What is the Employee Life Cycle?
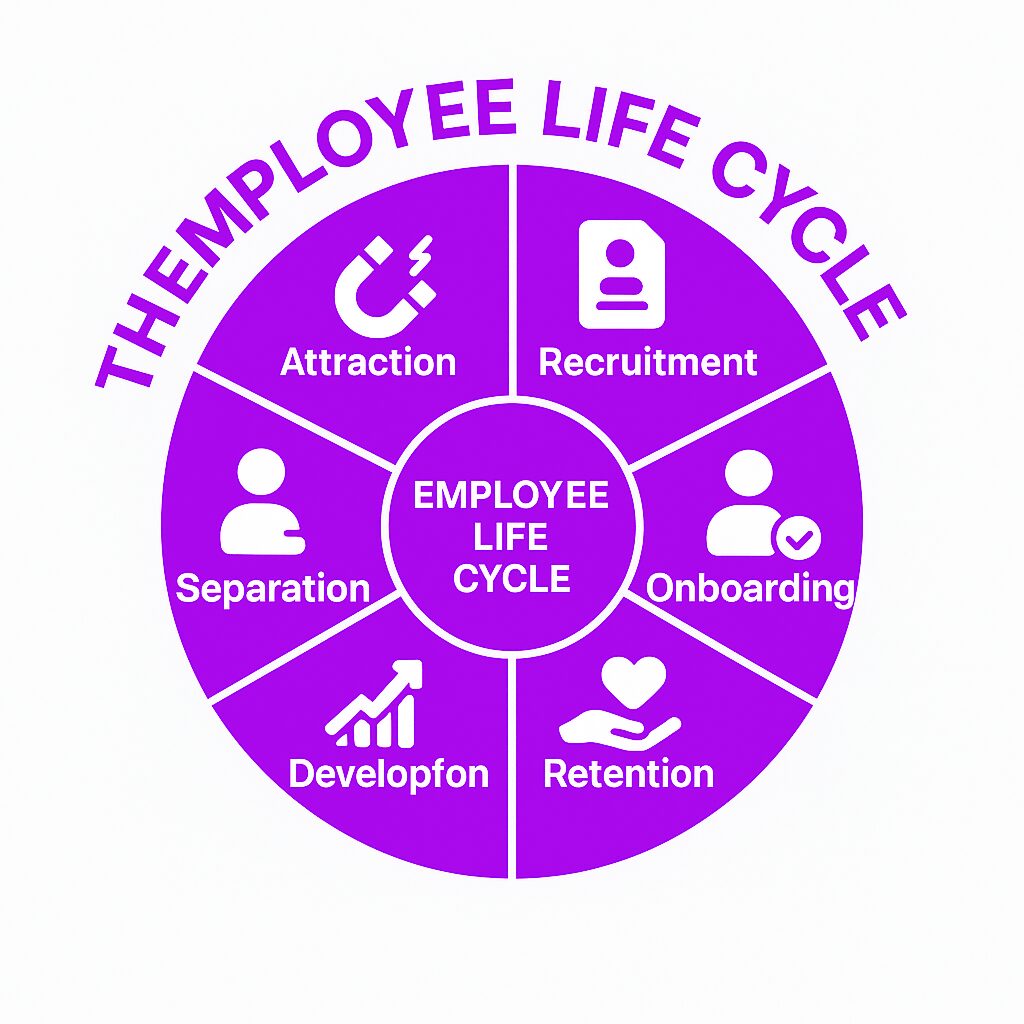
The employee life cycle is the journey every employee takes within a company, from their first interaction as a potential hire to their departure. Understanding why the employee life cycle is important can help businesses manage employee experiences more effectively. It includes key stages that define the employee’s experience and impact the company’s ability to attract, engage, and retain talent. Recognizing the employee life cycle phases is crucial for enhancing employee experience and addressing gaps in recruiting and onboarding processes. Businesses use the employee life cycle model to improve hiring, engagement, productivity, and long-term workforce planning.
Each stage of the cycle presents opportunities for companies to strengthen employee relationships. By understanding and optimizing each phase, organizations can create a workplace where employees feel supported, valued, and motivated to perform at their best.
Why the Employee Life Cycle Matters
Managing the employee life cycle helps businesses build a stronger workforce. Collecting employee feedback is crucial for measuring engagement and morale within the organization. Employees who experience a structured and supportive journey are more likely to stay engaged and contribute to the company’s success. When companies focus on the full employee experience, they create a culture where people feel connected to their work and the organization.
A well-managed employee life cycle leads to:
-
Higher employee retention
-
Improved job satisfaction
-
Stronger employer branding
-
Increased productivity
-
Better talent development and succession planning
Ignoring the employee’s journey results in higher turnover, disengagement, and a weaker workplace culture. Companies that fail to optimize these stages often struggle with recruitment, onboarding, and long-term employee engagement.
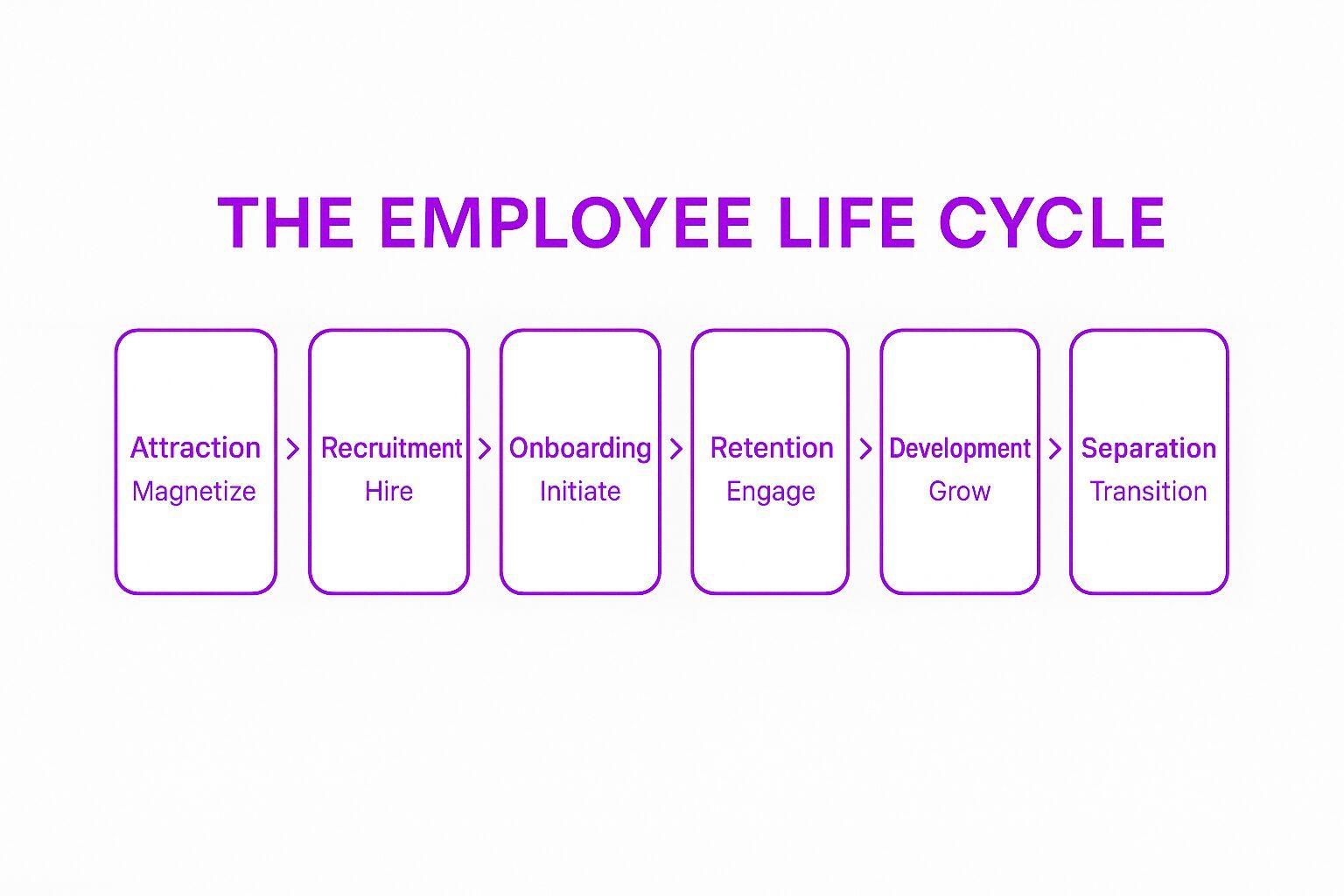
Key Stages of the Employee Life Cycle
1. Attraction
The employee life cycle begins before a candidate applies for a job. Attraction refers to how a company positions itself as an employer. Organizations with a strong reputation, clear values, and positive workplace culture attract better talent.
How Companies Attract Talent:
-
Employer Branding: Showcasing company culture, values, and benefits through social media, job sites, and employee testimonials.
-
Employee Advocacy: Encouraging current employees to share their experiences and refer candidates.
-
Competitive Compensation & Benefits: Offering attractive salary packages and perks that align with industry standards.
-
Diversity & Inclusion Initiatives: Creating an environment where diverse talent feels welcome.
2. Recruitment
Once interest is generated, companies must focus on the recruitment process to hire the right candidates. Recruitment involves finding, screening, and selecting individuals who align with company goals.
Best Practices for Hiring:
-
Clear Job Descriptions: Providing accurate details about roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
-
Structured Interview Process: Using standardized interview questions to ensure fair assessments.
-
Candidate Experience Focus: Keeping communication transparent, timely, and professional.
-
Technology in Hiring: Leveraging applicant tracking systems (ATS) and AI tools for streamlined hiring.
3. Onboarding
Onboarding sets the tone for new employees’ experience. A strong onboarding program ensures new hires feel welcomed and prepared for success.
Key Onboarding Elements:
-
Pre-boarding: Sending paperwork, company materials, and welcome messages before day one.
-
Orientation Programs: Introducing new hires to company culture, leadership, and team members.
-
Mentorship & Support: Assigning mentors or buddies to guide employees through their first few months.
-
Technology & Training: Providing access to tools, resources, and role-specific training.
4. Retention
Retention focuses on keeping employees engaged and motivated long-term. Companies that invest in employee satisfaction experience lower turnover rates and higher productivity.
Strategies to Retain Employees:
-
Competitive Compensation: Regular salary reviews and performance-based incentives.
-
Work-Life Balance: Flexible work arrangements and wellness programs.
-
Career Growth Opportunities: Training, mentorship, and internal promotions.
-
Recognition Programs: Acknowledging employee contributions through awards, bonuses, and peer recognition.
5. Development
The development stage and ongoing learning and career progression keep employees engaged. Without development opportunities, employees may feel stagnant and look for growth elsewhere.
How Companies Support Development:
-
Training Programs: Offering workshops, online courses, and leadership development initiatives.
-
Cross-Training: Encouraging employees to explore different roles within the company.
-
Tuition Reimbursement: Supporting continued education and skill-building.
-
Career Pathing: Creating clear advancement opportunities for employees.
6. Separation
All employees eventually exit a company, whether through retirement, resignation, or termination. Handling departures professionally maintains company reputation and relationships with former employees.
Best Practices for Employee Exits:
-
Exit Interviews: Gathering feedback to improve workplace culture.
-
Smooth Transitions: Ensuring knowledge transfer and proper documentation.
-
Maintaining Alumni Networks: Keeping connections open for future opportunities or referrals.
-
Ethical Layoffs & Resignations: Handling terminations with empathy and clear communication.
Employee Life Cycle Management
Employee life cycle management is a crucial aspect of human resources that involves understanding and managing the various stages of an employee’s journey within an organization. By focusing on each phase of the employee life cycle, companies can create a positive employee experience that boosts engagement and retention. Effective management of the employee life cycle can lead to increased productivity, better job satisfaction, and a stronger employer brand.
When organizations invest in employee life cycle management, they ensure that employees feel valued and supported from the moment they are attracted to the company until they exit. This holistic approach not only enhances the overall employee experience but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and growth. By paying attention to the needs and aspirations of employees at every stage, companies can build a loyal and motivated workforce that contributes to long-term success.
Benefits and Challenges of Employee Life Cycle Management
Benefits
-
Higher Engagement: Employees feel valued throughout their journey.
-
Lower Turnover: A positive experience encourages long-term commitment.
-
Stronger Employer Brand: Happy employees attract top talent.
-
Better Performance: Employees are more productive in a structured work environment.
-
Improved HR Strategy: Data-driven decision-making at every stage.
Challenges
-
Attracting the Right Talent: Competing in a tight job market.
-
Long Hiring Processes: Slowing down recruitment can lead to missed opportunities.
-
Employee Burnout: Failing to address workload balance.
-
Career Stagnation: Employees leaving due to lack of growth opportunities.
-
Exit Mismanagement: Poor offboarding experiences harming employer reputation.
Best Practices for Enhancing the Employee Life Cycle
Build a Strong Employer Brand
First impressions matter. Invest in showcasing company culture, employee testimonials, and workplace benefits to attract top candidates.
Streamline Recruitment and Onboarding
Use applicant tracking systems, automate hiring processes, and ensure new hires receive structured onboarding experiences.
Foster a Culture of Recognition
Employees want to feel appreciated. Implement regular recognition programs, celebrate milestones, and encourage peer-to-peer appreciation.
Offer Growth and Learning Opportunities
Keep employees engaged by providing skill development programs, mentorship, and career progression paths.
Gather Feedback and Adapt
Use surveys, one-on-one meetings, and pulse checks to continuously improve workplace experiences.
Related Sub-Concepts
Employee Engagement
Engagement is the emotional connection employees have with their work and company. The employee life cycle directly influences engagement levels.
Talent Management
A company’s strategy for hiring, developing, and retaining top talent aligns with managing the employee life cycle.
Succession Planning
Ensuring employees have a clear career path within the company is part of long-term workforce planning.
Employee Experience
The overall perception employees have of their workplace, influenced by every stage of the life cycle.
Employee Experience and Career Development
Employee experience and career development are critical components of employee life cycle management. Organizations should focus on creating a positive work environment that encourages growth and development. This can be achieved by offering comprehensive training programs, providing mentorship opportunities, and conducting regular feedback sessions.
Investing in employee development is key to improving employee engagement and job satisfaction. When employees see a clear path for career progression and feel supported in their professional growth, they are more likely to stay with the company and perform at their best. A culture of continuous learning not only benefits individual employees but also enhances the overall capabilities of the organization.
By prioritizing employee experience and career development, companies can reduce turnover rates and build a strong, committed workforce. This approach not only helps in retaining top talent but also strengthens the employer brand, making the organization more attractive to potential hires.
Real-World Examples of Employee Life Cycle Management
Google invests in every stage of the employee life cycle by offering competitive salaries, world-class onboarding, ongoing learning programs, and strong alumni networks.
Microsoft
Microsoft uses data-driven strategies to manage employee engagement, retention, and professional development.
Salesforce
Salesforce prioritizes employee wellness, flexible work arrangements, and career advancement to create a positive work environment.
Small Business Approach
Smaller companies may not have the resources of large corporations but can still enhance employee experiences through thoughtful onboarding, recognition programs, and career development initiatives.
The Future of Employee Life Cycle Management
As workplaces evolve, companies must adapt to new employee expectations. Remote work, AI-driven HR tools, and a greater focus on work-life balance are shaping the future of employee life cycle management.
Organizations that invest in improving each stage of the employee journey will not only retain top talent but also build a stronger, more engaged workforce. Managing the employee life cycle effectively is no longer optional—it’s essential for long-term business success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the employee life cycle model is a valuable tool for organizations to understand and manage the various stages of an employee’s journey. By implementing effective employee life cycle management strategies, organizations can improve employee engagement, increase employee retention, and create a positive work environment. It is essential to focus on employee experience and career development, provide opportunities for growth and development, and foster a culture of continuous learning. By doing so, organizations can reap the benefits of a happy, productive, and engaged workforce.
Managing the employee life cycle effectively is no longer optional—it’s essential for long-term business success. By investing in each stage of the employee journey, companies can build a stronger, more engaged workforce that drives organizational growth and success.