What is Prescriptive Analytics?
Prescriptive analytics is the process of using data to determine the best course of action. It is a key component of business analytics, a comprehensive process that encompasses prescriptive analytics, predictive analytics, and descriptive analytics. Data analytics employs various algorithms to analyze raw data and generate actionable insights.
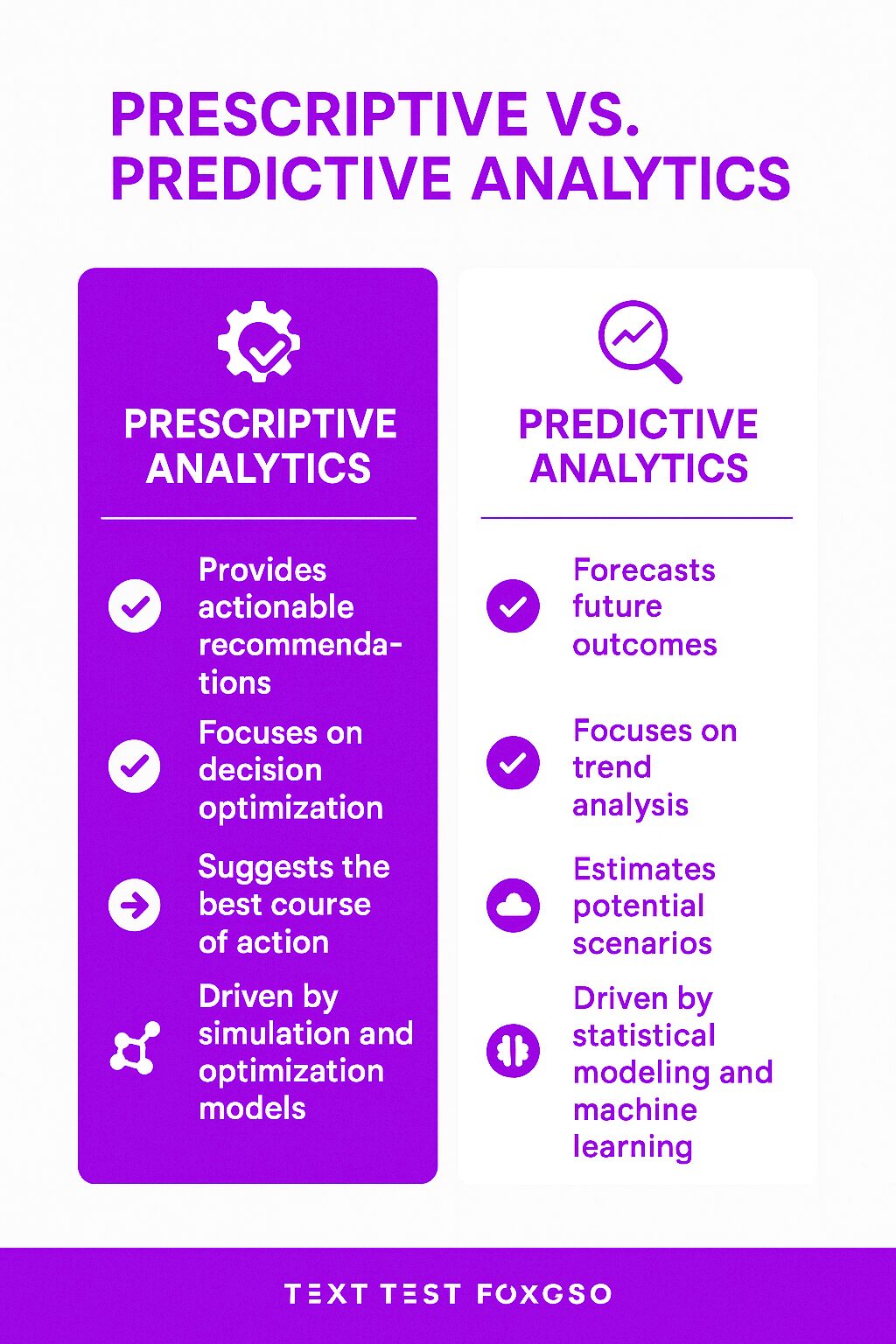
Businesses use prescriptive analytics to make informed decisions. It helps organizations understand what could happen, why it might happen, and what they should do about it. Unlike traditional data analysis, which focuses on hindsight or foresight, prescriptive analytics provides actionable solutions.
How Prescriptive Analytics Works
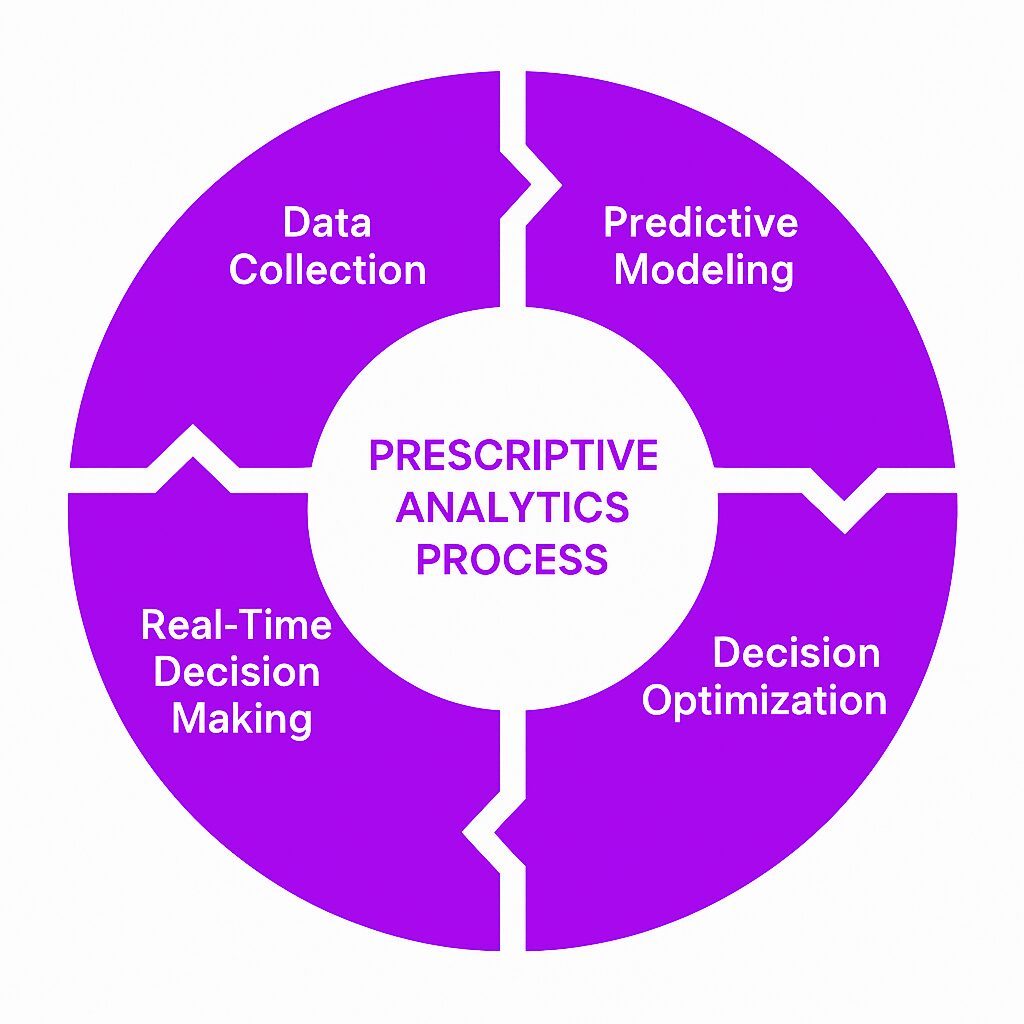
Prescriptive analytics uses advanced algorithms, AI, and statistical models to process large amounts of data. It also relies on current and historical data to analyze and forecast outcomes. The goal is to identify patterns and generate recommendations. This approach combines three key elements:
-
Data Collection: Gathering structured and unstructured data from various sources.
-
Predictive Modeling: Analyzing historical data to forecast potential outcomes.
-
Decision Optimization: Recommending the best course of action based on insights.
For example, an e-commerce company might use prescriptive analytics to determine the best pricing strategy. The system analyzes sales data, competitor pricing, and customer behavior to suggest price adjustments that maximize revenue.
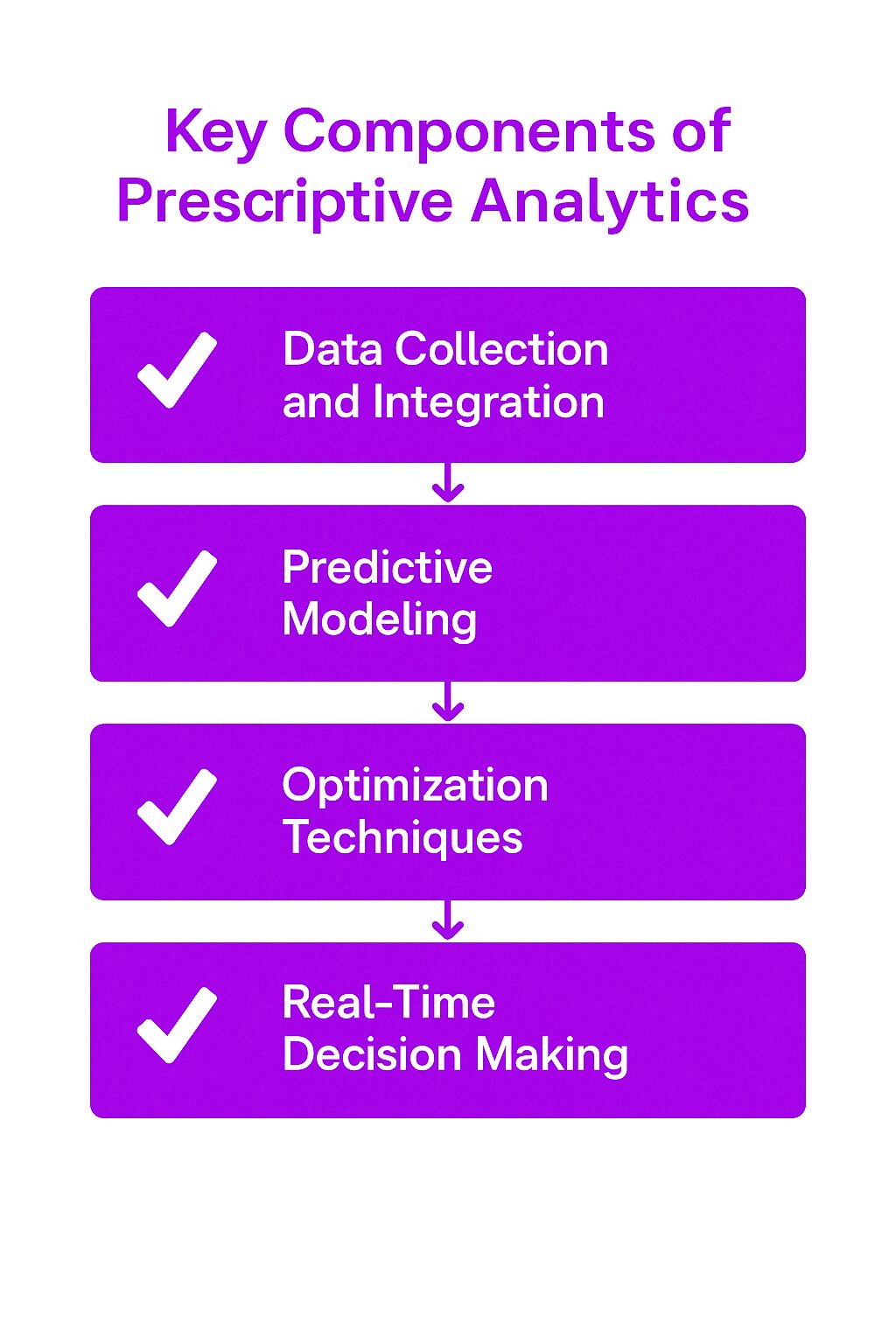
Key Components of Prescriptive Analytics
Data Collection and Integration
Prescriptive analytics relies on high-quality data. Optimizing business processes through data collection is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and patient outcomes. This includes historical records, real-time inputs, and external factors such as market trends. Business rules are essential for defining and guiding these data collection processes. The data is collected from multiple sources, including:
-
Internal databases (CRM, ERP, financial systems)
-
Sensor and IoT data
-
Social media interactions
-
Third-party market research
Predictive Modeling
Before prescribing actions, analytics models must first predict potential outcomes. Prescriptive analytics models are developed based on predictive modeling, utilizing current and projected market conditions and customer trends to optimize product focus within organizations. Predictive modeling uses statistical techniques such as:
-
Regression analysis
-
Machine learning algorithms
-
Time series forecasting
-
Neural networks
These models estimate what might happen under different conditions, creating a foundation for prescriptive analytics. Probability weighted projections are then used to make informed recommendations by simulating various scenarios and predicting outcomes, helping businesses navigate complex decisions and mitigate human biases.
Optimization Techniques
Optimization is a core function of prescriptive analytics. It ensures that recommendations are not just possible but also ideal. Techniques include:
-
Linear programming (for resource allocation)
-
Decision trees (for structured decision-making)
-
Simulation modeling (to test different scenarios)
-
Constraint optimization (to balance trade-offs)
Real-Time Decision Making
Many businesses require instant decision-making. Prescriptive analytics can integrate with automated systems to provide real-time recommendations. For example:
-
Retailers adjust product prices dynamically based on supply and demand.
-
Airlines optimize flight schedules based on weather and booking patterns.
-
Healthcare providers personalize treatment plans for patients.
Why Prescriptive Analytics Matters
Organizations make countless decisions daily. Without data-driven insights, these choices rely on intuition and experience alone. Prescriptive analytics eliminates guesswork by providing specific recommendations based on real data.
Prescriptive analytics is particularly valuable in:
-
Supply Chain Management: Optimizing inventory levels and logistics.
-
Customer Experience: Tailoring marketing campaigns to individual users.
-
Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential threats.
-
Healthcare: Recommending treatments based on patient data.
Benefits of Prescriptive Analytics
Better Decision-Making
Prescriptive analytics allows businesses to make informed choices using proprietary algorithms. Developing proprietary algorithms is crucial in executing prescriptive analytics, as it enables companies to create tailored solutions that drive data-informed decision-making. It provides clear, data-backed recommendations rather than relying on assumptions.
Optimized Resource Allocation
Companies can distribute resources more effectively. For example, manufacturers use prescriptive analytics to manage raw material procurement and reduce waste.
Improved Customer Experience
By analyzing customer preferences, businesses can personalize services. Streaming platforms use prescriptive analytics to suggest content based on viewing history.
Reduced Risks
Financial institutions use prescriptive analytics to detect fraud and minimize credit risk. It helps organizations prepare for potential disruptions before they occur.
Increased Efficiency
Automation powered by prescriptive analytics reduces manual intervention. Businesses streamline operations, cut costs, and improve overall performance.
Challenges of Prescriptive Analytics
Data Quality Issues
Poor data leads to inaccurate recommendations. Organizations must ensure that their data is clean, complete, and up to date.
Complex Implementation
Setting up prescriptive analytics requires significant investment in software, infrastructure, and expertise. Many businesses struggle with integration into existing systems.
Bias in AI Models
Prescriptive analytics relies on machine learning models, which can be biased if trained on flawed data. Companies must audit algorithms to ensure fairness and accuracy.
High Dependence on Technology
Organizations must maintain and update their analytics systems regularly. Technical failures or outdated models can lead to incorrect recommendations.
Best Practices for Implementing Prescriptive Analytics
Ensure High-Quality Data
Clean, accurate data is essential. Companies should invest in data governance policies to maintain integrity.
Align with Business Goals
Prescriptive analytics should serve specific business objectives. Organizations should identify key decision-making areas where analytics can provide value.
Invest in the Right Tools
There are various prescriptive analytics platforms available, such as:
-
IBM Watson Analytics
-
SAS Advanced Analytics
-
Google Cloud AI
-
Microsoft Azure Machine Learning
Choosing the right tool depends on the organization’s needs and existing infrastructure.
Monitor and Update Models Regularly
Analytics models must evolve with changing market conditions. Continuous monitoring ensures that recommendations remain relevant and effective.
Train Employees on Data Interpretation
While prescriptive analytics provides recommendations, human judgment is still required. Employees must understand how to interpret and act on analytics insights.
Related Concepts
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics focuses on past trends. It answers questions like “What happened?” by analyzing historical data.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics forecasts future trends. It uses statistical models to estimate what might happen next.
AI-Driven Decision Making
Artificial intelligence enhances prescriptive analytics by automating decision-making processes.
Big Data in Analytics
Prescriptive analytics depends on big data. The more diverse and comprehensive the dataset, the more accurate the recommendations.
Real-World Use Cases
Healthcare
Hospitals use prescriptive analytics to recommend treatment plans. AI-driven models analyze patient history, genetic factors, and medical research to suggest optimal care paths.
Retail
Retailers optimize pricing strategies using prescriptive analytics. Online stores adjust product prices in real time based on demand, competitor pricing, and inventory levels.
Finance
Banks use prescriptive analytics to detect fraudulent transactions. Machine learning models identify unusual spending patterns and trigger security alerts.
Manufacturing
Factories use prescriptive analytics for predictive maintenance. Sensors detect early signs of equipment failure, allowing repairs before major breakdowns occur.
Final Thoughts
Prescriptive analytics is changing how businesses make decisions. By using data-driven recommendations, organizations reduce risks, optimize resources, and improve customer experiences. While implementation can be complex, the benefits make it a valuable tool for companies looking to gain a competitive edge.