What Is an Enterprise Social Network?
An Enterprise Social Network (ESN) is an internal social networking platform designed for businesses to enhance communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing among employees. Unlike public social media platforms, ESNs are private and focus on improving workplace productivity, transparency, and engagement by aligning tools and practices with the company’s culture.
These platforms integrate social media features with business tools, allowing employees to share updates, exchange ideas, and collaborate in real time. A strong corporate culture can enhance employee engagement, productivity, and retention. ESNs serve as digital communities where employees can interact beyond traditional email and meetings, fostering a more connected work environment.
Definition and Purpose
An Enterprise Social Network (ESN) is a private, internal platform that enables employees to communicate, collaborate, and share knowledge within an organization. The primary purpose of an ESN is to facilitate social and informal communication, encourage team members to work together, and promote a sense of community and company culture. By providing a centralized hub for internal communications, ESNs aim to improve employee engagement, productivity, and overall job satisfaction.
How an Enterprise Social Network Works
ESNs operate as centralized hubs where employees can communicate, access resources, and participate in discussions relevant to their teams and departments, functioning similarly to enterprise social media networks. They often include the following features:
-
Newsfeeds: Employees stay updated on company announcements, team discussions, and industry news.
-
Messaging & Chat: Real-time communication options, including direct messaging and group chats.
-
Groups & Communities: Employees join groups based on projects, interests, or departments to foster collaboration.
-
File Sharing & Collaboration: Integrated document-sharing capabilities allow teams to work on projects together.
-
Analytics & Engagement Tracking: Organizations monitor participation levels and measure engagement.
Unlike traditional intranets, which are often static and one-way in communication, ESNs encourage interactive discussions and knowledge-sharing across an organization. An internal social network serves as a centralized platform that fosters communication, collaboration, and employee engagement, enhancing workplace culture and productivity.
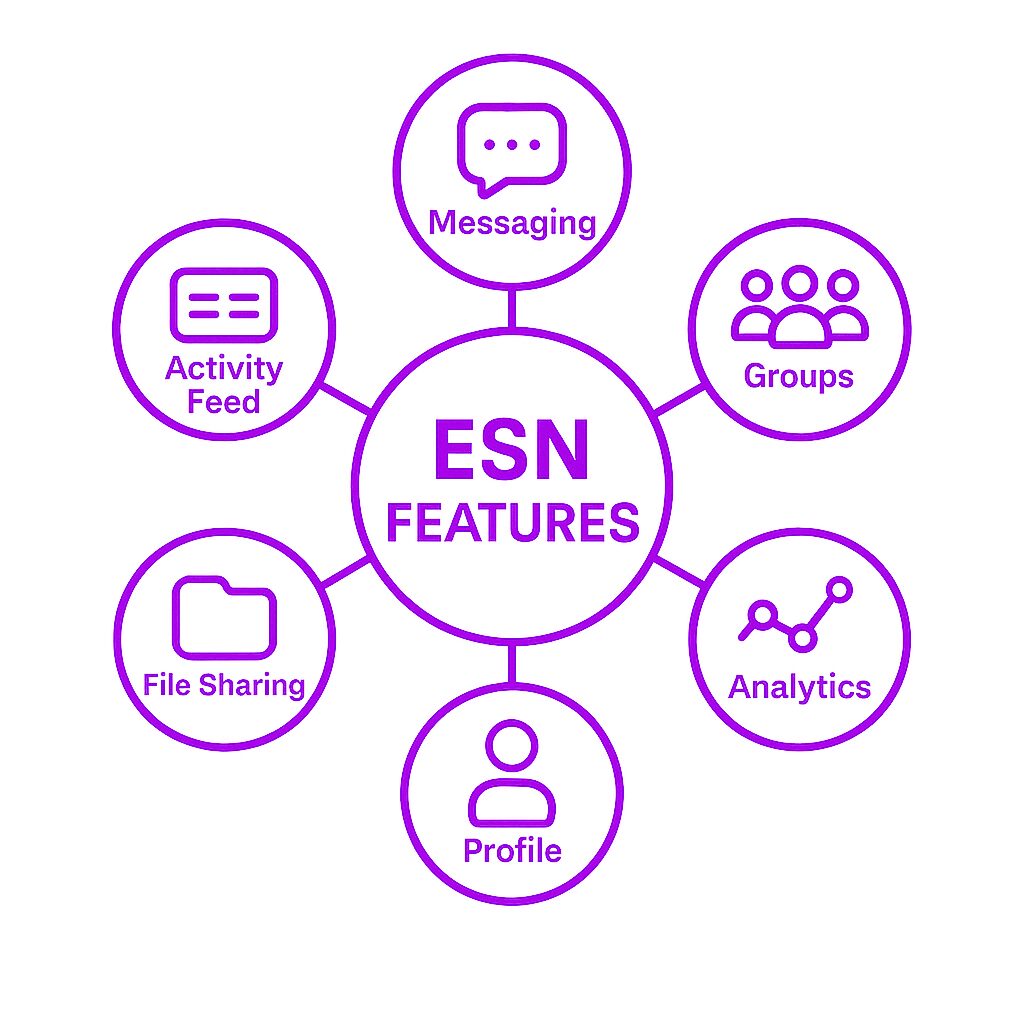
Key Features of an Enterprise Social Network
Core Features
-
Activity Feed: A dynamic hub where employees can browse company-wide announcements, updates from colleagues, and content from relevant groups and communities.
-
User Profiles: Employees can create profiles to share information about themselves, their skills, and their interests.
-
Groups and Communities: Employees can join or create groups based on shared interests, projects, or departments.
-
Instant Messaging: Employees can communicate with each other in real-time using instant messaging features.
-
File Sharing: Employees can share files and documents with each other, either individually or within groups.
Advanced Features
-
Knowledge Sharing: ESNs provide a platform for employees to share knowledge, expertise, and best practices.
-
Task Management: ESNs can integrate with project management tools to enable employees to assign and track tasks.
-
Document Management: ESNs can provide a centralized repository for company documents, policies, and procedures.
-
Analytics: ESNs can provide insights into employee engagement, content popularity, and platform usage.
-
Integration: ESNs can integrate with other enterprise systems, such as HR software, CRM systems, and productivity tools.
Key Stages and Components of an ESN
Adoption and Onboarding
Organizations must introduce the ESN in a way that encourages participation. Internal communication is significantly enhanced through ESNs, as they facilitate real-time conversations and streamline updates. This involves:
-
Educating employees on the platform’s benefits.
-
Providing training on how to use features effectively.
-
Offering incentives for early adopters.
Integration With Business Applications
To be effective, ESNs must integrate with existing business tools, such as:
-
Project management software (Trello, Asana, Microsoft Planner).
-
CRM systems for sales and marketing teams.
-
Cloud storage platforms for file sharing and accessibility.
User Engagement, Content Creation, and Knowledge Sharing
Once adopted, employees should actively contribute content such as:
-
Updates on projects and milestones.
-
Internal blog posts and thought leadership.
-
Peer recognition and shout-outs for achievements.
Analytics and Optimization
Organizations must track usage and engagement to refine their ESN strategies. Key metrics include:
-
Active user participation.
-
Most engaged discussion topics.
-
Areas where communication could be improved.
Why an Enterprise Social Network Matters
Faster Decision-Making
An ESN enables instant communication, eliminating the delays of traditional email chains. Teams make quicker, more informed decisions when discussions are transparent and easily accessible.
Improved Transparency
By allowing open discussions, ESNs create a culture of transparency. Employees stay informed about company goals, leadership updates, and internal initiatives.
Stronger Workplace Relationships
Employees build connections across departments, leading to increased collaboration and a sense of belonging. This is especially useful in large organizations or for remote employees, as it helps maintain connections and foster engagement despite physical distance.
Employee Empowerment
When employees have a platform to voice their ideas and contribute to discussions, they feel more engaged. An ESN encourages participation at all levels of the company.
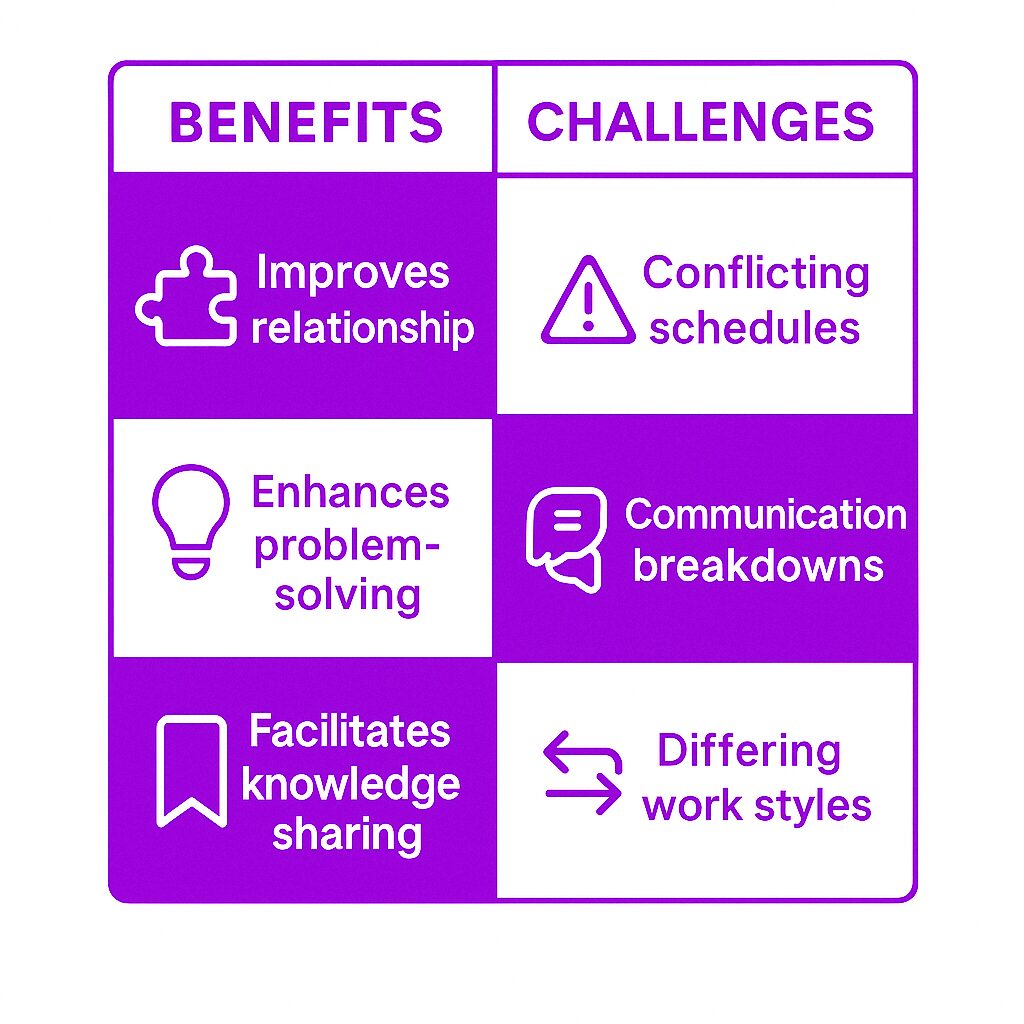
Benefits and Challenges of an Enterprise Social Network
Benefits
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Employees work together more effectively, regardless of location. Enterprise social network platforms enhance team collaboration and project management by facilitating real-time communication, enabling task coordination among team members, and providing a space for informal conversations, which is particularly beneficial in remote work environments.
-
Better Knowledge Retention: Important discussions and shared resources remain accessible for future reference.
-
Increased Productivity: Employees spend less time searching for information and more time completing tasks.
-
Higher Employee Engagement: Interactive features make workplace communication more engaging.
-
Stronger Company Culture: A well-maintained ESN fosters a sense of community and inclusion.
Challenges
-
Adoption Resistance: Some employees may be reluctant to move away from traditional communication methods.
-
Information Overload: Without moderation, excessive content can become overwhelming.
-
Security Risks: Organizations must ensure data privacy and restrict access to sensitive information.
-
Integration Complexity: Connecting the ESN with existing tools can require additional IT resources.
Enterprise Social Media Platform Options
-
Cloud-Based Knowledge Repository: A cloud-based platform that enables employees to access and share knowledge, documents, and best practices from anywhere.
-
Social Media Platforms: Traditional social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, can be used as ESNs, but may lack the security and features required for enterprise use.
-
Enterprise Social Networking Platforms: Specialized platforms, such as Yammer, Slack, and Microsoft Teams, are designed specifically for enterprise social networking and provide advanced features and security.
-
Intranet Platforms: Intranet platforms, such as SharePoint, can be used as ESNs, providing a centralized hub for internal communications and collaboration.
Best Practices for Implementing an ESN
Encourage Leadership Participation
If managers and executives actively use the ESN, employees are more likely to engage. Leadership involvement sets the tone for company-wide adoption.
Provide Clear Guidelines
Establish usage policies to ensure professional and constructive discussions. Guidelines should cover content sharing, appropriate communication, and security measures.
Use Gamification to Boost Engagement
Introduce features such as:
-
Recognition badges for active contributors.
-
Leaderboards for participation.
-
Rewards for employees who engage with the platform consistently.
Ensure Mobile Accessibility
Modern workplaces demand flexibility. An ESN should be accessible via mobile apps so employees can engage from anywhere.
Monitor and Optimize Usage
Use analytics to track participation and engagement trends. Regularly refine strategies based on user feedback and performance data.
Related Concepts
Intranet vs. Enterprise Social Network
Traditional intranets serve as information repositories, while ESNs facilitate interactive discussions. Many companies blend both to create a social intranet.
Collaboration Tools
ESNs differ from tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams, which focus on messaging and project collaboration rather than company-wide engagement.
Employee Engagement Platforms
ESNs contribute to engagement strategies by making workplace communication more dynamic and inclusive.
Real-World Applications of an ESN
Global Corporations
Large enterprises use ESNs to connect employees across multiple locations. International teams collaborate more effectively, reducing reliance on lengthy email threads.
Remote and Hybrid Workforces
With remote work becoming more common, ESNs help employees stay connected. Virtual teams use the platform to communicate, share updates, and maintain a sense of community.
Employee Resource Groups (ERGs)
ESNs provide dedicated spaces for ERGs to discuss initiatives, organize events, and promote inclusivity within the workplace.
Project Collaboration
Teams use ESNs to manage projects, assign tasks, and share progress updates. The centralized platform reduces miscommunication and enhances workflow efficiency.
Crisis Communication and Internal Communications
During emergencies, ESNs serve as a rapid communication channel for updates, ensuring employees stay informed and connected.
Final Thoughts
Enterprise Social Networks transform workplace communication by making it faster, more interactive, and accessible. Organizations that implement ESNs effectively create a connected workforce where employees engage, collaborate, and contribute to company success.