What is Employee Onboarding?
Employee onboarding is the structured process of integrating new hires into an organization. It includes training, familiarization with company culture, and ensuring that employees have the necessary tools and support to succeed in their roles. An effective onboarding process begins when an employee accepts a job offer and extends through their first few months on the job.
A well-planned onboarding program improves employee engagement, retention, and productivity. It helps new employees feel connected to the organization, reducing uncertainty and fostering a sense of belonging from day one.
Why Employee Onboarding Matters
New hires form their first impressions of a company during onboarding. Completing new hire paperwork is a crucial element of this process. A structured and engaging process helps employees become productive quickly, while a poorly managed onboarding experience can lead to disengagement and early turnover. Organizations that prioritize onboarding see benefits in:
-
Increased retention: Employees who feel welcomed and supported are more likely to stay.
-
Faster time-to-productivity: A strong onboarding process ensures employees understand their roles and responsibilities quickly.
-
Higher engagement: Employees who connect with company culture early on are more motivated and committed.
-
Reduced hiring costs: Retaining employees through effective onboarding reduces recruitment expenses and training costs.
Key Stages of Employee Onboarding
1. Preboarding
Preboarding occurs between the time a candidate accepts the job offer and their first day. It helps new hires feel prepared and excited about joining the company, setting the stage for a new hire’s successful integration.
Best Practices:
-
Send a welcome email with key information about the company and role.
-
Assign a mentor or buddy to help the new hire navigate the first few weeks.
-
Provide access to paperwork and company policies in advance.
-
Set up IT accounts and ensure necessary tools are ready before day one.
2. Orientation
Orientation introduces a new employee to company culture, values, and key policies. It often takes place on the first day or week and sets expectations for workplace behavior and job responsibilities.
Key Activities:
-
Welcome speech from leadership or HR.
-
Overview of company mission, values, and goals.
-
Explanation of employee benefits and policies.
-
IT and security training for digital tools and platforms.
-
Office or virtual workspace tour.
3. Training and Development
New employees need structured training to understand their roles and responsibilities. Training should be tailored to job-specific tasks and provide opportunities for hands-on learning.
Effective Training Approaches:
-
Role-specific training modules.
-
Online learning platforms and self-paced courses.
-
One-on-one coaching and mentorship.
-
Regular check-ins with managers for progress assessment.
4. First 30-90 Days
The first few months are critical for a new employee’s retention. Structured support during this period ensures that employees remain engaged and aligned with company goals.
Focus Areas:
-
Encouraging early contributions to projects and tasks.
-
Providing feedback through structured performance check-ins.
-
Ensuring social integration through team-building activities.
-
Addressing any concerns or challenges employees may have.
5. Long-Term Onboarding
Onboarding should not stop after the first few months. Continuous development opportunities help employees grow and stay engaged.
Best Practices:
-
Encourage professional development through training and learning opportunities.
-
Offer career growth discussions and internal mobility options.
-
Maintain open communication through ongoing feedback loops.
-
Ensure employees feel supported in their long-term career paths.
Pre-Onboarding Planning
Pre-onboarding planning is a critical stage in the employee onboarding process. It involves preparing necessary documents, equipment, and resources before the new hire’s first day. This stage is particularly important for remote employee onboarding, as it helps to ensure a smooth transition for new hires. Effective pre-onboarding planning sets the stage for a successful onboarding experience.
During this stage, HR professionals should:
-
Prepare and send necessary documents, such as the employee handbook and job description, to the new hire.
-
Set up equipment and resources, such as a computer and phone, for the new hire.
-
Communicate with the new hire to ensure they are prepared for their first day.
-
Provide information about the company culture and policies.
-
Schedule a meeting with the new hire to discuss their role and expectations.
Pre-onboarding planning helps to reduce anxiety and stress for new hires, and can make a significant impact on employee engagement and productivity.
Purpose and Importance of Employee Onboarding
A well-designed onboarding program benefits both employees and the organization. Onboarding employees requires a collaborative effort from various roles within the organization to facilitate the integration of new hires. It ensures employees feel supported from day one, improving retention and productivity. Effective onboarding also enhances workplace culture, as employees who experience a positive transition are more likely to contribute to a collaborative and motivated team.
Companies that invest in structured onboarding programs create an environment where employees are more likely to stay, perform better, and align with company values.
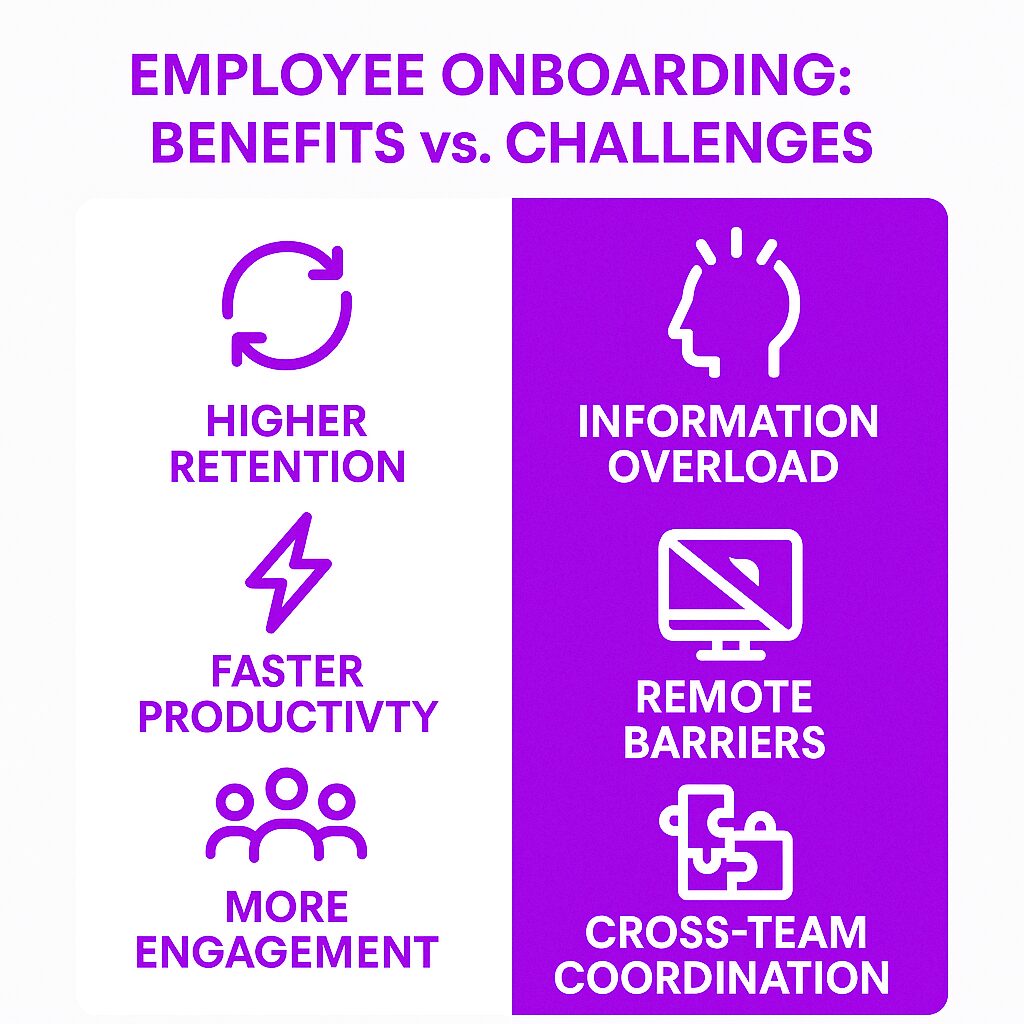
Benefits and Challenges of Employee Onboarding
Benefits for Employee Retention
-
Higher Retention Rates – Employees who experience a positive onboarding process are more likely to stay.
-
Stronger Workplace Culture – New hires who understand company values integrate more smoothly.
-
Faster Learning Curves – Structured training helps employees become productive sooner.
-
Increased Engagement – Employees who feel supported and valued contribute more effectively.
-
Accurate Job Descriptions – Aligning job descriptions with actual roles and responsibilities ensures clear expectations and aids in effective recruitment.
Challenges
-
Lack of Formal Structure – Many organizations fail to create a consistent onboarding experience.
-
Information Overload – New employees can become overwhelmed if too much information is presented at once.
-
Remote Work Onboarding – Virtual onboarding presents challenges in engagement and communication.
-
Cross-Department Coordination – HR, IT, and team managers must collaborate effectively.
Best Practices for Effective Employee Onboarding
Personalize the Experience
Every employee has different needs and learning styles. A personalized approach to onboarding ensures that each new hire feels supported.
Use Technology to Streamline Processes
Onboarding software and digital tools can automate administrative tasks, track training progress, and facilitate communication.
Assign a Mentor or Buddy for New Hires
Having a point of contact for questions and guidance helps new hires feel more comfortable and connected.
Encourage Early Contributions
Allowing employees to participate in meaningful work early on boosts confidence and engagement.
Gather Feedback and Adapt
Regularly collecting feedback from new hires about their onboarding experience helps refine and improve the process.
Employee Onboarding Software and Tools
Employee onboarding software and tools can help streamline the onboarding process and improve the new hire experience. These tools can automate tasks, such as sending paperwork and scheduling meetings, and provide a centralized platform for new hires to access information and resources.
Some popular employee onboarding software and tools include:
-
BambooHR: A comprehensive HR platform that includes onboarding software.
-
Workday: A cloud-based HR platform that includes onboarding tools.
-
Trello: A project management tool that can be used to create an onboarding checklist.
-
Slack: A communication platform that can be used to connect new hires with team members and provide information about the company culture.
When selecting an employee onboarding software or tool, consider the following factors:
-
Ease of use: Is the software easy to use and navigate?
-
Customization: Can the software be customized to meet the needs of your organization?
-
Integration: Does the software integrate with other HR systems and tools?
-
Cost: What is the cost of the software, and is it within your budget?
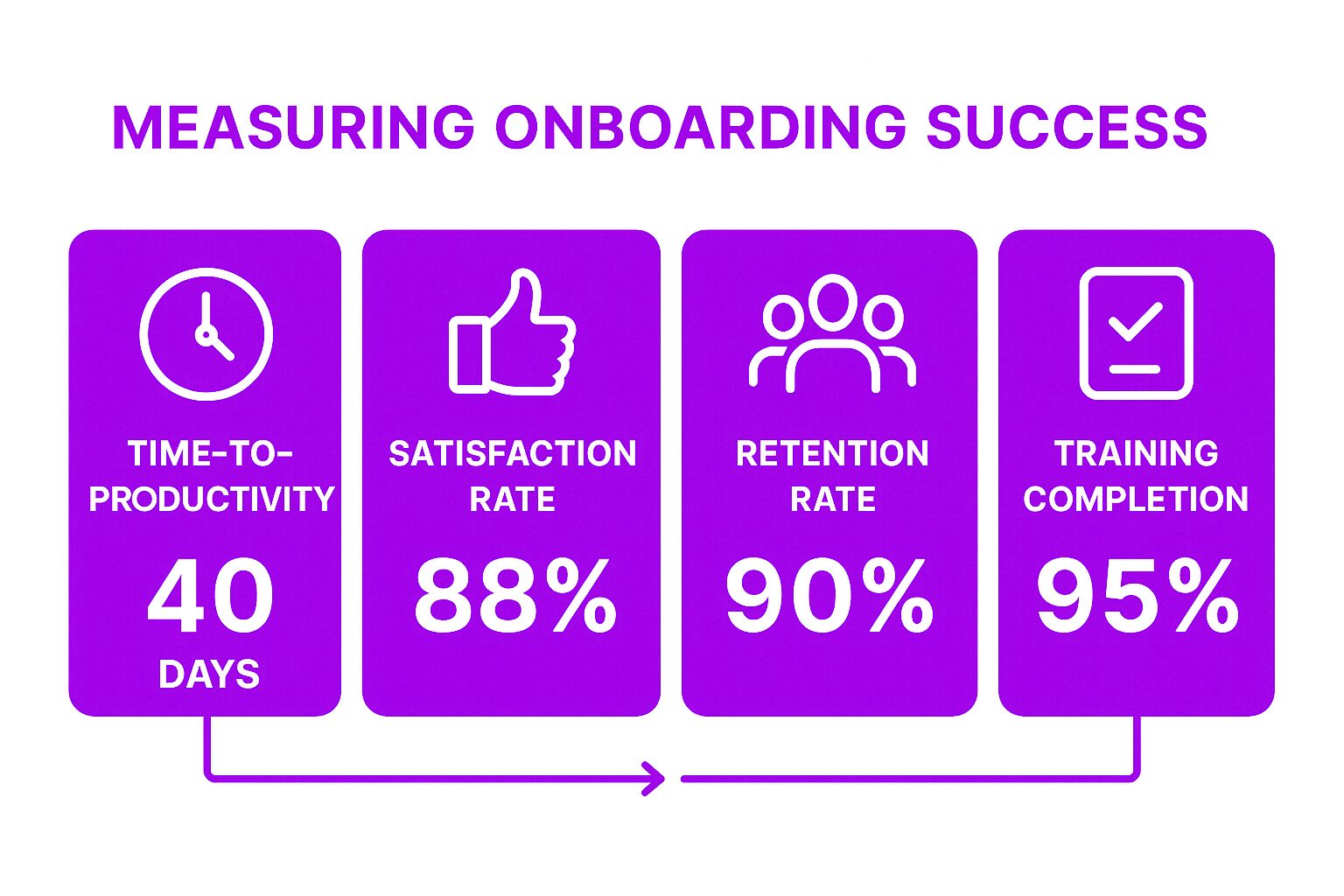
Measuring Onboarding Success
Measuring the success of an onboarding program is critical to ensuring that new hires are properly integrated into the organization. There are several metrics that can be used to measure onboarding success, including:
-
Time-to-productivity: How long does it take for new hires to become productive members of the team?
-
Employee satisfaction: How satisfied are new hires with the onboarding process?
-
Employee retention: What is the retention rate of new hires?
-
Training completion rate: What percentage of new hires complete the required training?
To measure onboarding success, HR professionals can use surveys, feedback forms, and metrics tracking. It’s also important to regularly review and adjust the onboarding program to ensure that it is meeting the needs of new hires and the organization.
Related Sub-Concepts
Employee Experience
The overall journey an employee has within a company, from hiring to exit.
Employee Engagement
The emotional connection employees feel toward their work and organization.
Talent Management
The strategy behind recruiting, retaining, and developing employees for long-term success.
Workplace Culture
The values, norms, and environment that define an organization’s work experience.
The Role of HR Leaders in Employee Onboarding
HR leaders play a critical role in employee onboarding. They are responsible for designing and implementing the onboarding program, and ensuring that it is aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Some key responsibilities of HR leaders in employee onboarding include:
-
Developing an onboarding program that meets the needs of new hires and the organization.
-
Ensuring that the onboarding program is aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
-
Providing training and support to new hires.
-
Communicating with new hires and providing feedback.
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of the onboarding program and making adjustments as needed.
HR leaders can also play a key role in promoting a positive company culture and ensuring that new hires feel welcome and included. By providing a comprehensive onboarding program, HR leaders can help to improve employee retention, satisfaction, and productivity.
Real-World Examples of Employee Onboarding Programs
Google uses a structured onboarding process that includes mentorship, learning modules, and team integration strategies. New hires are encouraged to contribute to meaningful projects early on.
Facebook (Meta)
Facebook’s onboarding program emphasizes social integration and collaboration, using internal communication platforms to keep employees engaged and informed.
Microsoft
Microsoft employs a blended learning approach, incorporating in-person training, virtual resources, and career development planning to support new employees.
The Future of Employee Onboarding
As workplace expectations evolve, companies must adapt their onboarding strategies. Remote and hybrid work models require digital-first onboarding approaches, and AI-driven personalization will play a larger role in customizing the experience.
Organizations that continuously improve their onboarding processes will build stronger, more engaged teams and retain top talent for long-term success.