What Is an Internal Knowledge Base?
An internal knowledge base is a centralized repository where organizations store information, documents, and resources for employees. It serves as a hub for company policies, standard operating procedures (SOPs), training materials, IT support guides, and project documentation. Unlike external knowledge bases, which are accessible to customers or the public, internal knowledge bases are restricted to employees and are designed to improve collaboration, streamline workflows, and reduce redundant inquiries. A well-structured internal company knowledge base allows employees to easily navigate and access necessary information, ensuring it serves as a comprehensive resource for all employees.
How an Internal Knowledge Base Works
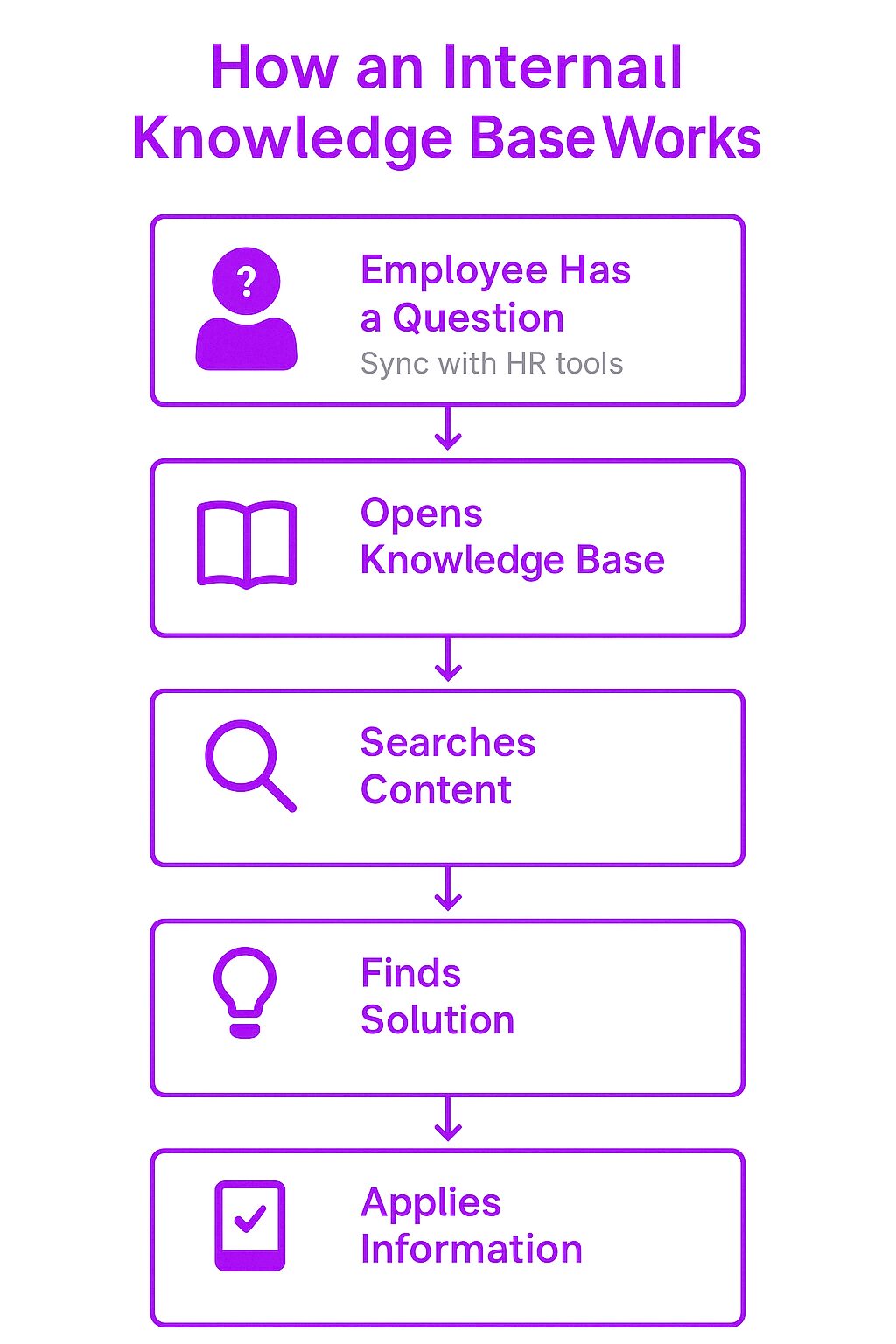
An internal knowledge base operates as a self-service system where employees can search for and retrieve information when needed. Instead of relying on emails, meetings, or direct communication with managers, employees can find solutions independently, saving time and improving overall efficiency.
Organizations use internal knowledge base software to organize and structure content, making it searchable and accessible. Many modern knowledge bases incorporate AI-powered search, tagging systems, and integration with communication tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams.
Key Components of an Internal Knowledge Base
Company Policies and Guidelines
Employees can access the latest workplace policies, compliance regulations, and corporate governance documentation. This ensures that all employees stay informed about expectations, ethical standards, and legal requirements.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
A well-maintained internal knowledge base contains step-by-step instructions for handling recurring tasks and processes. This standardization improves efficiency and reduces errors.
Training and Onboarding Materials
New hires can use the knowledge base to familiarize themselves with company procedures, best practices, and role-specific responsibilities. Interactive training modules, FAQs, and mentorship resources enhance the onboarding experience. Creating an internal knowledge base can further enhance employee training and productivity by centralizing information for easier access and fostering collaboration and team involvement.
IT and Technical Support
A dedicated IT section helps employees troubleshoot common technical issues, access software guides, and follow cybersecurity protocols. This minimizes the workload on IT support teams by enabling self-service troubleshooting.
Project Documentation
Employees can store and share project details, meeting notes, workflow charts, and historical data to ensure continuity. Teams working across different time zones or departments benefit from a single source of truth.
Internal Communications
The knowledge base serves as a platform for company-wide announcements, leadership updates, and team discussions. Employees can refer to past updates and stay informed about organizational changes.
Why an Internal Knowledge Base Matters
Reduces Redundant Questions
Employees frequently ask the same questions about HR policies, IT troubleshooting, and administrative procedures. A knowledge base reduces the need for repeated explanations, saving time for both employees and management.
Improves Productivity
A structured knowledge base minimizes the time employees spend searching for information. When employees can quickly find answers, they can focus on high-priority tasks and responsibilities. The productivity challenges faced by the average employee, who often spends hours each week locating necessary documents, can be significantly reduced with an internal knowledge base, thereby improving efficiency and reducing the financial burden on organizations.
Preserves Institutional Knowledge
When employees leave an organization, they take valuable knowledge with them. A knowledge base ensures that best practices, historical data, and internal insights remain accessible for future employees.
Enhances Onboarding and Training
New employees often have a steep learning curve. A knowledge base simplifies onboarding by providing structured guides and learning resources that help new hires integrate into the company faster.
Strengthens Compliance and Security
Having a well-documented knowledge base helps companies enforce compliance with industry regulations and internal policies. Employees can easily reference security protocols and best practices to minimize risks.
Benefits and Challenges of an Internal Knowledge Base
Benefits
Increases Employee Autonomy
Employees can independently access the information they need without waiting for a response from managers or colleagues.
Enhances Collaboration
Teams across different departments or locations can benefit from internal knowledge base creating, which improves team collaboration by providing a centralized space to share knowledge and insights, reducing silos and enhancing cross-functional cooperation.
Saves Time for IT and HR
Self-service resources reduce the number of support tickets and administrative inquiries, allowing IT and HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Boosts Employee Satisfaction
Employees are more engaged and confident in their roles when they have immediate access to necessary information.
Challenges
Content Maintenance
Information becomes outdated over time. Without regular updates, employees may rely on incorrect or irrelevant data.
Low Adoption Rates
A knowledge base is only valuable if employees use it. Organizations must encourage participation and provide training to maximize adoption.
Search Functionality Issues
If the search function is poorly optimized, employees may struggle to find relevant content. AI-driven search tools and tagging systems help improve accuracy.
Content Overload
A cluttered knowledge base with excessive, unorganized content can make it difficult for employees to locate essential information.
Best Practices for Managing an Internal Knowledge Base
Define Clear Goals and Use Cases
Determine the primary purpose of the knowledge base. Whether it’s for company policies, IT support, or project documentation, clear objectives help structure the content effectively.
Organize Content for Easy Navigation
Use categories, subcategories, and tags to ensure employees can locate information quickly. A well-structured hierarchy improves usability. An efficient knowledge management system is crucial for organizing content and enhancing usability, serving as a centralized repository for vital information.
Implement Role-Based Access
Sensitive information should only be accessible to authorized employees. Role-based access control ensures security and compliance.
Use AI-Powered Search
Advanced search capabilities allow employees to find relevant content faster, reducing frustration and increasing adoption rates.
Regularly Update and Audit Content
Assign team members to review and update outdated information. Content analytics can identify which documents need revisions or removals.
Encourage Employee Contributions
Allow employees to suggest edits or submit knowledge base articles. Crowdsourcing content improves engagement and ensures a diverse range of insights.
Integrate With Collaboration Tools
Connecting the knowledge base with platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Trello enhances accessibility and usability.
Choosing the Right Knowledge Base Software
Choosing the right knowledge base software is crucial for creating an effective internal knowledge base. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to decide which one to choose. Here are some key features to look for in a company knowledge base:
Features to Look for in a Company Knowledge Base
-
Search Functionality: A robust search function is essential for a knowledge base. It should be able to search through all the content and provide relevant results quickly and accurately. Advanced search capabilities, such as AI-powered search, can significantly enhance the user experience by delivering precise information.
-
Collaboration Features: A good internal knowledge base should allow multiple users to contribute and edit content. Features like version control, commenting, and real-time collaboration ensure that the information remains accurate and up-to-date. These collaboration features also foster internal knowledge sharing and teamwork.
-
Customization: The knowledge base software should be customizable to fit your company’s needs. This includes the ability to create a custom layout, add your company’s branding, and create custom categories and tags. Customization ensures that the knowledge base aligns with your company’s identity and organizational structure.
-
Security: Robust security features are essential to ensure that only authorized users can access and edit content. Role-based access control, encryption, and regular security audits help protect sensitive company information and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
-
Integration: The knowledge base software should integrate seamlessly with other tools and systems that your company uses, such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, or project management tools. Integration enhances accessibility and ensures that the knowledge base becomes a central part of your company’s workflow.
Top Options for Best Knowledge Base Software
-
Confluence: Confluence is a popular knowledge base software that offers a range of features like collaboration, customization, and integration. It is widely used for its robust search functionality and user-friendly interface.
-
Notion: Notion is a versatile knowledge base software that provides extensive customization options and powerful collaboration features. Its integration capabilities make it a favorite among teams looking for a flexible solution.
-
Guru: Guru is a knowledge management platform designed to capture and share knowledge efficiently. It offers features like real-time collaboration, customization, and seamless integration with other tools.
-
ProProfs Knowledge Base: ProProfs Knowledge Base is known for its ease of use and comprehensive feature set, including collaboration tools, customization options, and strong search functionality.
-
Document360: Document360 is a knowledge base software that excels in providing a user-friendly experience with powerful collaboration and customization features. Its integration capabilities make it a strong contender for any organization.
Implementing an Internal Knowledge Base
Implementing an internal knowledge base requires careful planning and execution. Here are some steps to follow:
Plan and Create Your Content
-
Determine Your Goals: Start by defining what you want to achieve with your internal knowledge base. Identify the types of content you need, such as company policies, IT support guides, or project documentation. Understanding your goals will help you create a focused and effective knowledge base.
-
Build a Team: Assemble a team of content creators, editors, and reviewers. Assign specific roles and responsibilities to each team member to ensure a smooth content creation process. Collaboration features in your knowledge base software can facilitate teamwork and streamline content management.
-
Set Content Guidelines: Establish clear content guidelines, including tone, style, and format. Consistency is key to creating a professional and user-friendly knowledge base. Ensure that all content adheres to these guidelines to maintain a cohesive informational resource.
-
Create Content: Develop content that is relevant, accurate, and up-to-date. Use a variety of formats, such as text, images, and videos, to cater to different learning preferences. Interactive elements like FAQs and step-by-step guides can enhance the user experience.
-
Review and Edit: Regularly review and edit content to ensure its accuracy and relevance. Implement a version control system to track changes and maintain a history of edits. This process helps keep your knowledge base current and reliable.
By following these steps, you can create an effective internal knowledge base that improves employee productivity and performance. A well-implemented knowledge base not only serves as a centralized knowledge database but also enhances internal communication and collaboration, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and better overall company performance.
Related Concepts
Internal vs. External Knowledge Bases
An internal knowledge base is for employees, while an external knowledge base serves customers and the public. Both share information, but their audiences and content differ.
Document Management Systems (DMS)
A DMS helps organizations store, organize, and track digital documents. While similar to a knowledge base, a DMS primarily focuses on document control rather than broad knowledge sharing.
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
An LMS delivers training and educational content, often integrating with an internal knowledge base to support employee development.
Real-World Use Cases of an Internal Knowledge Base
Technology Companies
Tech firms use internal knowledge bases to document software development processes, troubleshoot common bugs, and store API references.
Healthcare Organizations
Hospitals and clinics rely on knowledge bases for medical protocols, compliance guidelines, and patient care procedures.
Retail and Customer Support Teams
Retail businesses and support teams document standard operating procedures for handling customer inquiries, refunds, and inventory management.
Remote Workforces
Distributed teams benefit from knowledge bases by maintaining a single repository for company updates, meeting notes, and project tracking.
Final Thoughts
An internal knowledge base is a powerful tool that enhances productivity, preserves institutional knowledge, and streamlines internal communication. Organizations that invest in well-maintained knowledge bases experience fewer inefficiencies, stronger collaboration, and better employee engagement. By implementing best practices—such as optimizing search functionality, keeping content updated, and integrating with workplace tools—businesses can maximize the value of their internal knowledge management systems.






