What is Talent Acquisition?
Talent acquisition refers to the strategic process of identifying, attracting, evaluating, and hiring top talent to fill key roles within an organization. Unlike recruitment, which tends to focus on filling immediate vacancies, the recruitment process in talent acquisition takes a long-term, proactive approach. It emphasizes creating a sustainable talent pipeline that ensures an organization’s leadership and workforce are always prepared for current and future challenges.
Talent acquisition involves more than just hiring employees; it is about identifying the right people who can contribute to the organization’s long-term success. It also involves engaging with candidates early on, even before specific roles become available, to build relationships and maintain a pool of potential talent.
Comprehensive Explanation
Talent acquisition is a comprehensive, strategic process that aligns hiring efforts with an organization’s long-term goals. Talent acquisition responsibilities include developing a strong candidate pipeline, employer branding, and future resource planning. It’s a combination of several key functions, including workforce planning, employer branding, sourcing, recruitment, and employee retention strategies. The process ensures that organizations are not only attracting qualified candidates but are also preparing them for success within the company.
Talent Acquisition vs. Recruitment
While both talent acquisition and recruitment involve hiring new employees, the scope and strategy of each are different:
-
Recruitment: Typically short-term and focused on filling specific, immediate job openings. Recruitment is a reactive process, often driven by the organization’s immediate needs.
-
Talent Acquisition: Proactive and strategic. It involves planning for the future by attracting, nurturing, and retaining top talent. Talent acquisition focuses on developing long-term relationships with potential candidates and ensures the organization has a sustainable pipeline of qualified candidates for various roles.
A talent acquisition specialist plays a crucial role in this strategic process, focusing on the skills required for the job, career progression, and salary expectations.
Talent acquisition is a continuous and dynamic process. While it includes recruitment, it also involves workforce planning and long-term engagement with prospective employees.
Building a Talent Acquisition Strategy
Framework and Pillars
Building a talent acquisition strategy is essential for ensuring that an organization has the right people to achieve its goals. A well-structured talent acquisition strategy provides a roadmap for attracting, engaging, and retaining top talent. Here’s a breakdown of the framework and pillars that guide this process:
Framework for a Talent Acquisition Strategy:
-
Define: Clearly define the organization’s talent acquisition goals and objectives. Understand what success looks like and set measurable targets.
-
Assess: Evaluate the current talent acquisition process to identify strengths and areas for improvement. This assessment helps in understanding the gaps and opportunities.
-
Design: Create a new talent acquisition process that aligns with the organization’s goals. This includes developing strategies for sourcing, recruiting, and onboarding.
-
Implement: Roll out the new talent acquisition process, ensuring that all stakeholders are trained and aware of their roles and responsibilities.
-
Evaluate: Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the talent acquisition process. Use feedback and data to make necessary adjustments.
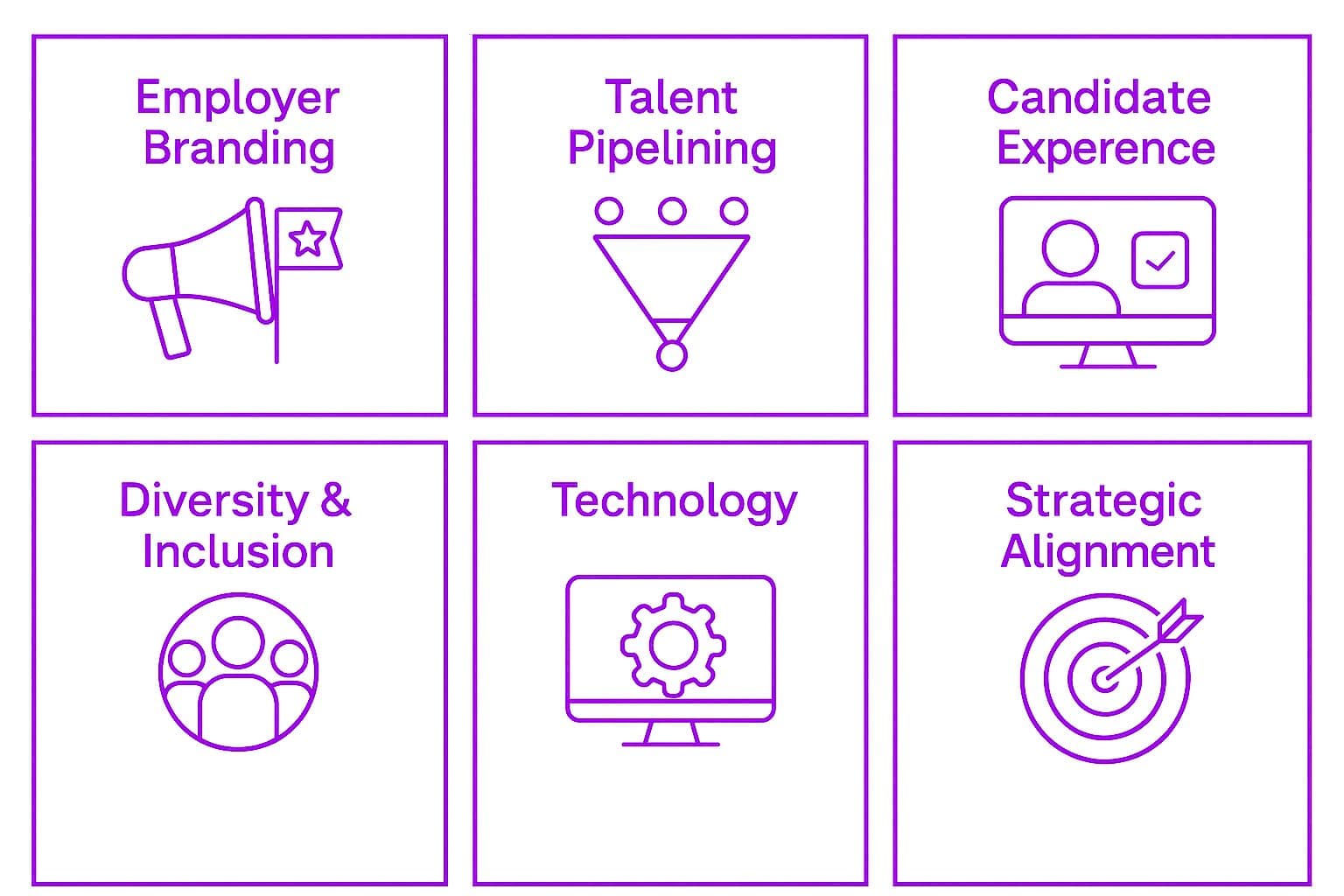
Pillars of a Talent Acquisition Strategy:
-
Employer Branding: Develop a strong employer brand that resonates with potential candidates. Highlight what makes the organization a great place to work, including company culture, values, and mission.
-
Talent Pipelining: Build a pipeline of qualified candidates for future openings. Engage with potential candidates early and maintain relationships to ensure a steady flow of talent.
-
Candidate Experience: Provide a positive candidate experience throughout the hiring process. Ensure that candidates feel valued and respected, from the initial job posting to the final interview.
-
Diversity and Inclusion: Ensure that the talent acquisition process is fair and inclusive. Proactively seek out diverse candidates and create an environment where everyone feels welcome.
-
Technology: Leverage technology to streamline the talent acquisition process. Use tools like Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) to improve efficiency and make data-driven decisions.
By building a talent acquisition strategy that includes a clear framework and strong pillars, organizations can ensure they attract and retain the best talent to achieve their goals.
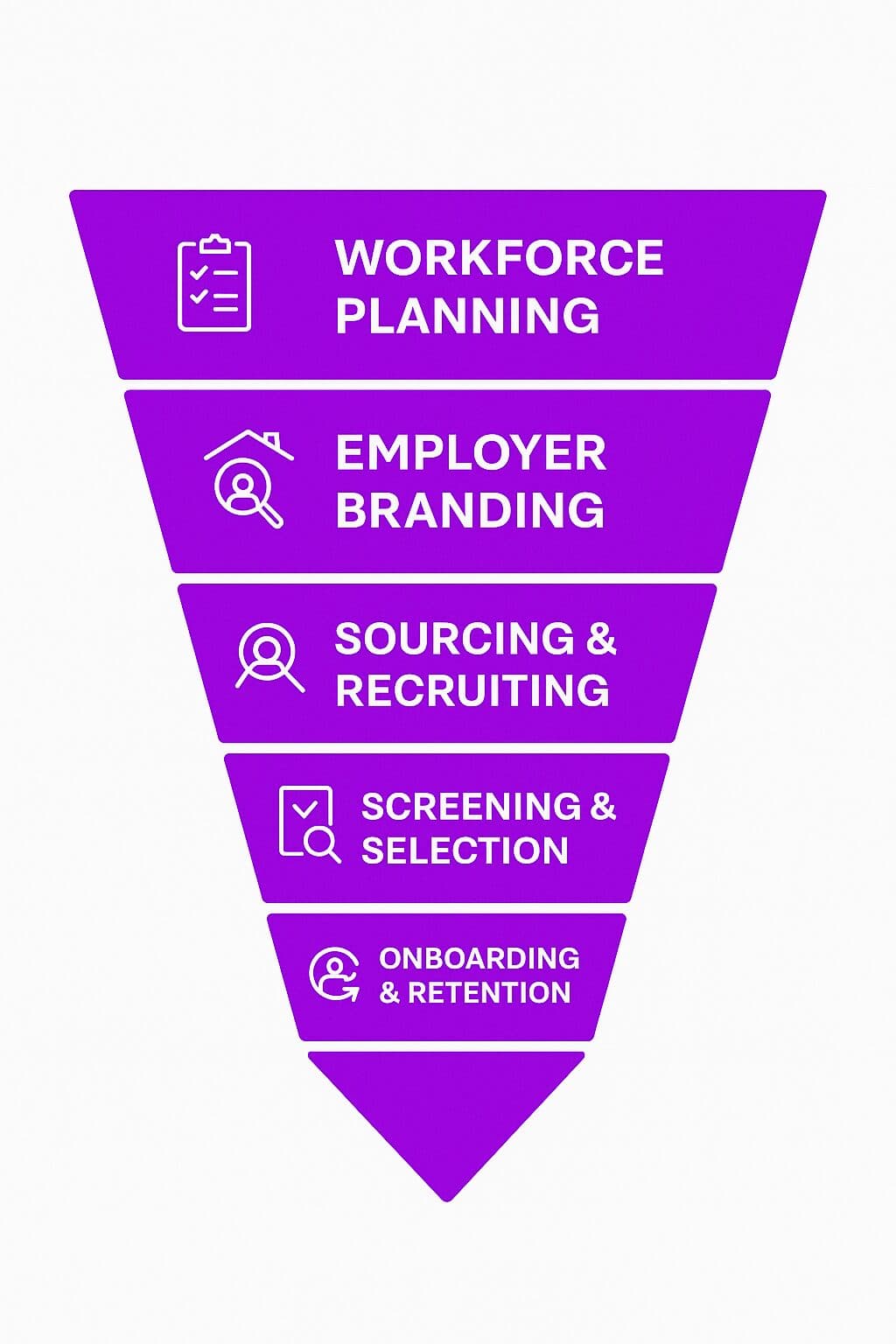
Key Stages/Components of the Talent Acquisition Process
1. Workforce Planning
Workforce planning is the first and most critical step in the talent acquisition process. It involves forecasting the organization’s current and future hiring needs based on business objectives, projected growth, and any potential challenges that may arise. By understanding the gaps in the current workforce and anticipating future needs, organizations can begin to prepare a strategy to address them.
Key aspects of workforce planning include:
-
Understanding business goals: Identifying the roles that will be crucial for meeting the organization’s objectives.
-
Identifying skill gaps: Understanding where current teams may be lacking in key skills and knowledge.
-
Planning for future growth: Anticipating future hiring needs based on projected business expansion.
2. Employer Branding
Employer branding is the process of promoting the organization as an attractive place to work. It is about conveying the company’s values, culture, and mission to potential candidates to ensure that they understand what makes the organization unique. A strong employer brand can help attract top talent who align with the company’s values.
Strategies for building a strong employer brand include:
-
Showcasing company culture: Highlighting the work environment, team dynamics, and the values that drive the company.
-
Leveraging employee testimonials: Sharing the experiences of current employees to illustrate what makes the organization a great place to work.
-
Social media presence: Using platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram to promote the company’s mission, achievements, and values.
3. Sourcing and Recruiting Candidates
Sourcing is the proactive effort to find and engage potential candidates, while recruitment refers to the process of interviewing and hiring. Crafting effective and inclusive job descriptions is crucial in attracting diverse candidates and building a strong employer brand. The sourcing process includes identifying candidates who may be a good fit for current or future roles, whether they are actively seeking a job or not.
Effective sourcing strategies include:
-
Job boards and recruitment websites: Using platforms like Indeed, Glassdoor, and LinkedIn to post job openings and attract talent.
-
Social media and networking: Engaging with professionals in your industry and maintaining a presence on platforms like LinkedIn to attract passive candidates.
-
Employee referrals: Encouraging current employees to refer qualified candidates who fit the organization’s culture and values.
Recruitment then takes these sourced candidates and focuses on evaluating them for fit within the organization.
4. Screening and Selection
Once candidates are sourced, it’s crucial to collaborate with the hiring manager to assess whether they align with the organization’s needs. Screening is the process of reviewing resumes, evaluating the candidates’ skills and qualifications, and determining whether they are a fit for the role.
The selection process typically includes:
-
Interviews: One-on-one or panel interviews where candidates answer questions about their skills, experience, and ability to perform in the role.
-
Assessments: Using skill assessments, personality tests, or cognitive ability tests to evaluate the candidate’s competencies.
-
Reference checks: Verifying candidates’ previous job performance and character by speaking with their past employers or colleagues.
Effective screening and selection ensure that the organization hires individuals who can succeed in their roles and align with the company’s culture.
5. Onboarding and Retention
Once a candidate has been hired, the onboarding process begins. Onboarding is the process of integrating new hires into the organization, helping them understand their roles, expectations, and company culture. Proper onboarding ensures that new employees feel welcomed, supported, and prepared for success.
Retention strategies are closely linked with talent acquisition, as they focus on keeping top talent within the organization long-term.
Best practices for effective onboarding and retention include:
-
Structured onboarding programs: Ensuring that new hires have the resources, training, and support they need from day one.
-
Employee development opportunities: Providing opportunities for learning and career growth through mentorship programs, workshops, and training.
-
Regular feedback and recognition: Offering constructive feedback and recognizing employees’ achievements helps foster loyalty and engagement.
Purpose and Importance of Talent Acquisition
1. Long-term Organizational Success
Talent acquisition ensures that an organization can fill open positions with the right people to meet its goals, both in the short and long term. Having a steady pipeline of qualified candidates helps companies adapt to changing market conditions, grow strategically, and remain competitive.
2. Reduced Hiring Costs and Time-to-Hire
A well-structured talent acquisition strategy reduces the costs and time associated with hiring. By proactively sourcing candidates and building a pipeline, companies avoid scrambling to fill positions when they arise. Additionally, a more streamlined process can lead to better candidate matches, reducing turnover and minimizing the need for constant recruitment efforts.
3. Improved Employee Engagement and Retention
When talent acquisition efforts focus on cultural fit and long-term employee engagement, organizations benefit from higher retention rates. Employees who are hired for their alignment with the organization’s values are more likely to stay engaged and committed, leading to lower turnover and higher overall satisfaction.
4. Increased Competitive Advantage
Organizations with a strong talent acquisition strategy are able to attract and retain the best talent in their industry. This not only gives them a competitive edge in terms of productivity and innovation but also helps to build a reputation as an employer of choice, making it easier to attract talent in the future.
Benefits and Challenges of Talent Acquisition
Benefits
-
Attracts Top Talent: Talent acquisition strategies are designed to find the best candidates, improving the quality of hires. Talent acquisition professionals play a crucial role in navigating the evolving landscape of hiring, emphasizing the essential skills required for success, the various career paths available within talent acquisition and beyond, and the strategic methods used to attract and evaluate candidates effectively.
-
Long-Term Workforce Planning: It ensures that organizations have the right talent at every level and can plan for future growth.
-
Reduced Turnover: By focusing on hiring the right fit, both in terms of skills and culture, organizations are less likely to experience high turnover rates.
-
Diverse Talent Pool: Talent acquisition processes often focus on diversity and inclusion, ensuring a diverse talent pool that strengthens the organization.
Challenges
-
Finding Passive Candidates: Some of the best candidates may not be actively seeking a new job, which makes it challenging to engage with them effectively.
-
High Competition for Talent: In industries with high demand for skilled workers, it can be difficult to attract top talent who may be courted by multiple employers.
-
Maintaining a Consistent Process: As organizations grow, it can be difficult to maintain consistency in the talent acquisition process, particularly with different teams or departments involved.
-
Balancing Speed and Quality: While quick hiring processes are desirable, they must not compromise the quality of hires. Finding the balance can be difficult, especially when filling high-priority roles.
Talent Acquisition Tools and Software
Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
An Applicant Tracking System (ATS) is a vital tool for talent acquisition teams, enabling them to manage job postings, candidate applications, and resumes electronically. An ATS streamlines the hiring process, making it more efficient and effective.
Benefits of Using an ATS:
-
Improved Efficiency: An ATS automates many administrative tasks, such as screening resumes and scheduling interviews. This allows talent acquisition teams to focus on more strategic activities, like engaging with top talent and improving the candidate experience.
-
Enhanced Candidate Experience: An ATS provides a seamless application process for candidates. They can easily apply for jobs, track the status of their applications, and receive timely updates, which enhances their overall experience.
-
Better Data Analysis: An ATS offers valuable insights into the hiring process, such as time-to-hire and source of hire. These analytics help talent acquisition teams make data-driven decisions and continuously improve their strategies.
Criteria for Selecting an ATS:
-
Ease of Use: The ATS should be user-friendly for both talent acquisition teams and candidates. A simple, intuitive interface ensures that everyone can navigate the system efficiently.
-
Customization: The ATS should be customizable to meet the specific needs of the organization. This includes tailoring workflows, job postings, and candidate communication to align with the company’s processes.
-
Integration: The ATS should integrate seamlessly with other HR systems, such as Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) and performance management systems. This ensures a smooth flow of information across different platforms.
-
Security: Robust security features are essential to protect candidate data. The ATS should comply with data protection regulations and have measures in place to safeguard sensitive information.
By selecting the right ATS, organizations can enhance their talent acquisition process, improve efficiency, and provide a better experience for both candidates and hiring managers.
Practical Tips and Best Practices for Talent Acquisition Strategies
-
Proactively Build a Talent Pipeline: Consistently engage with potential candidates, even if there are no immediate vacancies. Building relationships early on ensures that your organization has a pool of qualified candidates when a need arises.
-
Leverage Technology: Use applicant tracking systems (ATS) and AI tools to streamline sourcing, screening, and interviewing. Talent acquisition analytics can provide vital insights for strategic planning and informed decision-making, ultimately improving hiring efficiency and candidate experience while addressing potential biases in recruitment. These technologies can help you identify the best candidates faster and more efficiently.
-
Promote Your Employer Brand: Ensure that your organization’s culture, mission, and values are visible across multiple channels, from your company website to social media platforms. A strong employer brand will help attract top candidates.
-
Invest in Employee Development: Developing internal talent is just as important as acquiring external talent. Offer training programs, mentorship, and growth opportunities to help employees develop within the organization.
-
Create a Seamless Candidate Experience: From the initial job posting to the final interview, ensure that candidates have a positive experience with your company. A transparent, respectful, and well-organized hiring process will improve your chances of securing top talent.
Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Example 1: Google’s Talent Acquisition Strategy
Google is renowned for its meticulous approach to talent acquisition. The talent acquisition team plays a crucial role in strategic workforce planning and forecasting to meet future hiring needs. The company has developed an extensive interview process and uses data-driven insights to assess candidates for the right fit. By focusing on hiring for cultural fit as well as skills, Google has built a team of employees who are highly innovative and dedicated to the company’s mission.
Example 2: Salesforce’s Commitment to Diversity
Salesforce has built a talent acquisition strategy focused on diversity and inclusion. Staying updated on talent acquisition trends, such as technological advancements and demographic changes, has been crucial in shaping this strategy. By proactively reaching out to underrepresented groups and ensuring a fair, inclusive hiring process, Salesforce has created a more diverse and engaged workforce. This commitment to diversity has strengthened its employer brand and helped attract top talent from diverse backgrounds.