A recent study* found that 52% of US workers often feel frustrated because they can’t find the information they need. And even when they do find it, 69% are not sure if it’s accurate or relevant.
So what are the numbers really telling us? Maybe it’s time for businesses to take their company knowledge base seriously, rather than just a dumping ground for files and documents.
The knowledge you gain and accumulate over time as a company is your primary competitive advantage. This might look like something rather universal such as an employee handbook or employee equipment agreement form, or something uniquely yours like customer insights, operational IP, and domain expertise, among many others. Those within your industry might have similar resources, but never exactly the same.
It’s safe to say no one else has the experience and insights that you do. So there is no reason to make this wealth of understanding difficult to find, especially for people who actually need to access and use it almost every day—your employees.
And this is where company knowledge base comes in.
What is company knowledge base?
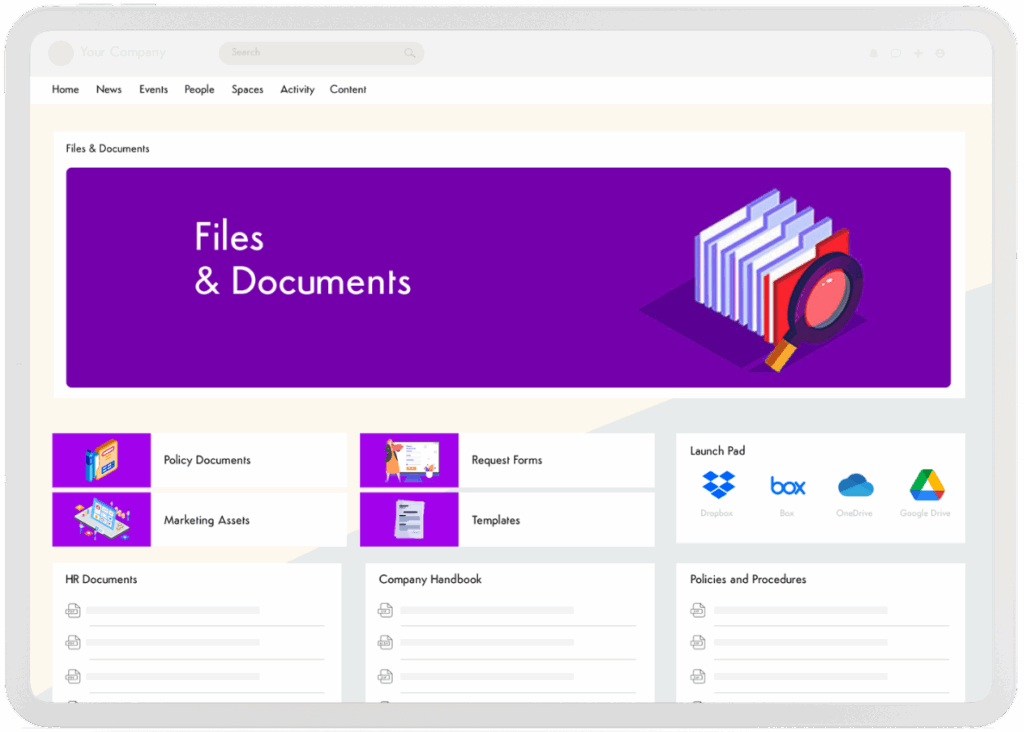
Just like search engines most of us use every day, think of a knowledge base as your company’s personal Google. Everything that is pertinent to day-to-day operations is searchable and always accessible. From company policies to training materials, employees can find answers fast, no matter where they are, and without having to rely on others.
In fact, 1 in 5 US knowledge workers struggles to work efficiently every day due to a lack of access to the right resources. The case is clear that access to relevant information can directly boost productivity and even enhance autonomy at work.
Now the question is, where does the “knowledge” come from?
In all honesty, it can come from anyone within your company (or even outside of it, but more on that later). Knowledge doesn’t necessarily always originate in formal documentation. In fact, it often begins organically.
Take this scenario: A salesperson might ask, “What’s the latest messaging we are using against Competitor X?” Someone replies, then someone else chimes in. Suddenly, there’s a full-blown thread: an OG rep shares what worked (or didn’t), another drops a nugget of insight that never made it to the CRM, and another shares a recording of a sales call that actually converted.
And this is the turning point. Unless someone recognizes that this very conversation is knowledge to capture and put it on the knowledge base, it goes nowhere, gets buried in Slack, lost in personal notes, or fades into distant memory.
In the same vein, when prospects and clients tell you what messaging resonates, what their pain points are, which features they love, which CTA gives them that final nudge to fill out the form, or even what your competitors are promising, this is external knowledge. And it’s gold. These insights are incredibly valuable, and they deserve to be fed back into your internal knowledge base.
Ok then, where exactly should the company knowledge base live?
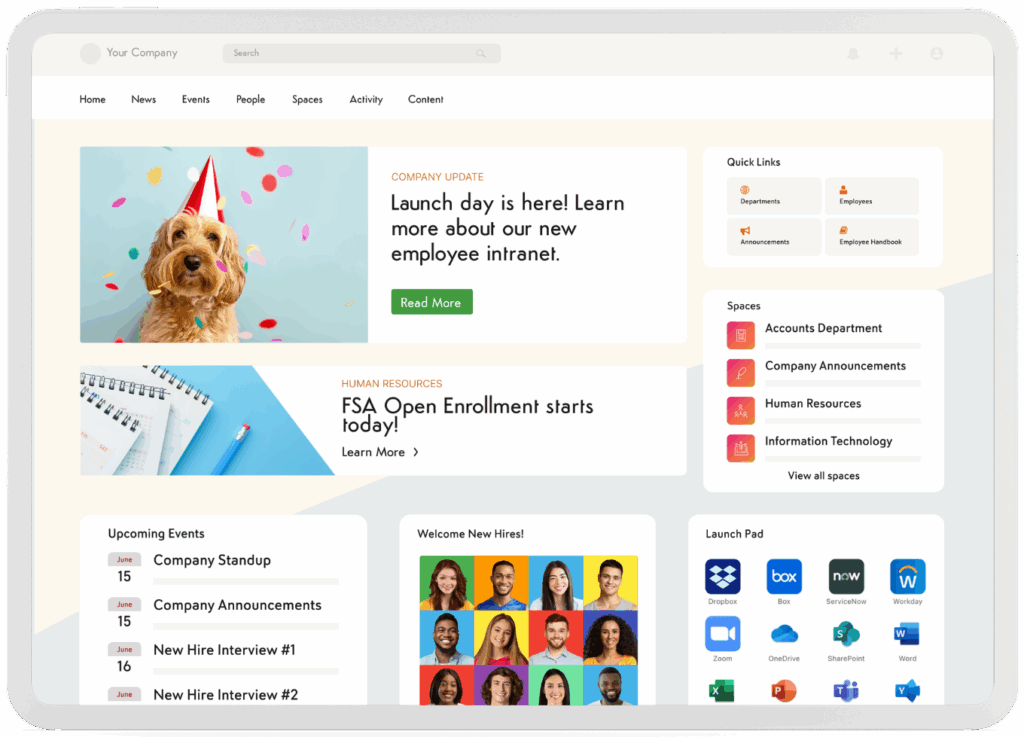
When it comes to what you use for your company knowledge base, your intranet is the perfect solution, as long as it supports knowledge management.
One might argue, “I can just use Google Drive or OneDrive!” Well, you could. However, those platforms are not built for knowledge sharing or management. They are built for file storage, which is also literally what they are officially called.
While Google Drive and OneDrive are great for storing files, they often lack what makes knowledge easy to find and understand. Think mystery folders from deactivated users, five conflicting versions of the same doc, or that one teammate who swears “it’s in the Drive somewhere” but never finds it.
A proper knowledge base within your intranet goes far beyond storage. With modern intranet like Axero, you have a host of intuitive tools that enables employees and teams to:
- Search intuitively and find exactly what they need, fast
- Collaborate in context; add comments, suggestions, and updates in one place
- Track ownership and versioning so knowledge stays fresh and accurate
- Contribute with visibility and recognition baked in
The best part? One less platform for your people to shuffle through means more time saved, especially when knowledge workers in the US spend an average of 10 hours per week* searching for information, that’s 1/4 of a workweek!
At the end of the day, it’s really up to you to make sure your employees are equipped with what they need to thrive. So, if you’re ready to take that leap and build the best company knowledge base ever, here’s how.
Capture knowledge (yes, really)
It might seem like a given, but it’s surprisingly easy to overlook. For a company knowledge base to exist and (hopefully) thrive, knowledge needs to be captured. But this – capturing of knowledge – should not fall on the shoulders of a single person or team, and it should also not feel like extra work on top of your day-to-day responsibilities.
And for knowledge capturing to be natural and not burdensome, a culture of knowledge sharing needs to be encouraged at work. This means that everyone, from interns to C-suite, should feel comfortable sharing whatever they believe could be of benefit to others, whether that’s in their roles, processes, or overarching goals, among many.
When knowledge sharing is instilled in every aspect of your business, your entire workforce benefits from up-to-date information, which ultimately breaks silos and increases productivity. Imagine your sales rep could just search for and instantly access that messaging against Competitor X, your new hires could look up how-to guides, and your staff could actually receive accurate and relevant results every time. Now that is the true power of company knowledge base.
Make it easy
To turn your company knowledge base into a genuinely helpful resource, your content needs to be easy to access, digest, and update. Think about who the content is for, and what they need from it.
Chances are that some of your teams run into the same problems over and over again. Instead of seeing this as a problem, consider it a valuable opportunity to identify where your employees need support. For instance, if your customer support team keeps getting asked the same questions, it makes sense to pull those answers into FAQs. This kind of self-service content saves time and keeps things consistent.
Other teams, say legal at HQ or staff on the factory floor, might need more detailed, technical documentation. But please don’t just dump a load of PDFs into your knowledge base with no structure or proper search functionality. Go through the content with a fine-tooth comb. The information you provide should be clear, useful, and tailored to the way your people actually work.
Take advantage of different content types
The right knowledge base software should support a wide range of content formats. This might include, but is not limited to:
- Blog posts and articles
- FAQ pages
- Support tickets and their archives
- Wikis
- Troubleshooting guides
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Onboarding checklists
- How-to guides
- Video tutorials
- Infographics and visual aids
Not only does this variety ensure that information can be communicated in ways that make the most sense, say an infographic of public holidays and events or a step-by-step instruction on how to submit business expenses, but it also accommodates different learning styles and audience preferences. Some users may quickly absorb information from visuals, while others prefer written, informative articles or searchable FAQs.
At the end of the day, your company knowledge base should cater to a broader range of users, not just one specific group.
Keep content fresh
What’s worse than having no company knowledge base at all? Definitely having one that’s full of unhelpful content.
In fact, 56% of US employees admit there is a significant amount of outdated and irrelevant information within their business. When your team can’t trust the information in front of them, they spend even more time double-checking, second-guessing, or recreating resources from scratch. It is inconvenient, confusing, and only bound to dampen productivity.
That said, your company knowledge base should be regularly updated, or your employees won’t get and find much value from it. It should house new insights and data whenever they become available. For example:
How many deals did you close in Q2 of last year?
What were the results of your customer happiness survey?
Do you have a library with all key marketing assets for your sales team?
This is all information that should live in your knowledge management system. It helps your employees do their jobs well, stay informed about progress, and reduce bottlenecks. As employees interact with the company knowledge base, they can continue to review, update, and add feedback on the content, as well as what works and what doesn’t when it comes to the system itself.
If there are errors, anyone—or a select few—can update the content or bring it to the attention of admins or those in charge. This keeps your company knowledge base an inviting space where your employees work as a community and contribute to overall growth.
Leverage artificial intelligence
There’s no denying that AI is taking the world by storm, workplaces included. In fact, McKinsey’s 2025 report on AI in the workplace shows 92% of companies plan to invest more in generative artificial intelligence, or gen AI, over the next 3 years. You can only deny using AI so much so that you will likely fall behind.
And AI can take company knowledge base to the next level. Let’s take our very own Axero Copilot as an example. Think of it like one of your colleagues who is on standby ready to find answers to your questions and then some. What do we mean by this? Axero Copilot AI agent doesn’t just understand your requests, it anticipates what you might need next.
Let’s say you are a senior designer helping a new junior designer get up to speed on brand guidelines for different clients. Instead of manually digging through folders and pages, you can simply ask Axero Copilot AI agent, “Can you help me get all of our customers’ brand guidelines?”
Within seconds, it surfaces relevant information, pulls files from your company knowledge base, and suggests next steps, whether that be quick links to brand assets and materials, recent deliverables for reference, or key design do’s and don’ts.
Sure, you could do all of this manually (hey, we don’t judge). But if AI can help you move faster and focus on the work that actually matters, why not give it a try?
Make it social
Another way to keep your company knowledge base fresh, fun, and engaging (and as far away as possible from turning into a SharePoint graveyard no one has set foot in in years) is to make it social!
Your company knowledge base can store articles, files, and resources for everyone to access today, tomorrow, months, or years from now. And, especially today, you can and should expect social features like commenting, liking, tagging, @mentioning, and sharing to be available right out of the box with modern knowledge management system.
When employees can comment, like, and share content among and across teams, it enables continuous improvement not just for the content itself, but for how your teams learn from each other and work together.
Encourage (or even incentivize!) content creation
When employees regularly document processes, insights, and solutions, you keep information silos and knowledge loss at bay, especially when team members move on or shift roles. A rich, up-to-date company knowledge base becomes a powerful self-service resource that helps save time, boost productivity, and cut down on repetitive questions and duplicated work.
To make it even more engaging, why not throw in some incentives for contributions? Incentives don’t always have to be monetary. For example, if a customer support agent regularly logs frequently asked questions and their answers, which help reduce response times for the whole team, award them a “Top Contributor” badge next to their profile. Not only might this inspire others to follow suit, but it’s also a great example of employee recognition in action!
Utilize it externally
The benefits of a company knowledge base extend beyond internal use. It can also serve as a helpful resource for external communications with potential leads, current customers, and visitors to your public website.
In fact, you might already be using a knowledge base without realizing it. Anytime you browse an FAQ section or find relevant articles in a support centre, you are tapping into that business’s external knowledge base. It’s their way of sharing helpful, curated information to enhance your experience, and it could be yours too.
But does that mean all your knowledge is out in the wild? Definitely not. A good knowledge management system should support fine-grained permission controls, so you can decide exactly who sees what, whether it’s private content for internal teams, restricted access for specific clients, or public-facing information for everyone to benefit from.
Integrate your knowledge base into your intranet
Your intranet is the perfect home for your company’s internal knowledge because it simplifies how your employees do their jobs. When everything lives in one place, employees don’t waste time searching for files, bouncing between different platforms, or accidentally viewing outdated versions of documents.
With modern intranet like Axero, you get a centralized, intelligent hub that makes it easy for your employees to create, organize, and access knowledge. Teams can collaborate, updates are available instantly, and everyone stays aligned with what’s most current, all in one secure location.
It’s worth noting that, once you have it, you need to treat your company knowledge base like a growing, living system that needs to evolve over time. Look for ways to improve. We recommend talking to your employees as they are the ones who understand firsthand what’s working and what could use some TLC.
Get your knowledge organized with Axero

Don’t let insights get lost in emails, forgotten threads, or chaotic shared drives. When you centralize your knowledge, you empower your teams and strengthen knowledge sharing that grows as your business scales.
Knowledge is power. And when it’s easy to access, update, and share, your entire organization benefits. Book a demo now and see what’s possible with Axero.
*https://obrizum.com/resources/empowering-the-modern-knowledge-worker/
















 info@axerosolutions.com
info@axerosolutions.com 1-855-AXERO-55
1-855-AXERO-55


