Capacity planning is the process businesses use to determine the resources they need to meet future demand. It ensures that organizations can fulfill customer expectations without overcommitting resources. Capacity management is a critical process in operations management that involves balancing supply and demand through effective resource management. The goal is to strike a balance—avoiding waste while ensuring operations run smoothly.
Definition and Importance
Understanding Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is a strategic process that involves determining the production capacity needed to meet changing demand for products or services. It is a crucial aspect of project management and operations, as it helps organizations anticipate and prepare for future demand. By evaluating the organization’s resources—such as workforce, equipment, and materials—capacity planning ensures that the right amount of resources is available to complete a project or meet customer demand. This process is vital for maintaining a balance between resource availability and demand, thereby preventing both shortages and excess capacity.
Importance in Operations and Project Management
Effective capacity planning is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their operations and improve financial performance. It enables organizations to match their resources with project needs, identify potential bottlenecks, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and capacity expansion. By aligning resources with demand, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, boost client satisfaction, and increase team productivity. This strategic approach is particularly critical in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and professional services, where the ability to meet demand promptly can significantly impact overall success.
Why Capacity Planning Matters
Without proper capacity planning, businesses risk running out of resources or overspending on unnecessary assets. Understanding how much capacity is available is crucial to prevent resource shortages and overspending. This process helps companies predict demand and adjust their workforce, technology, and infrastructure accordingly. Organizations that fail to plan for capacity often experience production delays, customer dissatisfaction, and financial losses.
Business Impact
Every company, regardless of industry, faces fluctuations in demand. Managing resources across multiple projects is crucial to enhance capacity planning and prevent burnout. A retailer must prepare for seasonal shopping spikes. A manufacturer needs to ensure it can fulfill large orders without delaying shipments. An IT company must manage server loads to prevent website downtime. Capacity planning helps businesses stay competitive by keeping operations efficient and responsive.
Preventing Waste
Capacity planning isn’t just about avoiding shortages. Overestimating needs leads to excess inventory, wasted labor, and unnecessary operational costs. Underestimating, on the other hand, results in lost sales, frustrated customers, and overworked employees. A well-executed plan prevents both extremes.
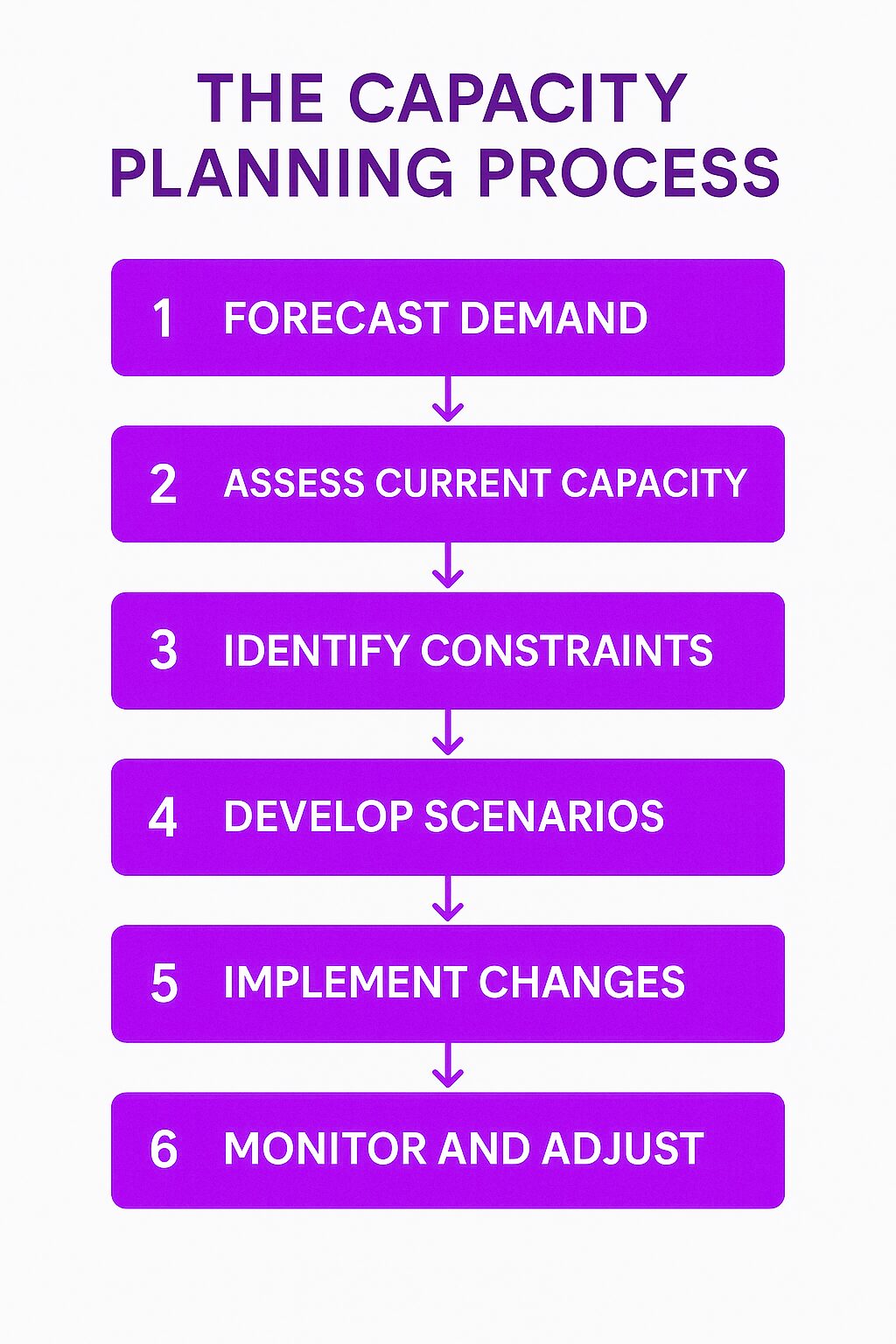
The Capacity Planning Process
1. Forecast Demand
Businesses analyze past data and market trends to estimate future needs. Having a well-defined capacity planning strategy is crucial to anticipate future challenges and enhance overall operational efficiency. They look at historical sales, seasonal patterns, and industry shifts to anticipate demand fluctuations.
2. Assess Current Capacity
Understanding current capabilities is essential. Companies evaluate their workforce, equipment, facilities, technology, and resource capacity as key factors in effective project planning. If there’s a gap between capacity and projected demand, adjustments are necessary.
3. Identify Constraints
Even the best forecasts can be limited by real-world constraints. Resource capacity planning is crucial for managing and allocating resources effectively, ensuring that organizations can meet current project demands and forecast future needs. Businesses must consider budget limits, regulatory requirements, and physical space. Identifying these limitations early helps prevent last-minute disruptions.
4. Develop Scenarios
Markets change. Customers adjust their buying habits. Supply chains get disrupted. Companies create multiple planning scenarios to prepare for these variables. Capacity planning tools play a crucial role in streamlining project management and optimizing resource allocation to ensure timely project delivery. Having contingency plans ensures flexibility.
5. Implement Changes
Once a plan is in place, businesses implement resource management strategies to make adjustments and align capacity with demand. This might include hiring new employees, investing in technology, or adjusting production schedules. The key is to align capacity with demand before issues arise.
6. Monitor and Adjust
Capacity planning is an ongoing process. Resource planning is equally important, as it involves the tactical allocation of specific individuals to projects based on their skills and roles. Organizations must continuously track their performance and adjust their strategies. Regular evaluations help businesses stay ahead of potential problems.
Capacity Planning Strategies
Lead Strategy
The lead strategy involves planning capacity to meet forecasted demand rather than current demand. This proactive approach ensures that organizations have the necessary resources to address unexpected demand spikes almost immediately. The lead strategy is particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing high demand variability or where a surge in demand significantly increases the required resources. However, this approach can result in idle resources if actual demand falls short of forecasts. To implement a lead strategy effectively, organizations need a robust forecasting process and the ability to allocate resources efficiently. This strategy requires careful planning and continuous monitoring to balance the risks and benefits, ensuring that the organization remains agile and responsive to market changes.
Benefits of Capacity Planning
Meeting Customer Expectations
Customers expect products and services to be available when they need them. Managing a team’s capacity is crucial to optimize resources for project completion. Capacity planning helps businesses maintain a consistent supply, reducing delays and backorders.
Cost Savings
Planning ahead prevents costly last-minute fixes. Businesses can avoid rush orders, emergency staffing, and unexpected expenses by preparing in advance.
Resource Efficiency
A structured approach ensures that resources are used effectively. Companies can allocate staff, machinery, and materials more efficiently, reducing waste.
Risk Management
Market conditions change quickly. A solid capacity plan allows businesses to adapt, minimizing the impact of unexpected disruptions.
Challenges in Capacity Planning
Uncertain Demand
Predicting future demand isn’t easy. Consumer behavior, economic shifts, and industry changes can all affect demand. Companies must use the best available data while remaining adaptable.
Budget Constraints
Not every business has unlimited resources. Expanding capacity requires investment, whether in new equipment, staff, or technology. Balancing financial limitations with growth goals is a challenge.
Bottlenecks
One weak link in the supply chain can disrupt the entire operation. A lack of skilled workers, machine failures, or vendor delays can create bottlenecks that slow production.
Technology Costs
Automation and AI-driven forecasting tools can improve capacity planning, but they require investment. Small businesses may struggle to afford these technologies, limiting their ability to optimize resources.
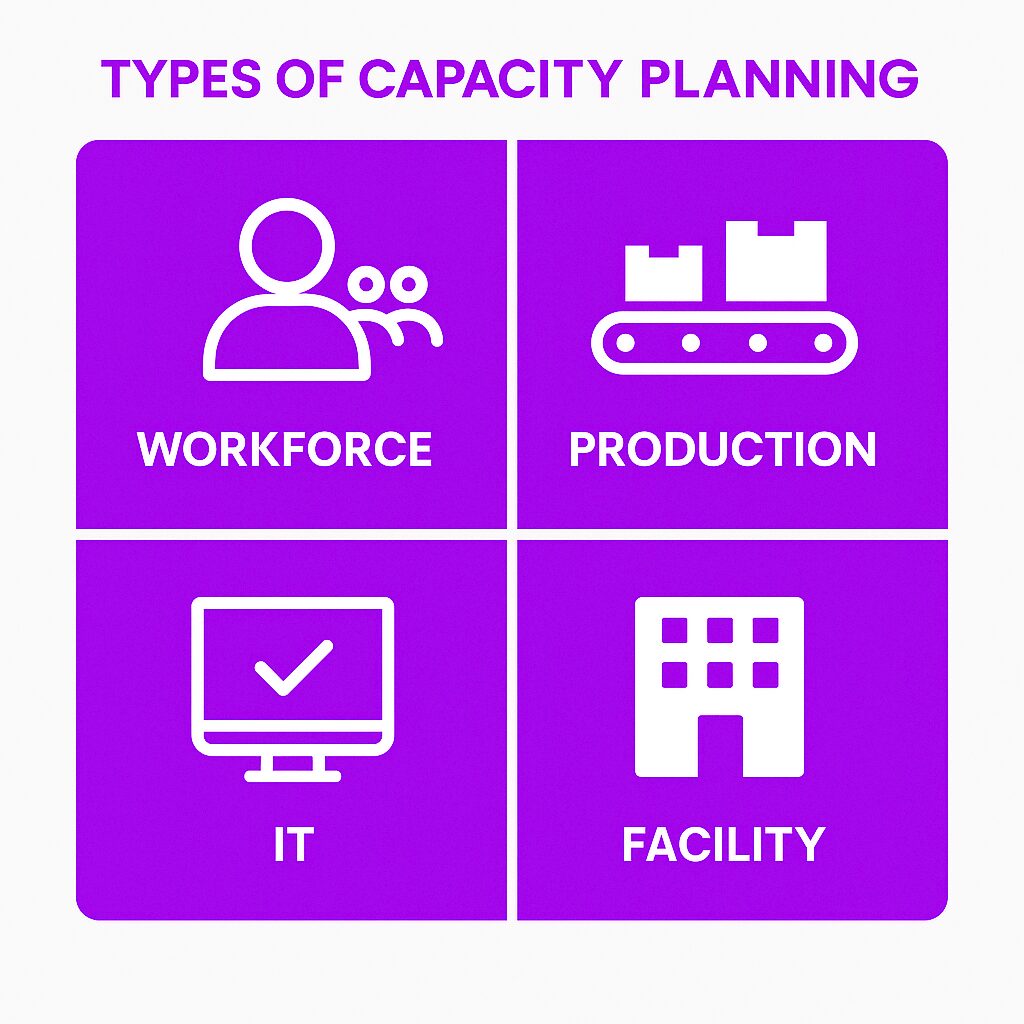
Types of Capacity Planning
Workforce Resource Capacity Planning
Businesses assess their staffing levels to ensure they have enough employees to handle projected workloads. A project manager plays a crucial role in creating a capacity plan to support teams and prevent bottlenecks. This includes hiring, training, and scheduling adjustments.
Production Capacity Planning
Manufacturers evaluate their production lines, equipment, and supply chains to ensure they can meet future orders without delays. A well-developed resource plan is essential in identifying required roles and managing resource availability, ensuring smooth operations and project reliability.
IT Capacity Planning
Tech companies and IT departments monitor server loads, data storage, and network capacity to prevent slowdowns and downtime. Project managers play a crucial role in adjusting resources based on project demands and team availability, ensuring that capacity planning aligns with fluctuating workload and resource allocation.
Facility Capacity Planning
Companies assess physical space to determine if they have room for expansion, additional inventory, or increased production.
Best Practices for Capacity Planning
Use Data-Driven Forecasting
Historical data provides a strong foundation for future planning. Businesses should analyze past trends and incorporate real-time market insights to improve accuracy.
Implement Scalable Capacity Planning Software Solutions
Flexibility is key. Businesses should adopt scalable systems, whether in staffing, production, or technology. This allows for adjustments without major disruptions.
Monitor Performance Continuously
Capacity planning isn’t a one-time event. Businesses should regularly review their capacity needs and adjust as necessary. Technology tools can help automate monitoring and alert companies to potential issues.
Invest in Employee Training
A well-trained workforce improves efficiency. Cross-training employees helps businesses adapt to shifting demands without over-relying on new hires.
Develop Contingency Plans
Unexpected events happen. A backup plan ensures businesses can respond quickly to demand spikes, supply chain disruptions, or economic downturns.
Real-World Applications
Retail
Retailers use capacity planning to prepare for peak seasons. Stores stock up on inventory, hire temporary workers, and adjust hours based on expected demand.
Manufacturing
Factories adjust production schedules based on sales projections. They evaluate machine output, workforce availability, and raw material supply to ensure smooth operations.
IT and Cloud Computing
Tech companies analyze server capacity to prevent website crashes and slowdowns. Cloud storage providers use capacity planning to allocate resources efficiently.
Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics manage patient intake, staffing, and medical equipment availability to ensure they can handle emergencies and routine care.
Logistics
Shipping companies use capacity planning to optimize fleet management. They assess delivery schedules, fuel costs, and vehicle availability to meet customer demands.
Final Thoughts
Capacity planning helps businesses avoid shortages, reduce costs, and operate efficiently. It requires continuous monitoring and adaptation, but the benefits outweigh the effort. Organizations that invest in capacity planning can respond to market changes, meet customer expectations, and maintain long-term stability.