What Are Employee Resource Groups?
Employee Resource Groups (ERGs) are voluntary, employee-led groups that bring together individuals with shared interests, backgrounds, or experiences. These groups focus on creating an inclusive workplace by providing support, advocacy, and professional development opportunities.
ERGs often align with Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) initiatives, aiming to create a sense of belonging among underrepresented groups. Common ERGs include groups for women, racial and ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ employees, veterans, and employees with disabilities.
How Employee Resource Groups Work
ERGs function as structured communities within an organization. Business Resource Groups (BRGs), on the other hand, focus on both diversity and specific business objectives, helping companies navigate markets, develop strategies, and address organizational challenges. They typically have defined leadership roles, clear objectives, and specific activities that support employee engagement. While membership is voluntary, ERGs are most effective when they receive company support in the form of funding, leadership sponsorship, and recognition.
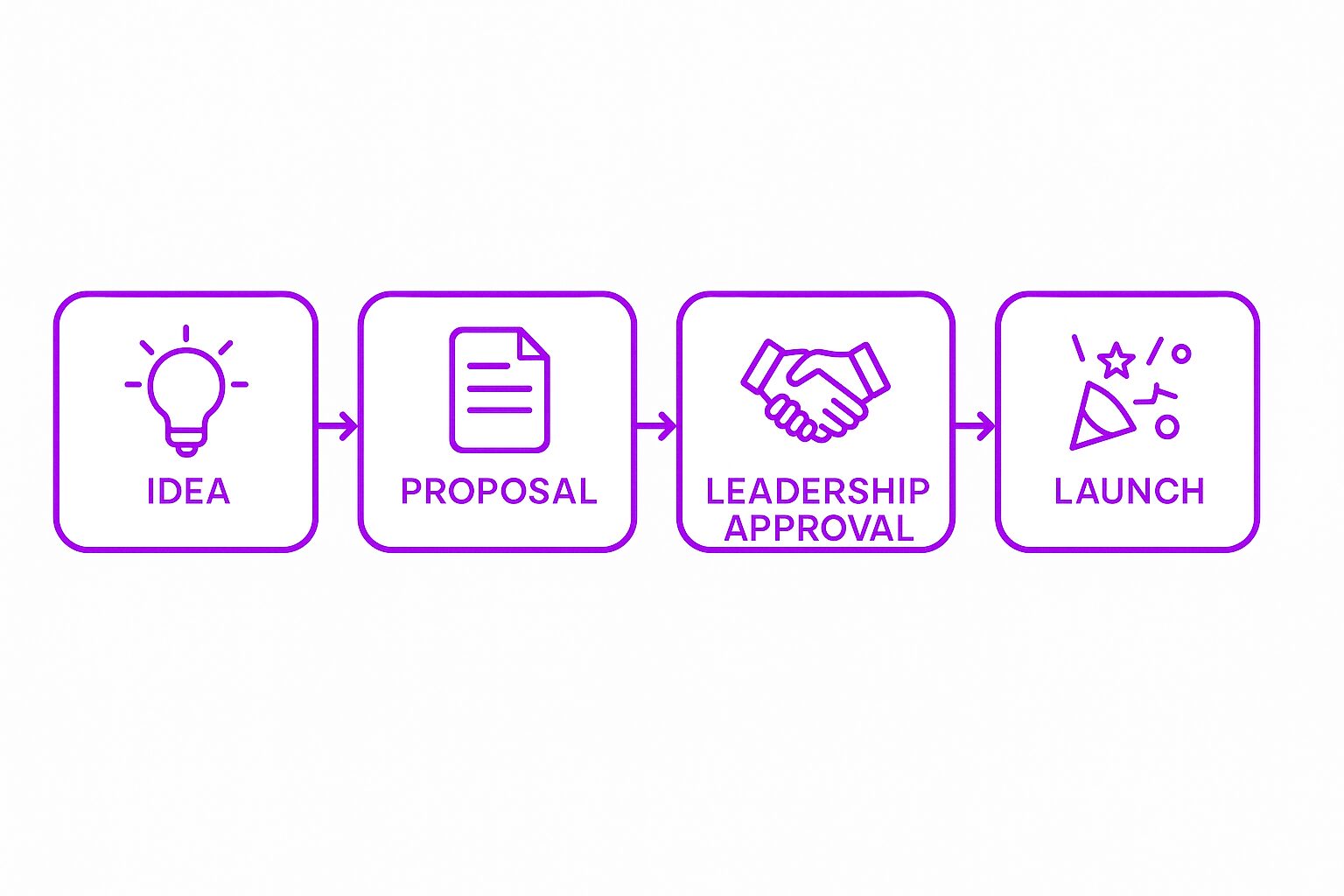
Key Components of an ERG
Formation
ERGs start with employees who share a common experience or interest. To gain company support, they often submit a proposal outlining their mission, goals, and intended activities. Leadership approval and backing are critical for long-term success.
Leadership & Membership
ERGs usually have a leadership team responsible for organizing meetings, planning initiatives, and engaging members. Leadership roles might include a chairperson, communications lead, and event coordinator. Some organizations provide executive sponsors to ensure ERG activities align with business goals. It is crucial for company leaders to support these efforts, as their involvement can help demonstrate the value of ERGs and ensure they address business challenges effectively.
Objectives & Initiatives
ERGs focus on a range of objectives, such as professional development, networking, mentorship, and social impact. In addition to these goals, ERGs can also support business objectives by helping to reach new markets and solve business challenges. They may host workshops, panel discussions, or social events to foster community and drive change within the organization.
Funding & Support
Many organizations allocate resources to ERGs, including financial support, meeting spaces, and access to leadership. Budgeting allows ERGs to fund events, sponsor community initiatives, or invest in employee development programs.
Measuring Impact
ERGs track their effectiveness through participation rates, event attendance, and employee feedback. Some companies incorporate ERG metrics into overall employee engagement assessments.
Why Are Employee Resource Groups Important?
ERGs contribute to a company’s culture and long-term success. They provide employees with a safe space to discuss shared experiences, offer mentorship opportunities, and advocate for policy changes that promote inclusivity.
Employee Engagement & Retention
ERGs create a workplace where employees feel valued and heard. When employees are part of a supportive community, they are more likely to stay engaged and committed to their company. Effective Employee Resource Groups (ERGs) can significantly enhance employee retention by fostering a supportive workplace culture, ultimately leading to reduced recruitment and training costs.
Professional Development
ERGs offer leadership opportunities and skill-building experiences. ERGs also provide professional development opportunities, such as mentorship and leadership training, to nurture talent and build a diverse leadership pipeline. Employees who participate in ERG leadership often gain visibility and career advancement opportunities.
Strengthening DEI Initiatives
ERGs play a key role in advancing workplace diversity by attracting and retaining a diverse workforce. They help companies understand and address the needs of diverse employees by providing insights that shape policies and hiring practices, thereby enhancing organizational culture and aligning with potential employees’ desires for inclusive workplaces.
Building Cross-Departmental Connections
ERGs bring together employees from different teams and departments, fostering collaboration and broadening professional networks.
Benefits and Challenges of ERGs
Benefits
-
Creates a more inclusive and supportive work environment
-
Helps companies attract and retain diverse talent
-
Encourages leadership development among employees
-
Improves communication between employees and leadership
-
Provides a platform for advocacy and social impact
-
Fosters a positive work environment by being voluntary, employee-led initiatives that support both diversity and the organization’s business goals
Challenges
-
ERGs require ongoing leadership support and funding
-
Some employees may feel excluded if ERGs focus too narrowly on specific groups
-
Engagement can decline without clear goals or company backing
-
Measuring impact can be difficult without structured metrics
Best Practices for Establishing and Running ERGs
Gain Leadership Buy-in and Executive Sponsorship
For ERGs to thrive, company leaders must provide visible support. This can include executive sponsorship, funding, and participation in ERG events.
Keep Membership Open
ERGs should welcome all employees, including allies who want to support their colleagues. This helps create an inclusive culture and encourages cross-group collaboration.
Define Clear Goals
Successful ERGs set measurable objectives, such as improving mentorship opportunities, increasing diversity hiring efforts, or organizing professional development events.
Create a Communication Plan
ERGs need effective communication to keep members informed and engaged. Internal newsletters, company intranets, and social platforms can help promote activities and events.
Measure and Share Impact
Organizations should track ERG participation, event success, and employee feedback. Sharing successes with leadership and the broader workforce reinforces the importance of ERGs.
Related Concepts
Affinity Groups vs. ERGs
Affinity groups are informal employee communities based on shared interests, whereas ERGs are structured with defined objectives and company sponsorship. ERGs often function as professional development groups, facilitating learning and skill development through workshops and seminars that enhance employees’ career advancement and alignment with company goals.
DEI Programs
ERGs complement broader DEI programs by providing grassroots support and firsthand perspectives on workplace inclusivity.
Employee Engagement
ERGs contribute to higher engagement levels by fostering a culture of belonging and participation.
Real-World Examples of ERGs in Action
Tech Industry ERGs
Companies like Google and Microsoft support ERGs focused on gender equality, racial diversity, and sexual orientation, promoting diversity and inclusion for LGBTQ+ employees. These groups help shape company policies and employee benefits.
ERGs in Financial Services
Large banks have ERGs that support mentorship and career development for women and minority employees, helping them advance into leadership roles.
ERGs for Social Impact
Some ERGs focus on community service, partnering with nonprofits to support causes aligned with their mission, such as education, environmental sustainability, or mental health awareness.
Final Thoughts
Employee Resource Groups play a critical role in fostering inclusive workplace cultures. When organizations invest in ERGs, they create environments where employees feel supported, empowered, and engaged. By recognizing and supporting these groups, businesses can drive meaningful change and strengthen their commitment to diversity and inclusion.