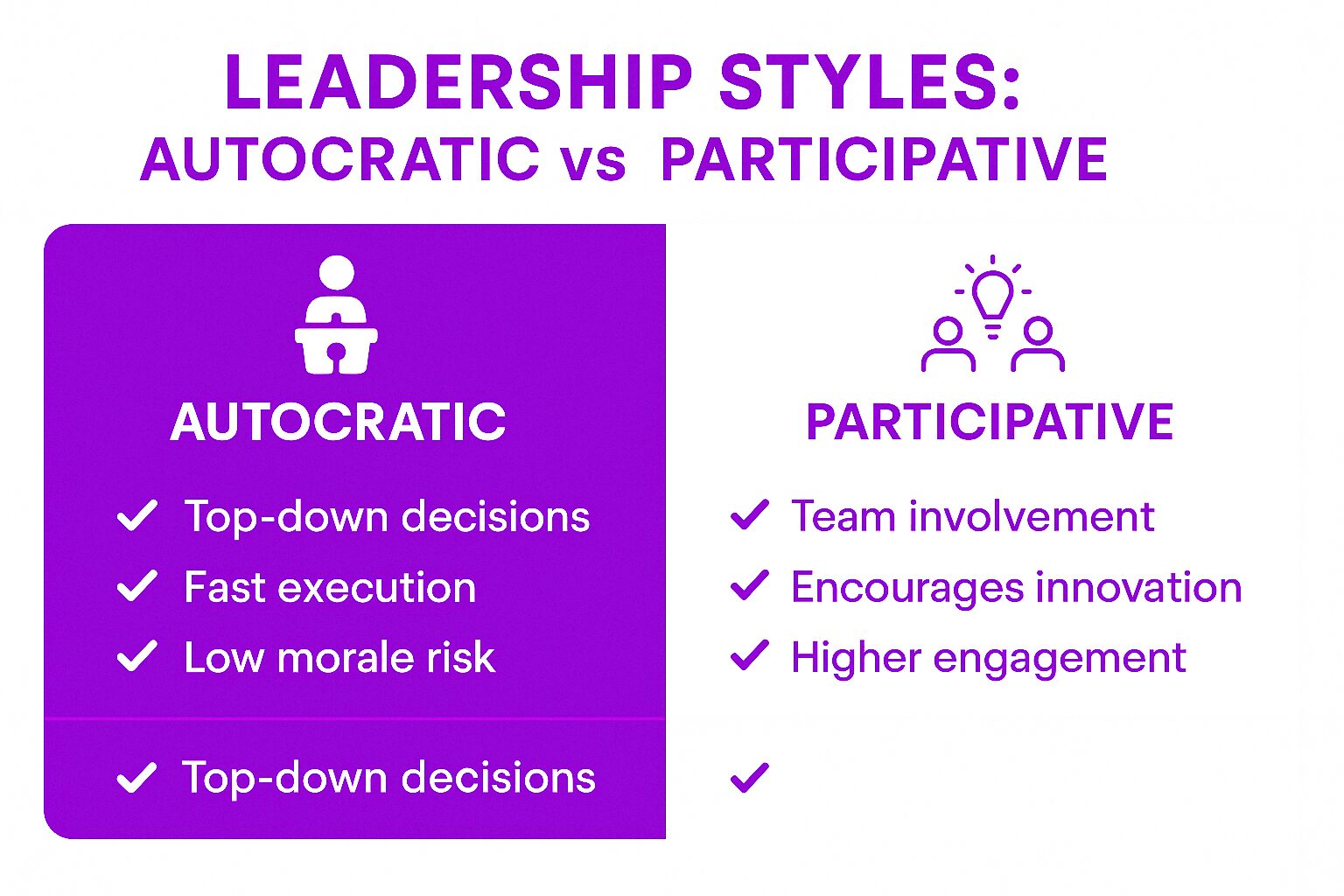
Leadership Styles
Leadership styles refer to the way in which leaders approach their role and interact with their teams. Some key leadership styles include:
Autocratic or Authoritarian
Autocratic leaders make decisions without consulting their teams. They prioritize control and efficiency over collaboration and creativity. While this style can lead to quick decision-making, it often results in low morale and motivation among team members due to the lack of input and autonomy.
Participative or Democratic
Participative leaders involve their teams in decision-making and prioritize collaboration and creativity. They empower their teams to take ownership and make decisions, fostering a sense of inclusion and high morale. This leadership style encourages diverse perspectives and innovation, leading to a motivated and engaged team.
Why Leadership Matters
Drives Business Success
Organizations thrive when they have strong leadership. Leaders make strategic decisions that shape a company’s future and ensure its competitive edge.
Improves Employee Engagement
Engaged employees are more productive and committed to their work. Leaders create an environment where employees feel valued and motivated.
Encourages Innovation
Leaders who foster creativity and risk-taking inspire teams to think differently and develop new solutions.
Builds Stronger Teams
A great leader unites individuals with different skills and perspectives, creating a cohesive, high-performing team.
Facilitates Change
Leadership is essential in times of transition. Whether a company is scaling, restructuring, or navigating uncertainty, strong leadership ensures a smooth process.
Benefits and Challenges of Leadership
Benefits
Increased Productivity
A well-led team operates efficiently, with clear expectations and minimal confusion.
Higher Employee Retention
Employees stay longer in workplaces where they feel supported, valued, and aligned with leadership.
Stronger Workplace Culture
A leader’s values and behavior set the tone for the entire organization.
Better Decision-Making
Good leaders use strategic thinking and collaboration to make informed choices.
Challenges
Balancing Authority and Collaboration
Leaders must maintain authority while encouraging team input.
Managing Conflict
Navigating interpersonal challenges is a key leadership responsibility.
Sustaining Motivation
Keeping a team engaged during difficult times requires strong leadership skills.
Continuous Learning
Leadership evolves with business trends, requiring leaders to stay adaptable and open to new strategies.
Best Practices for Effective Leadership
Encourage Open Communication
Leaders should create a culture where feedback flows freely. Regular check-ins and open discussions keep teams aligned.
Lead by Example
Employees look to their leaders for behavioral cues. Demonstrating accountability, respect, and dedication encourages others to do the same.
Recognize and Reward Contributions
Acknowledging employees’ efforts fosters motivation and a sense of appreciation.
Invest in Employee Development
Strong leaders prioritize training, mentorship, and growth opportunities for their teams.
Foster Collaboration
Creating an inclusive environment where all voices are heard strengthens team relationships and drives innovation.
Stay Resilient
Leaders must remain steady and solution-focused during setbacks, setting a positive example for their teams.
Related Concepts
Management vs. Leadership
While management focuses on processes, leadership is about inspiring and guiding people.
Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
The ability to understand and regulate emotions enhances decision-making and team interactions.
Leadership in Remote Work
With more organizations operating remotely, leadership now requires additional communication skills and digital collaboration tools.
Real-World Examples of Leadership
Corporate Leadership
Successful companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon have thrived under strong leadership that fosters innovation and strategic growth.
Healthcare Leadership
Hospitals and medical institutions require decisive leadership to manage patient care, crisis response, and healthcare regulations.
Small Business Leadership
Entrepreneurs and small business owners must lead with vision and adaptability to build successful enterprises.
Final Thoughts
Leadership is not about having authority—it’s about inspiring action, driving progress, and supporting those around you. Whether leading a team of two or an organization of thousands, the ability to communicate, adapt, and empower others is essential. Great leaders don’t just direct—they elevate the people and businesses they serve.