What is Talent Management?
Talent management refers to the strategic approach organizations use to attract, develop, retain, and optimize the performance of their employees. It focuses on ensuring that the right people are in the right roles, equipped with the skills necessary to drive business success through strategic talent management. Talent management goes beyond just hiring people—it encompasses the entire employee lifecycle, including recruitment, onboarding, training, performance management, career development, and succession planning.
The key objective of talent management is to align an organization’s human capital with its business goals, ensuring that employees can meet current demands while preparing for future challenges. This approach is crucial in today’s competitive business environment, where organizations must attract top talent and continuously develop and retain their workforce to maintain a competitive edge.
Comprehensive Explanation of Talent Management
Talent management is not just about hiring people; it’s about ensuring that they stay with the company, grow in their roles, and are empowered to perform at their best. It involves a holistic approach to human resource practices, focusing on both individual and organizational growth.
At its core, talent management connects the right people with the right roles, ensuring that each individual’s skills and strengths are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. The talent management process begins with understanding the workforce’s current and future needs, sourcing and recruiting candidates, and continues throughout an employee’s journey in the organization.
Talent management is also about creating an environment where employees feel engaged and valued. When employees see opportunities for growth and development, they are more likely to remain with the company, perform well, and contribute to its long-term success.
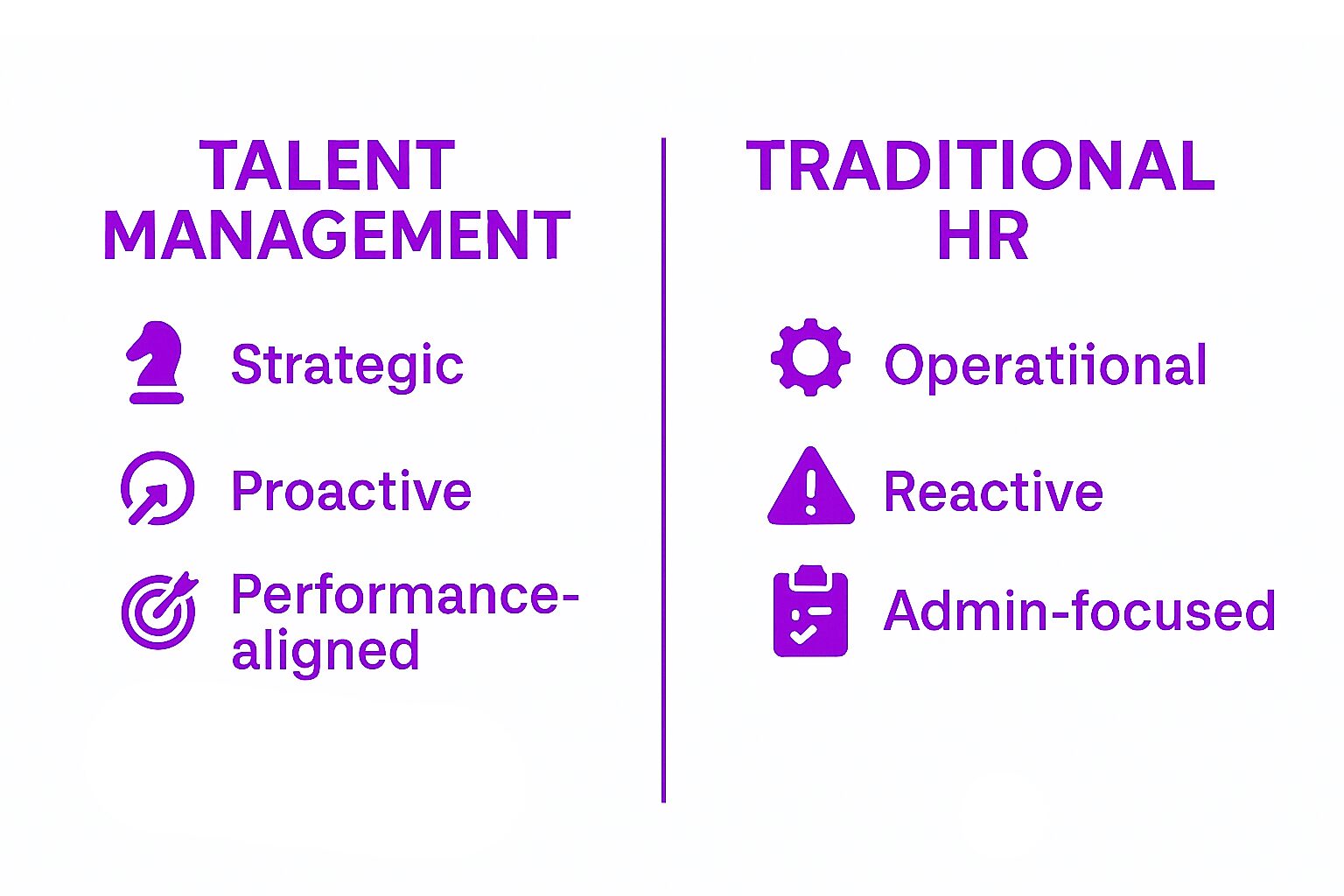
Talent Management vs. Traditional HR Practices
While traditional HR functions like payroll, benefits administration, and compliance are still essential, talent management goes beyond these operational aspects. It is a strategic, forward-thinking approach to managing human resources, focusing on the alignment between employees’ strengths and organizational goals through effective management practices. Traditional HR is reactive, responding to immediate needs like filling vacancies, while talent management is proactive, ensuring that the right people are in place for long-term success.
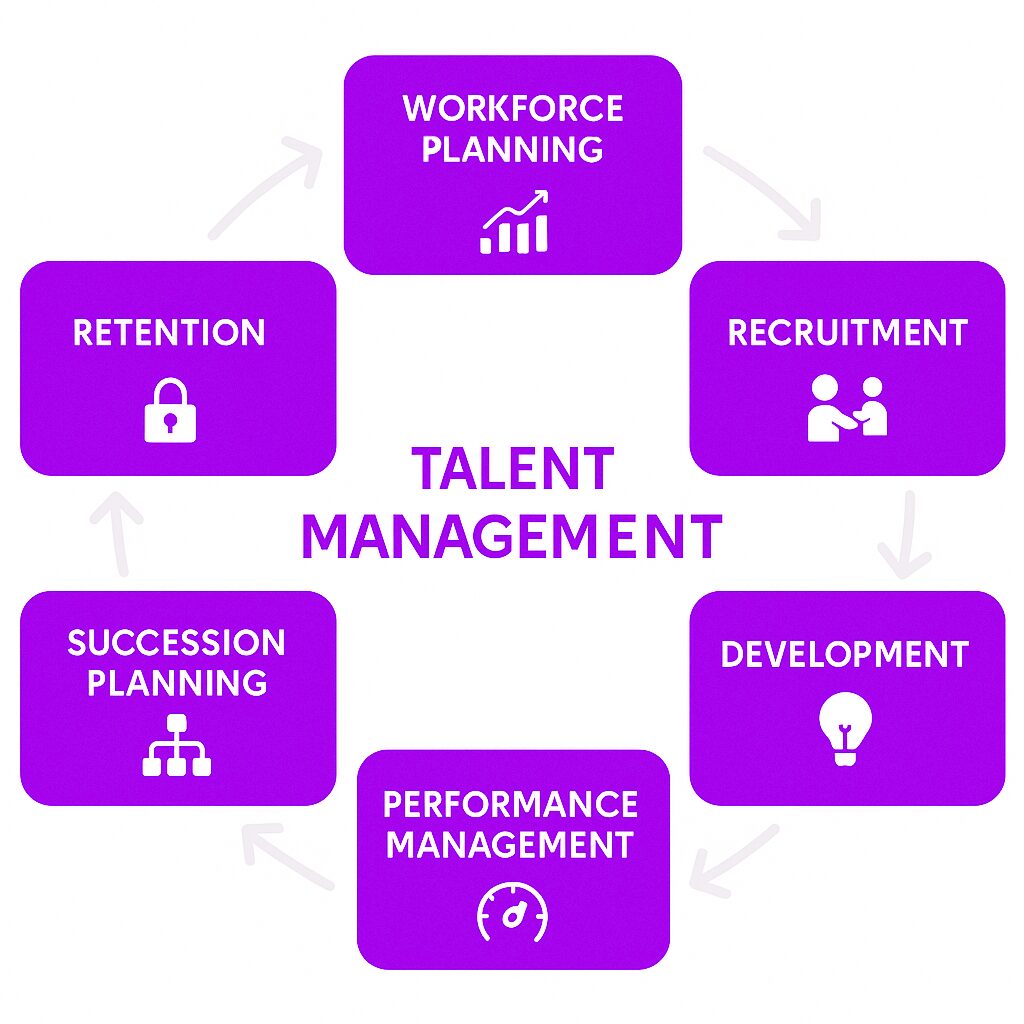
Key Stages and Components of Talent Management
Talent management is a continuous cycle that involves several interconnected stages. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
Introducing a talent management model provides a framework that outlines these stages and emphasizes the need for organizations to adapt and refine their approach to meet evolving trends and current challenges.
1. Workforce Planning
Workforce planning is the foundation of talent management, and developing a comprehensive workforce plan is essential for identifying human capital requirements. It involves understanding current and future organizational needs and determining what kind of skills, experience, and expertise will be required to meet those needs. Effective workforce planning helps organizations anticipate talent shortages and gaps, enabling them to proactively address these issues before they impact operations.
-
Key Steps in Workforce Planning:– Assessing current workforce demographics and capabilities.
-
Identifying the skills needed to achieve business goals.
-
Predicting future hiring needs based on business growth and market conditions.
2. Recruitment and Talent Acquisition
Recruitment is the first step in acquiring talent. Attracting diverse talent is crucial for building a workforce that represents a variety of backgrounds and perspectives. Talent acquisition is a broader and more strategic function that includes building a talent pipeline, employer branding, and sourcing the best candidates from both internal and external pools.
-
Effective Recruitment Strategies:– Developing a strong employer brand to attract top talent.
-
Leveraging digital tools and social media to engage candidates.
-
Implementing employee referral programs to tap into networks.
-
Using data-driven methods to identify and attract high-quality candidates.
Attracting Top Talent
Attracting top talent is a cornerstone of any effective talent management strategy. It involves more than just filling vacancies; it’s about bringing in individuals who can drive business success and align with the company’s long-term goals. To achieve this, organizations must develop a strong employer brand that resonates with potential candidates. This can be done by showcasing the company’s values, culture, and career development opportunities through various channels, including social media and company websites.
Creating a positive candidate experience is also crucial. From the initial application to the final interview, every touchpoint should reflect the organization’s commitment to excellence and inclusivity. Leveraging digital tools and platforms can streamline the recruitment process, making it easier to engage with top talent.
Building a diverse and inclusive workplace culture is another key aspect of attracting top talent. Diverse teams bring a variety of perspectives and ideas, which can lead to more innovative solutions and better business outcomes. Organizations should actively seek to attract candidates from a wide range of backgrounds and ensure that their recruitment practices are free from bias.
Employee engagement plays a significant role in talent acquisition. Engaged employees are more likely to refer high-quality candidates to the organization, acting as brand ambassadors. Performance management systems can help identify and develop high-potential employees, ensuring that the organization has a robust talent pipeline.
Succession planning is also essential. By identifying and nurturing future leaders, organizations can ensure continuity and stability. This strategic approach to talent management aligns talent acquisition with organizational goals, ensuring that the right people are in place to drive business success.
Regularly reviewing and updating talent management processes is vital to keep them effective and aligned with the organization’s evolving needs. This proactive approach helps organizations stay competitive in the talent market and ensures they can attract and retain the best talent.
3. Onboarding and Integration
Onboarding is crucial in ensuring that new hires feel welcomed, informed, and supported from the first day they join the company. A structured onboarding program helps new employees integrate smoothly into the company culture and understand their roles and expectations.
-
Key Aspects of Onboarding:
-
Introducing new hires to the company’s values and culture.
-
Providing the tools, resources, and training they need to succeed.
-
Assigning mentors or buddies to help new employees adjust to the workplace.
-
4. Employee Development
Employee development is central to talent management. It involves continuous efforts to enhance employees’ skills, knowledge, and capabilities. Effective development programs help employees grow in their roles and prepare for higher responsibilities. Talent management planning is crucial for implementing best practices that enhance employee engagement and improve workplace efficiency.
-
Types of Employee Development:
-
Training Programs: On-the-job training, workshops, and certification programs.
-
Leadership Development: Focused development for employees with leadership potential.
-
Mentorship: Pairing employees with experienced leaders for guidance and support.
-
Cross-functional Experience: Giving employees the chance to work in different departments to broaden their skill set.
5. Performance Management
Performance management involves setting clear expectations, monitoring employee performance, providing regular feedback, and aligning individual goals with organizational objectives. A robust performance management system ensures that employees are motivated to reach their potential and contribute to the company’s success.
-
Performance Management Best Practices:
-
Establishing clear and measurable performance goals.
-
Providing continuous feedback rather than waiting for annual reviews.
-
Recognizing and rewarding top performers to boost morale and engagement.
-
6. Succession Planning
Succession planning is an integral part of talent management. It involves identifying and developing internal candidates to fill key leadership roles in the future. Succession planning ensures leadership continuity and minimizes disruptions when senior leaders leave the organization.
-
Steps in Succession Planning:
-
Identifying critical roles within the organization.
-
Assessing potential leaders within the company.
-
Providing targeted development opportunities for high-potential employees.
-
Creating a clear plan for smooth leadership transitions.
-
7. Employee Engagement and Retention
Talent management practices are crucial for improving employee engagement and retention. Engaged employees are more productive, innovative, and loyal. Retention strategies focus on keeping top talent by ensuring job satisfaction, offering growth opportunities, and fostering a positive work environment.
-
Retention Strategies Include:– Offering competitive compensation and benefits.
-
Creating a positive organizational culture that values employee well-being.
-
Providing opportunities for career advancement.
-
Ensuring work-life balance and offering flexibility.
Talent Management Framework
A talent management framework provides a structured approach to managing talent, encompassing key components such as workforce planning, talent acquisition, performance management, and succession planning. This framework should be closely aligned with the organization’s overall business strategy, ensuring that talent management initiatives support and drive business objectives.
Workforce planning is the foundation of the talent management framework. It involves assessing current workforce capabilities and predicting future needs based on business growth and market conditions. This proactive approach helps organizations identify potential skills gaps and develop strategies to address them.
Talent acquisition is another critical component. A robust talent management framework includes strategies for attracting, recruiting, and onboarding top talent. This involves building a strong employer brand, leveraging various recruitment channels, and creating a positive candidate experience.
Performance management is integral to the framework, ensuring that employees are aligned with organizational goals and are continuously developing their skills. Regular feedback, clear performance metrics, and recognition programs are essential elements of an effective performance management system.
Succession planning ensures that the organization has a pipeline of talented employees ready to step into key roles as needed. This involves identifying high-potential employees and providing them with targeted development opportunities to prepare them for future leadership positions.
Employee engagement is also a crucial part of the talent management framework. Engaged employees are more productive, innovative, and likely to stay with the organization. The framework should include strategies for fostering a positive work environment, offering career development opportunities, and recognizing employee contributions.
To measure the effectiveness of the talent management framework, organizations should establish clear metrics and benchmarks. These might include employee satisfaction scores, turnover rates, performance outcomes, and leadership development progress. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps ensure that the framework remains effective and aligned with the organization’s needs.
Integrating the talent management framework with other HR systems and processes is essential for a cohesive approach to managing talent. This integration ensures that all aspects of talent management are aligned and working towards the same goals.
By following a structured talent management framework, organizations can build a strong employer brand, attract and retain top talent, and develop a high-performing workforce. Regularly reviewing and updating the framework ensures it remains relevant and effective in supporting the organization’s strategic objectives.
Purpose and Importance of Talent Management
Talent management is essential for several key reasons:
-
Aligning Workforce with Organizational GoalsTalent management ensures that the workforce is aligned with the company’s strategic vision and objectives. It helps organizations maintain focus on their goals by placing the right people in the right positions.
-
Attracting and Retaining Top TalentIn a competitive market, attracting and retaining skilled employees is crucial. Effective talent management ensures that organizations can fill key roles with qualified candidates and keep high-performing employees engaged and satisfied.
-
Improving Employee Performance and ProductivityBy continuously developing employees’ skills and aligning their work with organizational goals, talent management drives better performance and increases overall productivity.
-
Enhancing Organizational AgilityTalent management helps organizations respond to changing market conditions by ensuring they have a flexible, skilled workforce that can adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
-
Fostering a Positive Work CultureWhen talent management is done well, employees feel valued, supported, and engaged. This leads to higher job satisfaction and a more positive company culture.
A robust talent strategy not only aligns with organizational goals but also drives measurable outcomes, enhancing recruitment, employee engagement, and overall business performance.
Benefits of Talent Management
-
Competitive AdvantageOrganizations that manage their talent effectively are better positioned to outpace competitors. With a skilled and engaged workforce, they can innovate faster, respond to market changes, and maintain leadership positions. Additionally, utilizing talent management metrics allows organizations to assess the effectiveness of their strategies, leading to improved productivity, engagement, and retention among employees.
-
Lower Turnover RatesBy focusing on employee development and career progression, talent management helps retain top talent. Employees who see a clear path for advancement are less likely to leave for opportunities elsewhere.
-
Increased ProductivityA well-trained and highly engaged workforce is more productive, with employees performing at higher levels, driving innovation, and contributing to the organization’s growth.
-
Cost SavingsProactive talent management can reduce recruitment and turnover costs by filling positions with internal candidates, streamlining hiring processes, and improving employee retention.
Challenges of Talent Management
-
Identifying and Developing Future Leaders
One of the primary challenges in talent management is identifying employees with leadership potential and providing them with the right development opportunities. A lack of clear succession plans can lead to leadership gaps when senior leaders retire or leave the organization. -
Attracting Top Talent in a Competitive Market
With high demand for skilled workers, attracting top talent can be difficult. Organizations need to continuously build a strong employer brand and offer compelling reasons for candidates to choose them over competitors. -
Aligning Talent Management with Business Goals
Ensuring that talent management strategies align with overall business objectives can be challenging, especially in fast-growing companies or organizations undergoing major structural changes. -
Managing Employee Expectations
Talent management requires balancing employee development with organizational needs. Employees may have different expectations about their career progression, and managing these expectations while ensuring they align with company goals can be difficult.
Practical Tips and Best Practices
-
Develop a Clear Talent Management StrategyOrganizations should have a clear, well-defined talent management strategy that aligns with business objectives. This strategy should cover all aspects of talent management, from recruitment and onboarding to performance management and succession planning.
-
Use Technology to Streamline ProcessesLeveraging talent management software can help streamline various aspects of the process, including recruitment, performance tracking, learning and development, and employee engagement. A talent management system (TMS) can automate tasks, manage job postings, and track employee performance, enhancing overall workforce efficiency.
-
Invest in Continuous Learning and DevelopmentProvide ongoing training opportunities for employees to enhance their skills and stay up-to-date with industry trends. This not only helps improve performance but also increases employee engagement and retention.
-
Measure the Effectiveness of Talent Management ProgramsRegularly assess the effectiveness of your talent management strategies through metrics such as employee satisfaction, performance outcomes, turnover rates, and leadership development progress.
-
Foster a Culture of Feedback and RecognitionRegular feedback and recognition are essential for employee engagement and development. Create an environment where employees feel their contributions are valued, and provide constructive feedback to help them improve.
Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Example 1: Google’s Talent Management Strategy
Google is known for its innovative approach to talent management. The company invests heavily in employee development, offering extensive training programs and leadership opportunities. Google also focuses on hiring for cultural fit, ensuring that new employees align with the company’s values and mission. This commitment to talent management has helped Google maintain its competitive edge and attract top talent in the tech industry.
Example 2: IBM’s Leadership Development Programs
IBM has a long history of investing in leadership development, with a focus on preparing the next generation of leaders within the organization. Through its leadership development programs, IBM identifies high-potential employees and provides them with opportunities for growth through mentorship, training, and stretch assignments. This proactive approach has helped IBM ensure that it has a pipeline of capable leaders ready to step up as needed.
Example 3: Zappos’ Employee-Centric Culture
Zappos is known for its employee-centric culture and commitment to talent management. The company places a strong emphasis on hiring for cultural fit, ensuring that new employees align with the company’s values. Zappos also invests in employee development, providing opportunities for training and career growth. This approach has helped Zappos build a loyal, engaged workforce and maintain a positive company culture.