What Is Customer Experience?
Customer experience (CX) is how customers perceive their interactions with a company at every touchpoint. It includes everything from a brand’s website and customer service to in-store experiences and post-purchase support. CX is not just about a single transaction—it’s the sum of all customer interactions, shaping their overall perception of a business.
A great customer experience fosters loyalty and repeat business, while a poor experience drives customers away. Companies that focus on CX understand that satisfied customers are more likely to recommend their brand and spend more over time.
How Customer Experience Works
Customer experience covers the entire customer journey, from the moment someone becomes aware of a brand to their post-purchase interactions. A seamless experience ensures customers feel valued and supported at every stage.
Businesses must optimize multiple areas to create a strong CX, including:
-
Product usability – How easy it is for customers to use a product or service.
-
Customer service – The responsiveness and helpfulness of support teams.
-
Brand perception – How customers feel about a brand based on their interactions.
-
Omnichannel experience – Consistency across online, in-person, and mobile interactions.
Companies that focus on CX measure customer satisfaction, gather feedback, and make adjustments to improve interactions across all platforms by aligning business processes with customer experience strategies.
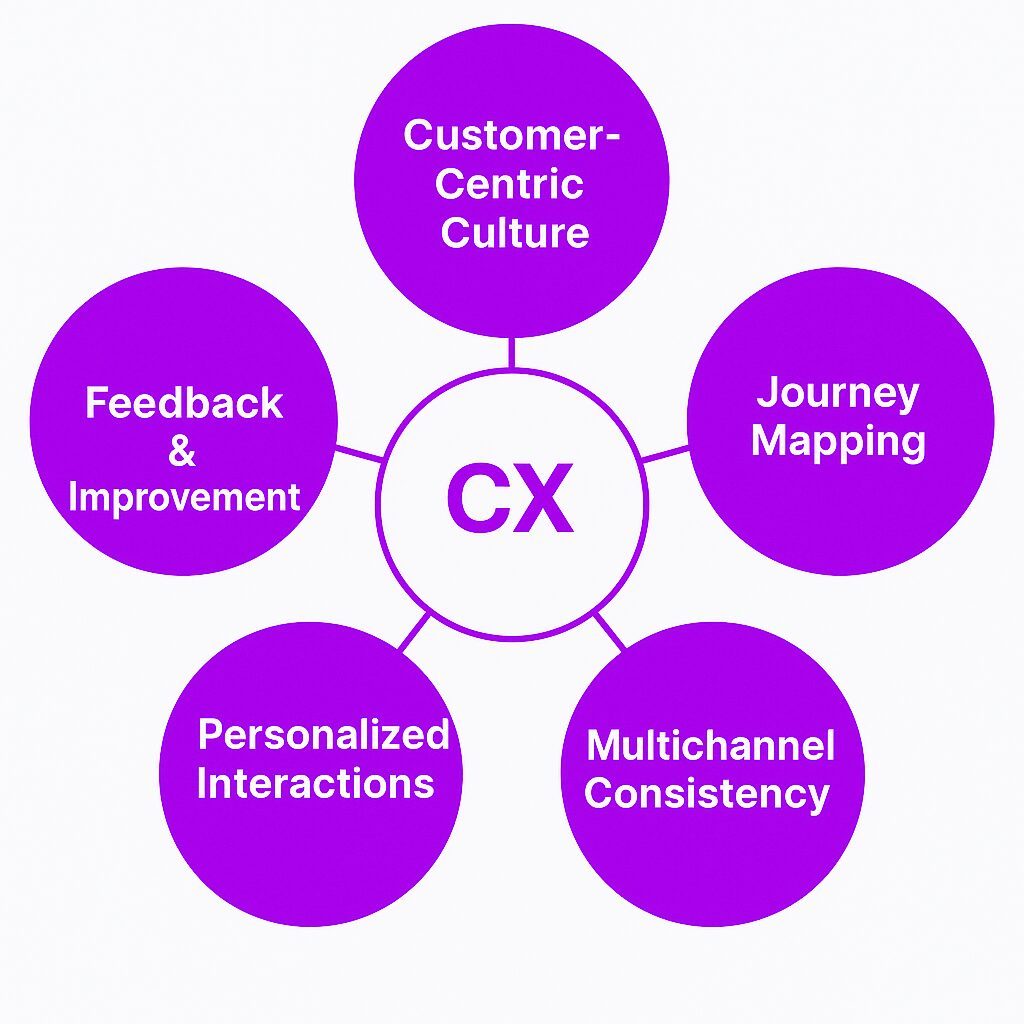
Key Components of Customer Experience
1. Customer-Centric Culture
Businesses that prioritize CX create a culture where employees focus on customer satisfaction. Every department, from sales to product development, plays a role in shaping the customer’s experience.
2. Customer Journey Mapping
Mapping customer journeys helps businesses identify gaps in the experience. This involves understanding each touchpoint, from discovery and purchase to support and retention.
3. Personalized Interactions
Customers expect personalized service based on their preferences, past purchases, and behavior. Companies use customer data to tailor experiences, providing relevant recommendations and support.
Customer relationship management (CRM) plays a vital role in developing and optimizing long-term relationships between customers and organizations, enhancing customer experience (CX) and leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Seamless Multichannel Experience
Customers interact with brands across multiple platforms—websites, social media, mobile apps, and physical stores. A great CX ensures consistency and smooth transitions between channels.
5. Customer Feedback and Improvement
Regularly collecting and acting on customer feedback is essential for improving CX. Companies use surveys, reviews, and analytics to understand pain points and make necessary changes.
Understanding Customer Behavior
Understanding customer behavior is crucial for creating a positive customer experience. By analyzing customer behavior, businesses can identify patterns, preferences, and pain points that can inform their customer experience strategy. This deep understanding allows companies to anticipate customer needs and tailor their interactions to delight customers at every touchpoint. When businesses invest time in understanding their customers, they can create more personalized and meaningful experiences that foster loyalty and satisfaction.
1. Creating a Customer Journey Map
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the customer’s experience across all touchpoints and interactions with a business. It helps businesses to understand the customer’s perspective, identify pain points, and optimize the customer experience. A customer journey map typically includes the following elements:
-
Customer personas: A detailed description of the target customer, including demographics, needs, and goals.
-
Touchpoints: A list of all the interactions a customer has with a business, including online and offline interactions.
-
Customer emotions: A description of the emotions a customer experiences at each touchpoint.
-
Pain points: A list of the challenges and frustrations a customer experiences at each touchpoint.
-
Opportunities: A list of opportunities to improve the customer experience at each touchpoint.
By creating a customer journey map, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs and preferences, and identify areas for improvement. This tool is invaluable for visualizing the entire customer journey and ensuring that every interaction contributes to a remarkable customer experience.
2. Identifying Pain Points in the Customer Journey
Identifying pain points in the customer journey is critical for creating a positive customer experience. Pain points are the challenges and frustrations that customers experience at each touchpoint. By identifying pain points, businesses can develop strategies to address them and improve the customer experience.
Some common pain points in the customer journey include:
-
Long wait times
-
Difficulty navigating a website or mobile app
-
Poor customer service
-
Lack of transparency and communication
-
Difficulty returning or exchanging products
By identifying and addressing pain points, businesses can create a more seamless and enjoyable customer experience. This proactive approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces customer churn and builds stronger customer relationships.
Customer Experience Management
Customer experience management (CEM) is the process of designing and delivering a positive customer experience across all touchpoints and interactions with a business. It involves understanding customer needs and preferences, and developing strategies to meet those needs. Effective CEM ensures that every customer interaction is optimized to create a positive and lasting impression.
1. Definition of Customer Experience Management
Customer experience management is a holistic approach to managing the customer experience. It involves understanding customer needs and preferences, and developing strategies to meet those needs. CEM includes the following elements:
-
Customer experience strategy: A plan for creating a positive customer experience across all touchpoints and interactions.
-
Customer journey mapping: A visual representation of the customer’s experience across all touchpoints and interactions.
-
Customer feedback: Collecting and analyzing customer feedback to understand customer needs and preferences.
-
Employee engagement: Engaging employees in the customer experience and empowering them to deliver a positive customer experience.
-
Technology: Using technology to support the customer experience, such as CRM systems and customer service software.
By implementing a customer experience management strategy, businesses can create a positive customer experience that drives loyalty, retention, and revenue growth. This comprehensive approach ensures that every aspect of the customer journey is carefully managed and continuously improved to meet and exceed customer expectations.
The Customer Experience Journey
1. Awareness
Customers first encounter a brand through advertising, word-of-mouth, or online search. Businesses must create a strong, positive first impression.
2. Consideration
Customers compare options before making a decision. Businesses that provide clear, useful information, product comparisons, and customer reviews improve their chances of winning customers.
3. Purchase
A smooth, hassle-free purchasing process is crucial. Complicated checkouts, unclear pricing, or hidden fees can frustrate customers and drive them away.
4. Onboarding
After purchasing, customers need guidance on how to use a product or service. Tutorials, FAQs, and dedicated support ensure they get the most value from their purchase.
5. Post-Purchase Support
Strong post-purchase interactions include proactive customer support, easy return policies, and follow-up emails to ensure satisfaction. A knowledgeable customer service representative is essential in these interactions, as they can significantly influence customer experiences.
6. Customer Loyalty and Advocacy
Satisfied customers become repeat buyers and brand advocates, recommending products to friends and family. Loyalty programs and incentives keep customers engaged.
Why Customer Experience Matters
A great customer experience sets a company apart from competitors. Positive customer experiences make customers feel happy and valued, and those feelings influence purchasing decisions.
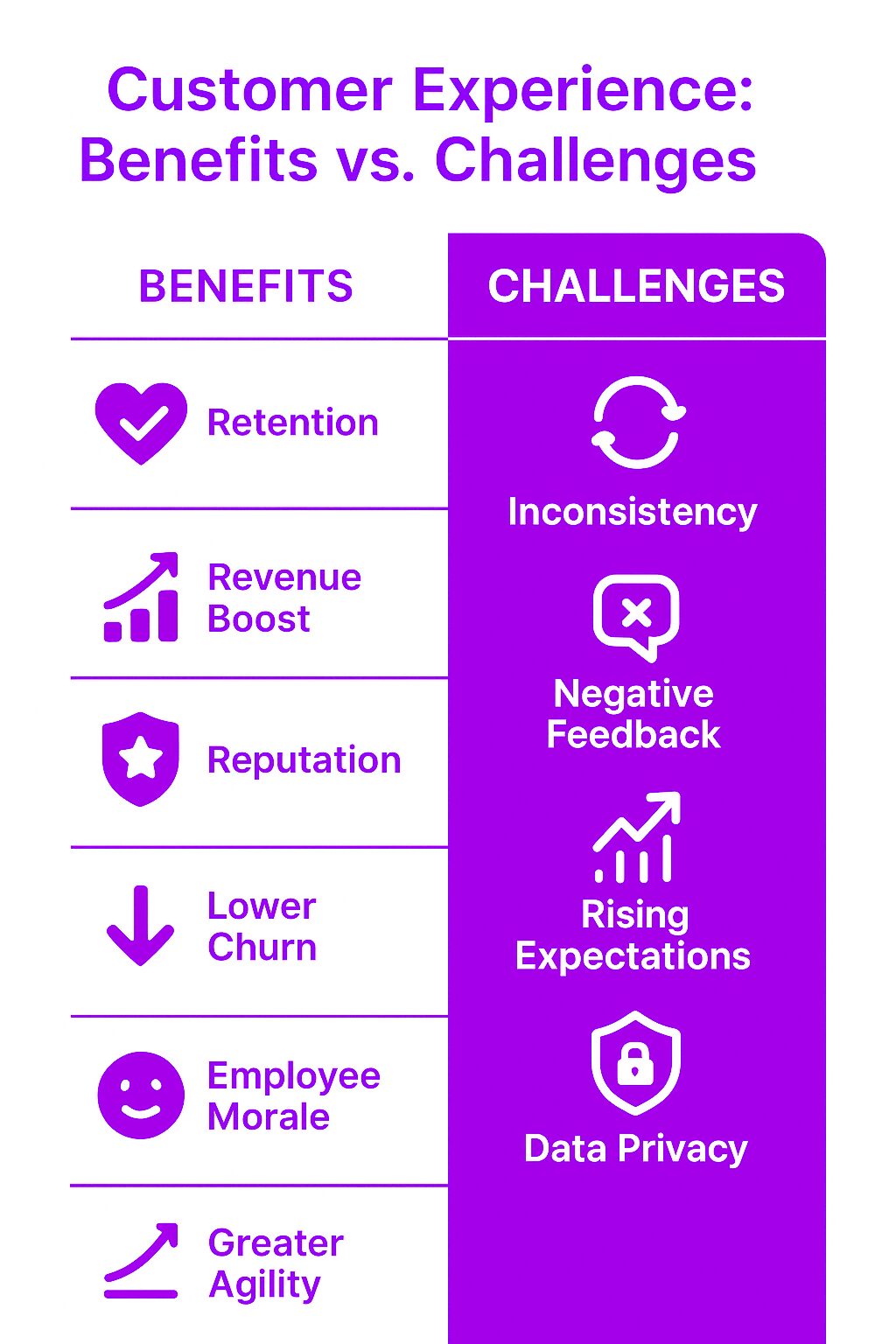
Benefits of Strong CX
-
Increases customer retention – Happy customers are more likely to return.
-
Boosts revenue – Customers are willing to pay more for better experiences.
-
Enhances brand reputation – Positive experiences lead to strong word-of-mouth marketing.
-
Reduces customer churn – Poor experiences drive customers to competitors.
-
Improves employee satisfaction – Employees thrive in customer-focused environments.
Common Customer Experience Challenges
1. Inconsistent Service
A poor experience in one channel can ruin the overall perception of a brand. Companies must ensure consistency across all interactions.
2. Handling Negative Feedback
Every company receives complaints. How businesses handle issues determines whether customers stay loyal or leave.
3. Keeping Up with Customer Expectations
Customers expect fast service, personalized recommendations, and seamless interactions. Meeting these expectations requires continuous improvement.
4. Privacy and Data Security Concerns
Personalization relies on customer data, but businesses must handle information responsibly. Trust is key to maintaining a positive experience.
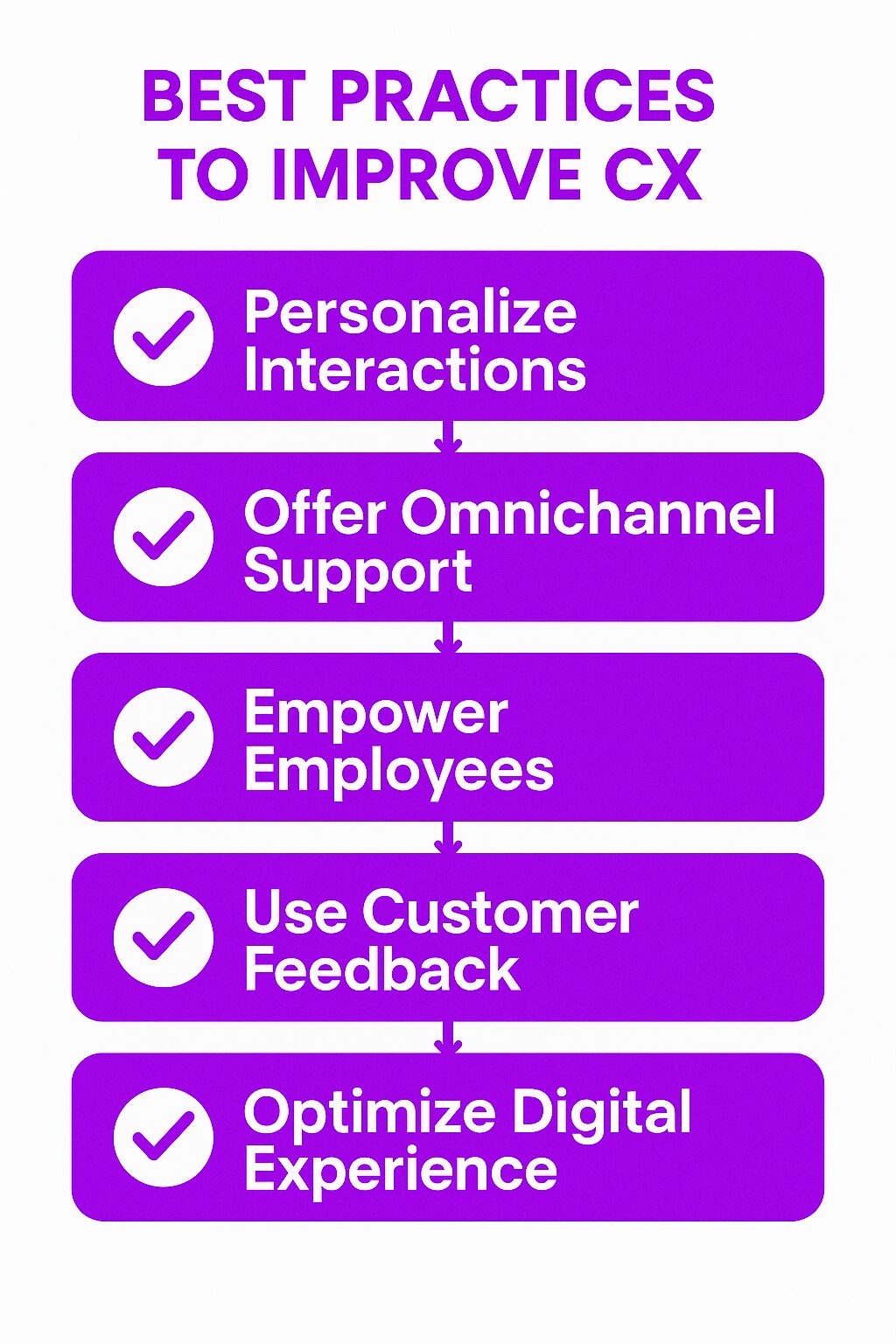
Best Practices for Improving Customer Experience
1. Personalize Customer Interactions
Customers appreciate when brands remember their preferences and purchase history. Use data to provide relevant recommendations and support.
2. Offer Omnichannel Support
Customers should receive the same level of service whether they contact a company via phone, email, live chat, or social media.
3. Empower Employees
Employees should have the tools and authority to resolve customer issues quickly. Training and support improve frontline service.
4. Leverage Customer Feedback
Surveys, online reviews, and social media monitoring help businesses identify areas for improvement.
5. Optimize Digital Experiences
Fast-loading websites, easy navigation, and clear product descriptions enhance online CX.
Customer Experience vs. Customer Service
Customer experience and customer service are related but distinct:
-
Customer experience covers every interaction a customer has with a company.
-
Customer service is one part of CX, focusing on support and issue resolution.
Great customer service enhances overall CX, but businesses must optimize all touchpoints to provide a seamless experience.
Real-World Examples of Great Customer Experience
1. Amazon
Amazon is known for its seamless shopping experience, fast delivery, and customer-friendly return policies.
2. Apple
Apple’s in-store experiences, product design, and customer support create a loyal customer base.
3. Disney
Disney focuses on creating magical experiences at every touchpoint, from theme parks to customer support.
4. Netflix
Netflix’s personalized recommendations keep customers engaged and coming back for more.
Companies That Struggle with CX
1. Comcast
Comcast has faced criticism for poor customer service, long wait times, and billing issues.
2. United Airlines
United’s handling of customer incidents has negatively impacted its reputation.
3. Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo lost trust due to unethical practices, damaging customer confidence.
Final Thoughts
Customer experience is a crucial factor in business success. Companies that invest in CX build stronger relationships, increase revenue, and differentiate themselves in the market. Businesses must continuously refine their strategies, listen to customer feedback, and adapt to changing expectations to create memorable and meaningful experiences.