What Are Cross-Functional Teams?
A cross-functional team is a group of professionals from different departments or areas of different expertise working together toward a common goal. Unlike traditional teams that operate within a single function, cross-functional teams integrate diverse skill sets, perspectives, and experiences to solve complex problems, drive innovation, and improve collaboration.
Organizations use cross-functional teams to break down silos, improve decision-making, and speed up project execution. These teams are common in product development, strategic planning, and operational improvements, where multiple departments need to align their efforts to achieve success.
How Cross-Functional Teams Work
Cross-functional teams operate by combining expertise from various departments, such as marketing, finance, product development, customer support, and IT. A marketing manager often collaborates with team members from engineering, finance, and customer support to ensure project objectives are met. By working together, these teams ensure that all aspects of a project or initiative are considered, reducing the risk of blind spots and inefficiencies.
These teams may be:
-
Temporary – Assembled for a specific project and disbanded upon completion.
-
Ongoing – Part of a continuous effort to foster collaboration across departments.
Successful cross-functional teams require clear leadership, defined goals, and strong communication. Without these elements, collaboration can become disorganized and ineffective.
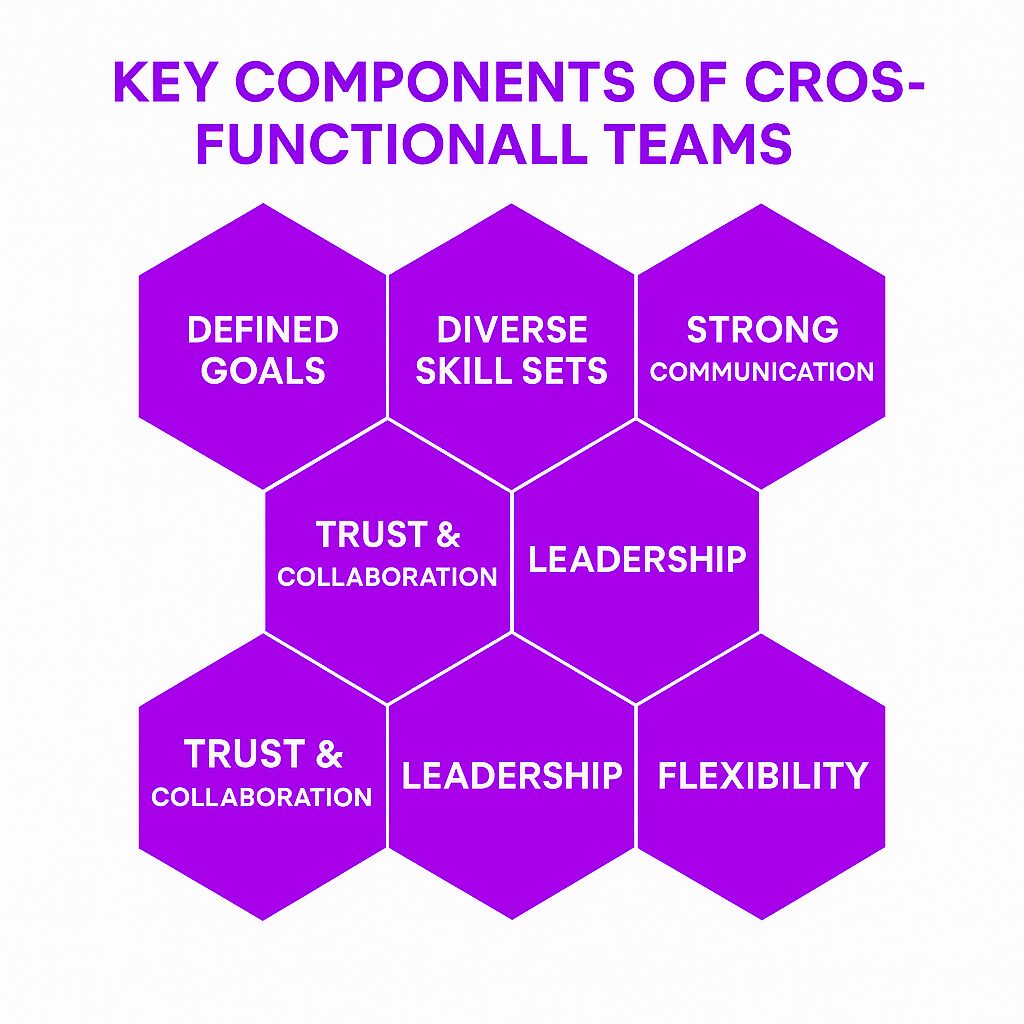
Key Components of Cross-Functional Teams
1. Defined Goals and Objectives
Every team must have a clear purpose, whether it’s launching a new product, improving customer service, or streamlining internal processes. Goals should be:
-
Specific
-
Measurable
-
Achievable
-
Relevant
-
Time-bound (SMART criteria)
These goals should align with the broader organizational goals to ensure that the team’s efforts contribute to the company’s overall success.
2. Diverse Skill Sets
Cross-functional teams thrive on diversity. Having professionals from different backgrounds leads to more comprehensive problem-solving and well-rounded decision-making. A product development team, for instance, benefits greatly from having members with diverse expertise to drive innovation and successful project execution.
3. Strong Communication
Since each team member comes from different areas of the organization, establishing clear communication guidelines is crucial. Teams should use standardized tools and platforms to ensure transparency and alignment.
4. Trust and Collaboration
Members must respect each other’s expertise and be open to different perspectives. A culture of trust fosters constructive discussions and better teamwork. Effective team work is essential for leveraging the diverse expertise within the team and achieving common goals.
5. Leadership and Accountability
A designated leader or facilitator helps keep the team focused and aligned. Leadership ensures accountability by defining responsibilities and tracking progress.
6. Flexibility and Adaptability
Cross-functional teams often work on evolving challenges. The ability to adapt and iterate based on new insights is essential for success.
Purpose and Importance of Cross-Functional Teams
Organizations rely on cross-functional teams to:
-
Encourage innovation by combining different perspectives.
-
Improve decision-making through diverse input.
-
Break down departmental silos for better collaboration.
-
Enhance efficiency by streamlining workflows.
-
Respond to market changes more quickly.
By leveraging the expertise of multiple departments, cross-functional teams help businesses remain agile and competitive.
Benefits of Cross-Functional Teams
1. Faster Innovation
Cross-functional teams bring together varied perspectives, leading to creative solutions. For instance, a marketing team working closely with designers and engineers can ensure that new products are both marketable and technically sound. Companies that foster collaboration between designers, engineers, and marketers, for example, can create products that are both functional and appealing.
2. Improved Problem-Solving
Complex challenges require multiple viewpoints. A cross-functional team ensures that solutions are well-rounded and practical, reducing the likelihood of oversight.
3. Higher Employee Engagement
Employees who collaborate outside their usual departments gain new insights and professional growth opportunities. This increased engagement leads to greater job satisfaction.
4. More Effective Communication
When teams work across departments, they naturally improve communication processes, ensuring alignment between different business areas.
5. Greater Organizational Agility
Cross-functional teams enable businesses to adapt quickly to new challenges, whether it’s a shift in market trends or an operational hurdle.
Challenges of Cross-Functional Teams
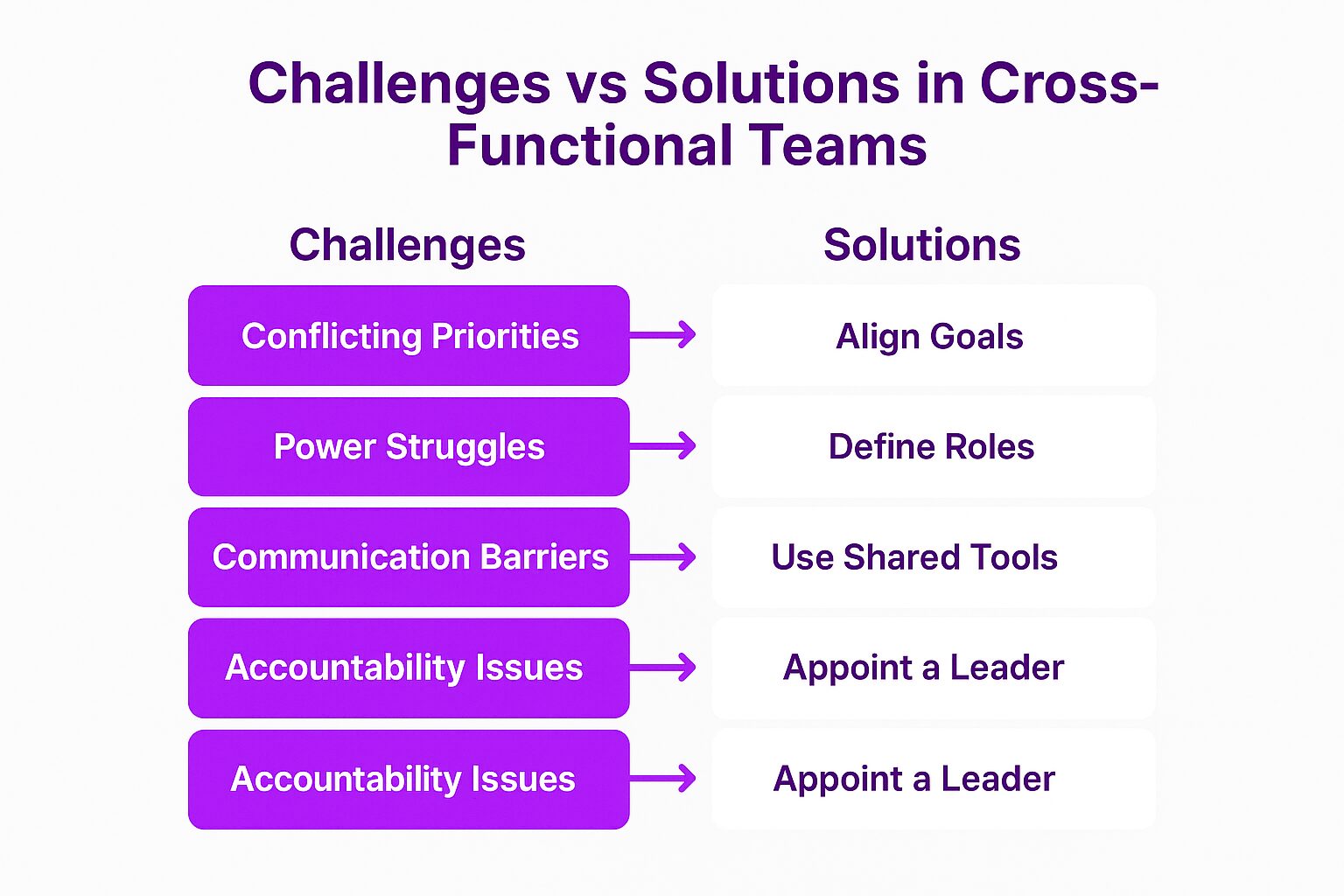
1. Conflicting Priorities
Different departments have different objectives. A sales team might prioritize closing deals, while an engineering team focuses on product stability. Aligning these priorities is essential for success. Ensuring that all members are working towards the same team objectives can help mitigate these conflicts.
2. Communication Barriers
Each department has its own terminology and workflow. Misunderstandings can occur when team members are not familiar with how other functions operate.
In software development, for instance, clear communication between developers, testers, and product managers is essential to avoid misunderstandings and ensure project success.
3. Power Struggles
Without clear leadership, disagreements may arise over decision-making authority. Teams need a structured approach to resolving conflicts.
4. Resistance to Change
Employees accustomed to working in silos may struggle with cross-functional collaboration. Organizations need to foster a culture that values teamwork and knowledge-sharing.
5. Accountability Issues
When multiple departments contribute to a project, it can be unclear who is responsible for what. Defining roles and responsibilities upfront prevents confusion.
Building a Cross-Functional Team
Creating a successful cross-functional team requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. Here are the essential steps to build a team that can effectively achieve its objectives:
How to Staff and Structure Cross-Functional Teams
-
Define the Team’s Purpose and Goals: Clearly articulate the team’s objectives, scope, and deliverables. This ensures that all team members are aligned and working towards the same outcome, whether it’s a specific project or an ongoing initiative.
-
Identify the Necessary Skills and Expertise: Determine the specific skills and expertise required to achieve the team’s goals. This might include professionals from marketing, sales, product development, customer service, and other relevant areas.
-
Select Team Members: Choose team members who possess the necessary skills and expertise. It’s crucial to select individuals who can work collaboratively and contribute to the team’s work towards a common goal.
-
Consider the Team’s Size and Structure: Determine the optimal team size and structure to ensure effective communication, collaboration, and decision-making. A well-balanced team composed of diverse expertise can drive more creative solutions.
-
Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define each team member’s role and responsibilities to avoid confusion and overlapping work. This clarity helps in maintaining accountability and streamlining the team’s work.
-
Foster a Culture of Collaboration and Open Communication: Encourage team members to share their ideas, concerns, and feedback. Promoting a culture of collaboration and open communication is essential for effective cross-functional collaboration.
By following these steps, you can build a cross-functional team that is well-equipped to achieve its objectives and drive business success. Such teams are integral to navigating the complexities of the modern business environment.
Cross-Functional Team Management
Managing a cross-functional team involves unique challenges and requires a strategic approach to ensure effective collaboration and productivity. Here are some key strategies for managing cross-functional teams:
Best Practices for Cross-Functional Teams
1. Set Clear Expectations
Teams need defined goals, timelines, and success metrics. Every member should understand their role and contribution.
Regularly reviewing the team’s work helps ensure that everyone is on track and meeting their objectives.
2. Establish Strong Leadership
A team leader or facilitator helps coordinate efforts, manage conflicts, and ensure accountability.
3. Use Collaboration Tools
Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, Asana, and Trello streamline communication and project tracking.
4. Encourage Open Communication
Regular check-ins and feedback loops keep everyone aligned. Encouraging open dialogue reduces misunderstandings and strengthens teamwork.
5. Promote Cross-Training
Employees should gain a basic understanding of other departments’ functions. Cross-training fosters mutual respect and improves collaboration.
6. Recognize and Reward Contributions
Acknowledging team achievements boosts morale and encourages continued participation in cross-functional projects.
Measuring Success
Evaluating the success of a cross-functional team requires a comprehensive set of metrics that measure performance, collaboration, and impact on the business. Here are some key metrics to consider:
Metrics for Evaluating Cross-Functional Teams
-
Team Performance Metrics: Measure the team’s performance against its goals and objectives. This includes project completion rates, quality metrics, and customer satisfaction. These metrics help assess whether the team is meeting its targets and delivering value.
-
Collaboration Metrics: Evaluate the team’s collaboration and communication. Metrics such as meeting attendance, email response rates, and feedback surveys can provide insights into how well team members are working together.
-
Innovation Metrics: Assess the team’s innovation and creativity. Track the number of new ideas generated, patents filed, and products developed. These metrics highlight the team’s ability to drive creative solutions and contribute to the company’s innovation pipeline.
-
Customer Satisfaction Metrics: Measure the team’s impact on customer satisfaction. Use customer feedback surveys, Net Promoter Score (NPS), and customer retention rates to gauge how well the team’s work is resonating with customers.
-
Financial Metrics: Evaluate the team’s financial impact. Metrics such as revenue growth, cost savings, and return on investment (ROI) provide a clear picture of the team’s contribution to the company’s bottom line.
-
Employee Engagement Metrics: Measure the team’s employee engagement and satisfaction. Employee feedback surveys, turnover rates, and training participation can indicate how engaged and motivated team members are.
By tracking these metrics, you can evaluate the success of your cross-functional team and make data-driven decisions to improve its performance and impact on the business. Effective cross-functional collaboration can lead to significant benefits, including faster innovation, improved problem-solving, and greater organizational agility.
Real-World Examples of Cross-Functional Teams
1. Apple’s Product Development
Apple’s ability to create seamless hardware and software experiences comes from cross-functional collaboration between engineers, designers, and marketers.
2. Tesla’s Automotive Innovation
Tesla’s electric vehicle development integrates expertise from software engineers, battery specialists, and design teams to produce high-performance vehicles.
3. Pixar’s Film Production
Pixar’s success in animation results from collaboration between artists, writers, and computer scientists, ensuring both storytelling and technical excellence.
4. Google’s Doodle Team
Google’s interactive homepage doodles are the result of teamwork between illustrators, animators, and software engineers.
5. Nike’s Sportswear Development
Nike collaborates with material scientists, designers, and professional athletes to develop high-performance sportswear.
Related Concepts
Cross-Functional Collaboration
While cross-functional teams focus on project execution, cross-functional collaboration refers to the broader process of departments working together on ongoing initiatives.
Agile Teams
Agile teams follow iterative work cycles, often incorporating cross-functional collaboration to develop products quickly and efficiently.
Interdisciplinary Teams
Similar to cross-functional teams, but often found in research, healthcare, and academic settings where diverse expertise is required to tackle specialized challenges.
Final Thoughts
Cross-functional teams are a powerful tool for organizations looking to improve collaboration, drive innovation, and solve complex problems. While challenges such as communication barriers and conflicting priorities exist, implementing best practices like clear goal-setting, strong leadership, and effective communication can ensure success. Companies that foster cross-functional teamwork gain a competitive edge by leveraging diverse expertise and improving decision-making processes.