What is Workflow Automation?
Workflow Automation refers to the process of automating repetitive tasks, processes, and the flow of information within an organization using technology. The goal of workflow automation is to make processes more efficient by eliminating manual tasks and reducing errors. It involves using software to automate business processes, improving productivity and streamlining operations. Workflow automation plays a crucial role in managing the flow of tasks, approvals, and documents within organizations, ensuring that work is done faster and more accurately.
At its core, workflow automation helps organizations reduce human intervention in routine tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work. By automating workflows, businesses can optimize resource allocation, improve consistency, and reduce the risk of errors.
Definition of Automation and Workflow
Automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks automatically, reducing the need for human intervention. It involves leveraging software and systems to execute repetitive tasks, ensuring consistency and efficiency. A workflow, on the other hand, is a series of tasks or processes that are completed in a specific order to achieve a particular goal. Workflows can range from simple, linear processes to complex, multi-step operations involving multiple teams and systems.
When we combine these two concepts, we get workflow automation. Workflow automation uses technology to automate the tasks and processes within a workflow, thereby increasing efficiency and productivity. By implementing workflow automation, businesses can streamline workflows, reduce manual tasks, and ensure that processes are carried out consistently and accurately. This not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of errors, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and value-driven activities.
Comprehensive Explanation
Workflow automation is the key to modern business efficiency, particularly in organizations that deal with large volumes of tasks and data. As businesses grow, manually managing workflows becomes increasingly complex, leading to inefficiencies and potential for errors. Workflow automation addresses these challenges by automating processes that would otherwise require extensive human intervention. Workflow automation examples include automating invoice processing, customer support ticketing, and employee onboarding, which streamline processes and improve productivity.
Key Concepts Behind Workflow Automation:
-
Automated Task Flow: In a typical manual workflow, tasks are completed sequentially by different individuals or teams. With automation, these tasks are executed based on defined rules without requiring manual input. Automation ensures that each step in the workflow is completed in the correct order, based on triggers such as time, status updates, or data entry.
-
Business Rules: These are predefined rules that dictate how specific tasks should be handled during a workflow. For example, a business rule could specify that an invoice should be sent for approval when it exceeds a certain amount or that a customer’s support ticket should be escalated after 24 hours without resolution. These rules ensure that workflows are carried out consistently and accurately.
-
Integration: Workflow automation systems integrate various business tools and applications, such as CRM systems, project management software, email platforms, and cloud storage, to ensure that information flows seamlessly across the organization. Integration is key to creating a unified system where tasks are automatically triggered based on data from multiple sources.
-
Data Flow Automation: In many organizations, data must be collected, processed, and shared between departments or systems. Automating this data flow can speed up processes like reporting, approvals, and customer support, ensuring that relevant information is available to the right people at the right time.
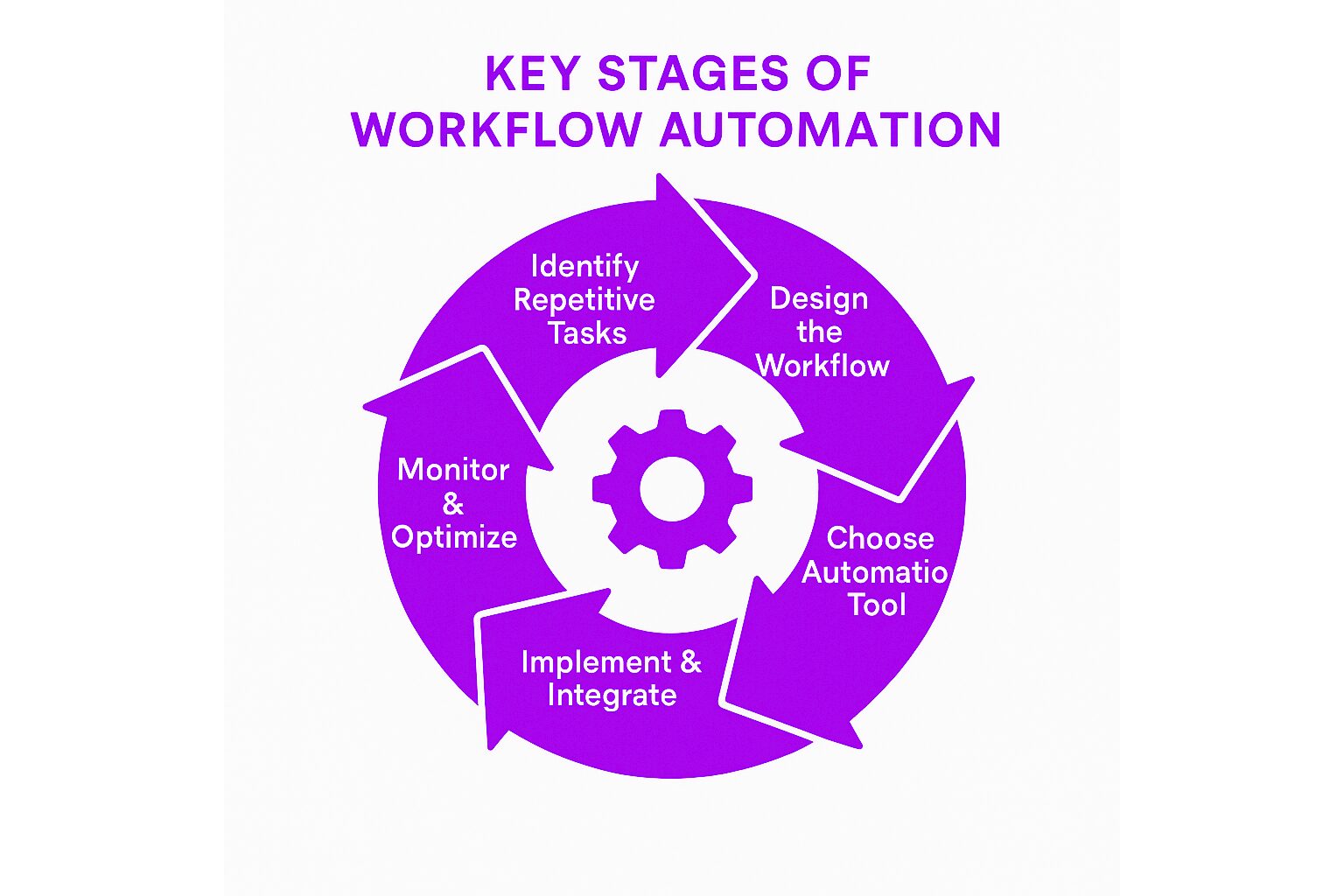
Key Stages/Components of Workflow Automation
1. Identifying Repetitive Tasks for Automation
The first step in workflow automation is to identify the tasks that are time-consuming and repetitive but do not require human judgment, including the process of assigning tasks. These tasks are prime candidates for automation and typically include data entry, scheduling, approvals, and notifications. Once identified, these tasks can be mapped out to create a structured workflow that automation tools can execute.
2. Designing the Workflow
A critical part of automation is designing the workflow. This step involves defining the steps that need to be automated, who is responsible for each step, and how tasks should flow. Workflow design includes:
-
Mapping out the process: Identifying each task involved, from the initiation of a process to its completion.
-
Setting business rules: Determining the conditions under which tasks should be triggered, paused, or escalated.
-
Defining roles: Assigning responsibilities for the tasks in the workflow, whether manual or automated.
This design phase ensures that the automation system will meet the organization’s needs and operate smoothly once implemented.
Choosing the Right Workflow Automation Tools
Various workflow automation tools are available in the market to cater to different needs. Tools like Zapier, Microsoft Power Automate, Trello, and Asana help automate tasks like project management, data entry, and document routing. Selecting the right tool depends on factors such as:
-
The complexity of the workflows
-
The level of integration needed with other systems
-
The scalability of the solution
-
The cost of implementation and maintenance
The goal is to choose a tool that best fits the organization’s requirements and seamlessly integrates into the existing ecosystem.
4. Implementation and Integration
Once a workflow automation solution is selected, the automation system must be integrated with existing systems and data sources. This may involve setting up APIs, integrating with cloud platforms, or connecting to legacy systems. The integration process is vital for ensuring smooth data flow and preventing bottlenecks in the workflow.
During this stage, companies also need to test the system to ensure it works as expected. This involves setting up test cases, running simulations, and ensuring that the automated processes handle all scenarios correctly.
5. Training and Support
As with any new technology, employees must be trained to use the automated systems. Training ensures that employees understand how to work with automated workflows, how to handle exceptions, and how to leverage the full potential of the system. Additionally, ongoing support is crucial to resolve any issues that arise during day-to-day operations.
6. Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization
Even after automation is implemented, continuous monitoring is necessary to ensure that the workflows are functioning as intended. Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), such as the time saved, errors reduced, or customer satisfaction, helps organizations assess the effectiveness of the system. Based on this data, businesses can make adjustments to optimize workflows further, adding new automation rules or modifying existing ones.
Purpose and Importance of Workflow Automation
1. Increased Efficiency
Workflow automation streamlines repetitive tasks and optimizes the flow of information by leveraging software tools to handle automated tasks. By automating these processes, organizations can complete tasks more quickly and reduce the time spent on low-value activities. This allows employees to focus on more strategic work, increasing overall productivity.
2. Error Reduction
Manual processes are prone to human error, which can lead to costly mistakes. Workflow automation eliminates the potential for errors, ensuring that tasks are completed consistently and accurately according to predefined rules. This is particularly crucial in industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, where accuracy is vital.
3. Cost Savings
Automating tasks reduces the need for human intervention, allowing organizations to lower labor costs and operational expenses. Workflow automation helps businesses streamline their operations, reducing overhead costs associated with manual processes and enhancing overall profitability.
Improved Collaboration and Transparency in Automated Workflows
Workflow automation often involves cross-departmental collaboration, and automating the workflow ensures that everyone involved has real-time visibility into the status of tasks. This improves communication between teams, streamlines approvals, and helps ensure that work is completed on time.
5. Better Compliance and Reporting
Automated workflows ensure that all necessary steps are followed in accordance with regulatory requirements. In industries with strict compliance rules, automation can help maintain records, monitor compliance, and generate reports automatically, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Benefits and Challenges of Workflow Automation
Benefits
-
Improved Efficiency and Speed: By automating manual processes, businesses can execute tasks faster and with less effort, freeing up resources for more important work.
-
Cost Reduction: Automation reduces the need for human labor in routine tasks, helping businesses cut costs and improve profitability.
-
Enhanced Accuracy: With automated processes, the risk of human error is significantly reduced, ensuring that tasks are completed accurately.
-
Increased Employee Satisfaction: Automation removes tedious tasks from employees’ workloads, allowing them to focus on more valuable and engaging work.
-
Scalability: Automated workflows can be easily scaled as the business grows, allowing companies to manage increased workload without significantly increasing staff.
Challenges
-
Initial Investment: Setting up workflow automation systems can require significant upfront investment in software, integration, and training.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist workflow automation if they fear job displacement or do not understand the benefits.
-
Integration Complexity: Integrating automation with existing systems can be complex and may require significant time and resources to ensure everything functions seamlessly.
-
Maintenance and Updates: Automated workflows require ongoing monitoring and adjustments to stay relevant and efficient. They also need to be updated when business processes change.
Business Process Automation
Definition and Examples
Business process automation (BPA) is the use of technology to automate and streamline business processes, making them more efficient and effective. BPA involves automating routine tasks and processes that are essential to the functioning of a business. This can include a wide range of activities across various departments, such as human resources, marketing, and customer service.
For example, in human resources, BPA can automate the employee onboarding process, ensuring that new hires receive all necessary information and complete required paperwork without manual intervention. In marketing, BPA can streamline lead generation by automatically capturing and nurturing leads through email campaigns and CRM systems. In customer service, BPA can manage support ticketing systems, routing customer inquiries to the appropriate agents and ensuring timely responses.
By automating these business processes, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance overall productivity.
Benefits of Automating Business Processes
Automating business processes can bring numerous benefits, including:
-
Increased Efficiency: Automation reduces the need for manual tasks, minimizing errors and freeing up staff to focus on higher-value activities. This leads to more efficient operations and faster completion of tasks.
-
Improved Productivity: By streamlining processes, automation reduces the time and effort required to complete tasks. This allows employees to work more effectively and achieve better results.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience: Automation enables businesses to respond to customer inquiries and requests more quickly and efficiently. This improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Cost Savings: Automation reduces labor costs by minimizing the need for manual intervention. It also helps businesses avoid costly errors and rework, leading to overall cost savings.
By automating business processes, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, productivity, and cost-effectiveness, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
Complex Workflows
Challenges and Solutions
Automating complex workflows can be challenging due to the intricacies involved in integrating multiple systems and applications, handling exceptions and errors, and ensuring data accuracy and integrity. However, with the right workflow automation software, these challenges can be effectively addressed.
Some common challenges in automating complex workflows include:
-
Integrating Multiple Systems and Applications: Complex workflows often involve various systems and applications that need to work together seamlessly. Integration capabilities are crucial for connecting these disparate systems and ensuring smooth data flow.
-
Handling Exceptions and Errors: In any automated workflow, exceptions and errors are inevitable. Effective error handling mechanisms are essential to manage these issues automatically and prevent disruptions.
-
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Integrity: Accurate and reliable data is critical for the success of automated workflows. Data validation features help ensure that the information used in workflows is correct and consistent.
To overcome these challenges, businesses can use workflow automation software that offers advanced features such as:
-
Integration Capabilities: These allow businesses to connect multiple systems and applications, ensuring seamless data flow and coordination across different platforms.
-
Error Handling: Advanced error handling features enable businesses to manage exceptions and errors automatically, ensuring that workflows continue to operate smoothly.
-
Data Validation: Data validation features ensure that the data used in workflows is accurate and reliable, minimizing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
By leveraging workflow automation software with these advanced features, businesses can streamline complex workflows, reduce manual tasks, and minimize errors, ultimately enhancing overall efficiency and productivity.
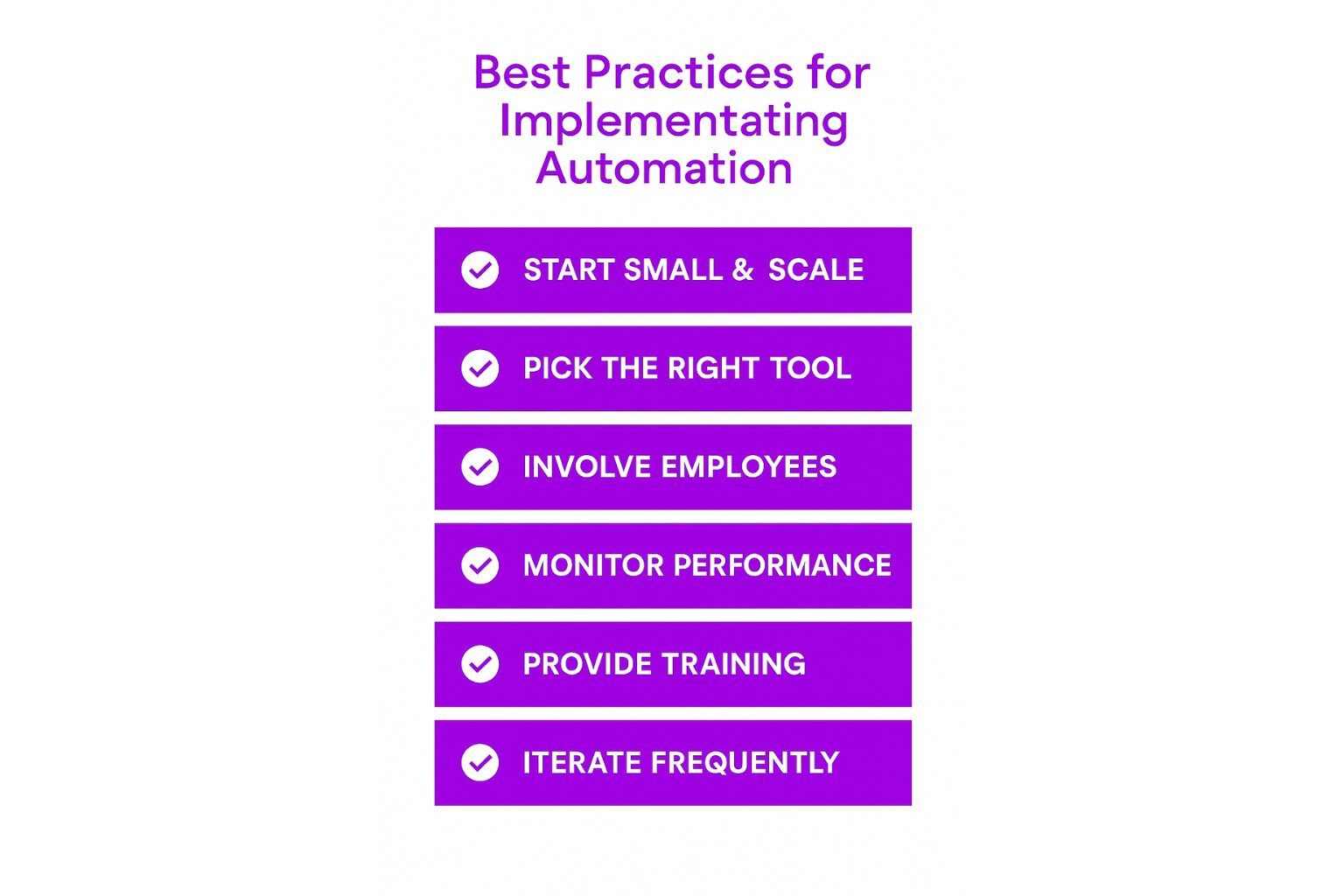
Practical Tips and Best Practices
-
Start Small and Scale Up
Begin by automating a few repetitive tasks and gradually scale the process as you become more comfortable with the technology. This allows for smoother adoption and minimizes the risk of disruption. -
Choose the Right Automation Tool
Select an automation tool that fits your organization’s needs. Consider factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. -
Involve Employees in the Process
Involve employees in the selection and implementation of automation tools. This helps to ensure the system meets their needs and reduces resistance to change. -
Monitor Performance
Continuously monitor your automated workflows to identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Regular performance reviews help ensure that the automation is delivering the desired results. -
Provide Ongoing Training and Support
As with any new technology, training and support are key to success. Ensure employees are equipped to use automation tools effectively and that any technical issues are addressed promptly.
Related Sub-concepts
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)Robotic Process Automation refers to the use of software robots to perform repetitive tasks that typically require human intervention. RPA is often used in conjunction with workflow automation for tasks like data entry and document processing.
-
Business Process Management (BPM)BPM involves managing and optimizing the processes within an organization. Workflow management systems are one aspect of BPM, as they help streamline processes by automating key steps.
-
Integration Platforms as a Service (iPaaS)iPaaS refers to platforms that allow businesses to integrate multiple software tools, applications, and data sources. These platforms are often used to connect different systems in automated workflows.
Real-world Examples and Use Cases
-
Customer Service AutomationCompanies like Zendesk automate customer service workflows, such as routing customer tickets and managing response times. Workflow management tools offer a more efficient alternative to traditional spreadsheets for automating and managing these work processes. Automation improves response time and ensures that customers receive timely, relevant support.
-
IT Service ManagementIT departments automate ticketing systems, service requests, and routine maintenance tasks. Tools like ServiceNow streamline these workflows, ensuring faster resolution and more efficient use of IT resources.
-
HR** Process Automation** HR departments use workflow automation to handle tasks like employee onboarding, time-off requests, and payroll. Companies like BambooHR and ADP offer automated HR services to reduce administrative burdens and ensure compliance.
Conclusion
Workflow automation is a powerful tool for improving business processes, enhancing productivity, and reducing operational costs. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can streamline their operations, reduce errors, and focus on more value-driven work. While there are challenges, such as resistance to change and integration complexity, the benefits far outweigh the initial investment. Workflow automation is a strategic advantage for businesses looking to stay competitive in an increasingly fast-paced world