A Chief Experience Officer (CXO) is a C-suite executive responsible for managing and improving the overall experience of customers, employees, and other stakeholders. The evolving role of the chief customer officer often overlaps with that of the CXO, though the former’s responsibilities are typically more limited to external customers. The CXO ensures that every interaction with the company aligns with its brand values and enhances satisfaction. This role has grown in importance as businesses realize that customer and employee experiences directly impact revenue, retention, and brand reputation.
The Role of a Chief Experience Officer
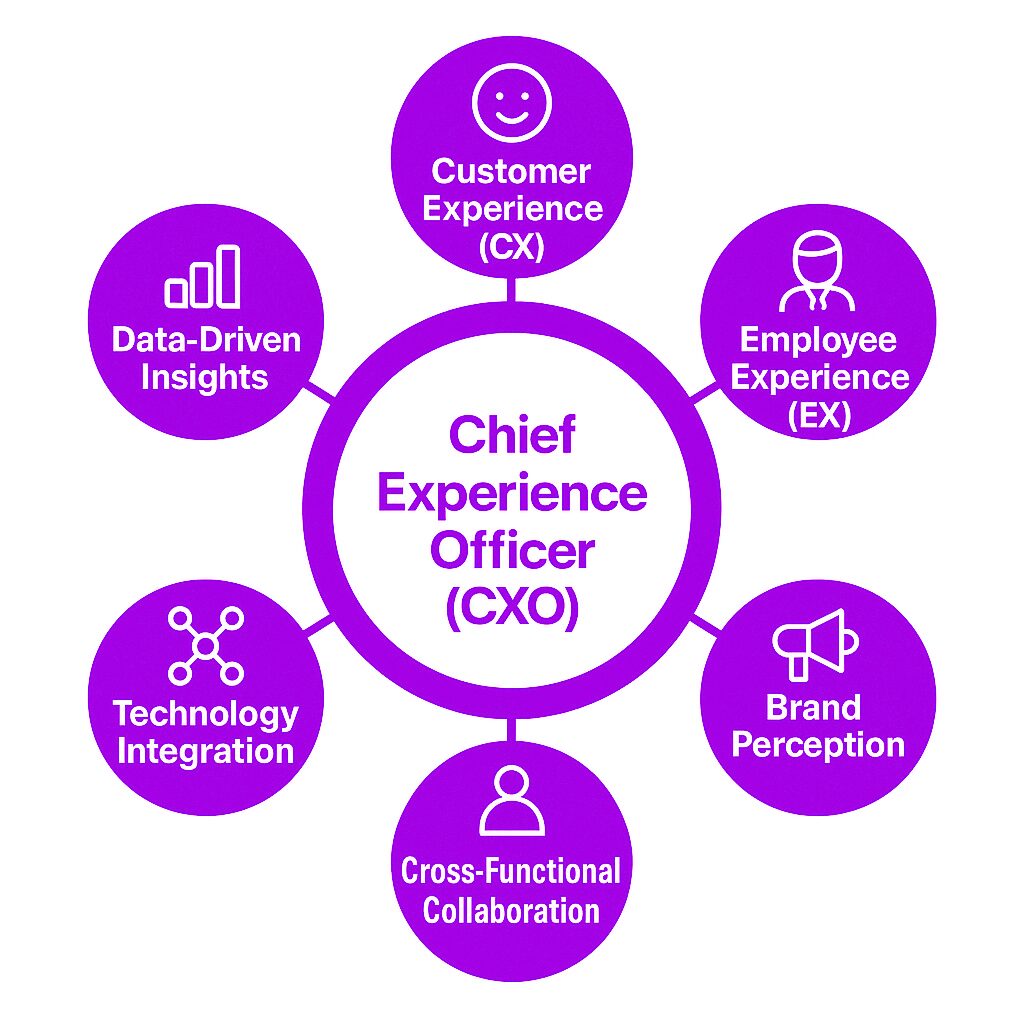
The CXO oversees various aspects of experience management, including customer service, employee engagement, and brand perception. Chief experience officers (CXOs) play a crucial role in enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty across various industries. Unlike traditional roles that focus on a single function, such as marketing or HR, the CXO integrates different departments to ensure a seamless experience across all touchpoints.
Key Responsibilities
-
Customer Experience (CX): Ensuring that customers have a positive interaction with the brand, from product discovery to post-purchase support.
-
Employee Experience (EX): Creating a workplace that fosters engagement, satisfaction, and productivity.
-
Brand Perception: Managing how the company is perceived externally and internally.
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Aligning departments like HR, marketing, IT, and sales to maintain a unified experience strategy.
-
Technology Integration: Leveraging digital tools to enhance user experience, such as AI chatbots, personalized recommendations, and automation.
-
Data Analysis: Using feedback, surveys, and analytics to identify pain points and improve processes.
Why Companies Need a CXO
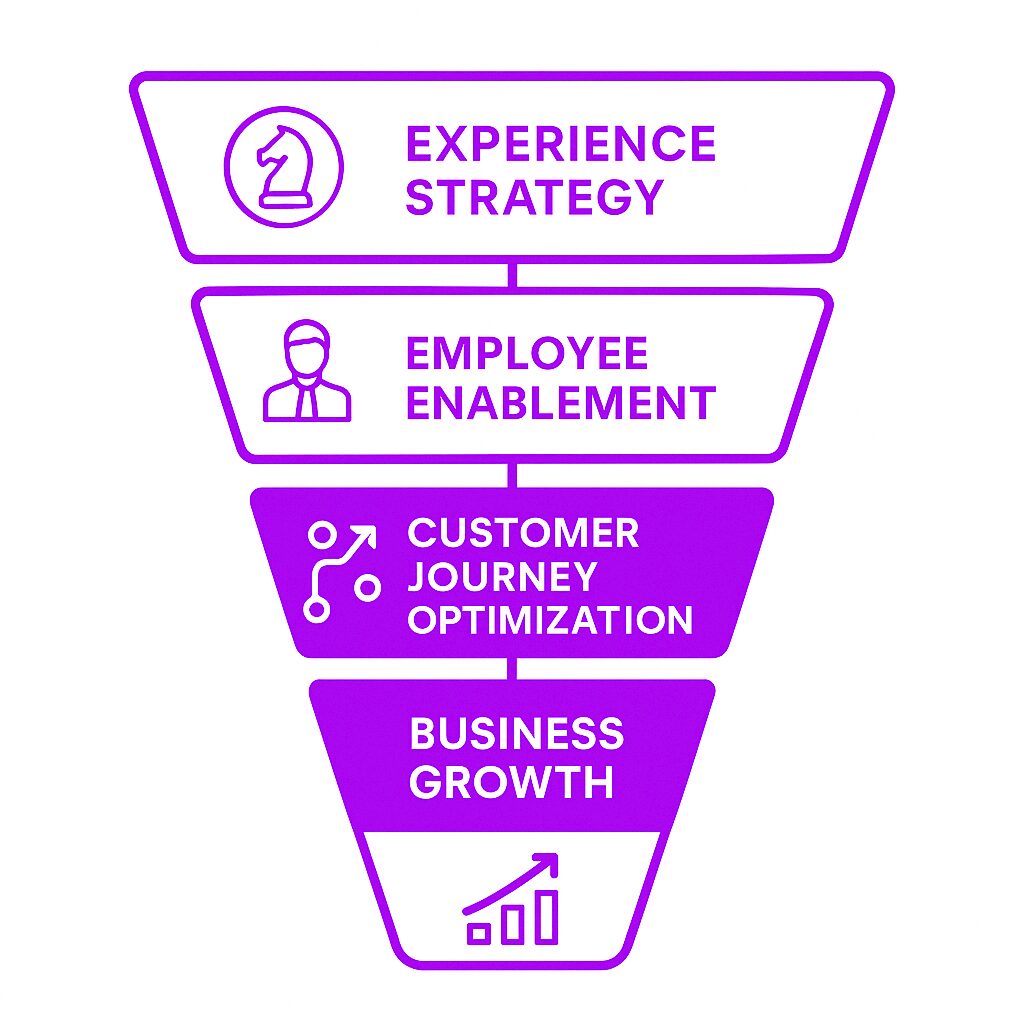
Customer expectations have changed. People no longer judge a company solely on its product or service—they evaluate the entire journey. A frustrating checkout process, slow customer support, or a lackluster work environment can drive people away. The CXO ensures that all these elements work together to create a seamless, enjoyable experience by focusing on the customer journey, which is critical in shaping customer experience strategies.
The Shift in Business Priorities
Traditionally, marketing, sales, and HR departments operated independently. The CXO role emerged to break down these silos and unify the approach to experience management. By developing customer-centric strategies, CXOs ensure that initiatives are aligned to optimize every touchpoint in the customer journey. A positive employee experience leads to better customer service, which strengthens brand loyalty.
How CXOs Drive Business Growth
A well-managed experience strategy can:
-
Increase customer retention by addressing pain points proactively.
-
Drive long-term business growth and a sustainable revenue stream by fostering customer loyalty.
-
Boost employee productivity by fostering a positive work environment.
-
Enhance brand reputation by ensuring consistent messaging and service quality.
-
Drive revenue growth through personalized experiences and customer satisfaction.
CXO vs. CMO
Differentiating Roles and Focus Areas
The Chief Experience Officer (CXO) and Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) are two distinct roles that often overlap in their responsibilities. However, they have different focus areas and priorities.
The CMO is primarily responsible for driving marketing strategy, which includes understanding the company’s position in the market, directing marketing campaigns, and overseeing branding strategies. The CMO’s focus is on promoting the company’s products or services to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
On the other hand, the CXO is responsible for driving the company’s overall customer experience strategy. This involves mapping customer journeys, overseeing the customer success and customer service teams, and digging into customer data analytics to inform decision-making processes. The CXO’s focus is on creating a seamless and personalized experience for customers across all touchpoints.
While the CMO is concerned with acquiring new customers, the CXO is focused on retaining existing customers and building long-term loyalty. The CXO’s role is more holistic, encompassing not only marketing but also customer service, product development, and employee experience.
In companies where both roles exist, the CMO and CXO must work closely together to ensure that marketing efforts align with the overall customer experience strategy. The CMO can provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, which the CXO can use to inform customer experience initiatives.
Ultimately, the CXO and CMO roles are complementary, and both are essential for creating a customer-centric organization. By understanding their different focus areas and priorities, companies can ensure that they are delivering a cohesive and effective customer experience.
The Challenges of Being a CXO
While the role of a CXO is crucial, it comes with its challenges. Customer experience management plays a vital role in maximizing customer engagement and satisfaction.
Common Obstacles
-
Measuring ROI: Unlike sales or marketing, the success of experience initiatives can be harder to quantify.
-
Organizational Resistance: Some executives may see the CXO role as redundant or overlapping with other leadership positions.
-
Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Experience improvements often require long-term investment, making it challenging to show immediate results.
-
Aligning Multiple Departments: Getting marketing, HR, IT, and sales to work together can be difficult.
How CXOs Overcome These Challenges
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: Using analytics to demonstrate the impact of experience improvements.
-
Clear Communication: Educating other executives on the value of experience management.
-
Small, Measurable Wins: Implementing quick, visible improvements to gain buy-in for larger projects.
The Key Components of Customer Experience Management
Customer Experience (CX)
Customers expect seamless, personalized interactions across all channels. The CXO ensures that every touchpoint—whether online, in-store, or through customer service—meets or exceeds expectations.
Employee Experience (EX)
Happy employees lead to happy customers. The CXO works closely with HR to create an engaging workplace that fosters collaboration, recognition, and growth.
Brand Experience (BX)
The way people perceive a brand is shaped by every interaction they have with it. A CXO ensures consistency in messaging, visuals, and customer interactions.
Qualities and Skills of a Successful CXO
Essential Attributes for Success
A successful Chief Experience Officer (CXO) possesses a unique combination of qualities and skills that enable them to drive exceptional customer and employee experiences. Some of the essential attributes of a successful CXO include:
-
Customer-Centric Mindset: A CXO must have a deep understanding of customer needs, preferences, and behaviors. They must be able to put themselves in the customer’s shoes and design experiences that meet their expectations.
-
Strategic Thinking: A CXO must be able to develop and implement customer experience strategies that align with the company’s overall business goals. They must be able to think critically and make data-driven decisions.
-
Collaboration and Communication: A CXO must be able to work effectively with cross-functional teams, including marketing, sales, customer service, and product development. They must be able to communicate complex ideas and strategies to stakeholders at all levels.
-
Emotional Intelligence: A CXO must be able to understand and manage their own emotions, as well as those of their team members and customers. They must be able to empathize with customers and design experiences that meet their emotional needs.
-
Data Analysis: A CXO must be able to analyze customer data and feedback to inform decision-making processes. They must be able to identify trends and patterns in customer behavior and develop strategies to address them.
-
Creativity and Innovation: A CXO must be able to think creatively and develop innovative solutions to customer experience challenges. They must be able to stay ahead of the curve and anticipate changing customer needs and preferences.
-
Leadership and Influence: A CXO must be able to inspire and motivate their team to deliver exceptional customer experiences. They must be able to influence stakeholders at all levels to prioritize customer experience initiatives.
By possessing these essential attributes, a CXO can drive business growth, improve customer satisfaction, and create a competitive advantage for their organization.
Industry Applications
Sectors Benefiting from a CXO
The Chief Experience Officer (CXO) role is highly adaptable and can be applied to various industries. Some sectors that can benefit from a CXO include:
-
Healthcare: A CXO in healthcare can focus on improving patient experiences, streamlining clinical workflows, and enhancing patient engagement.
-
Retail: A CXO in retail can focus on creating seamless omnichannel experiences, improving customer service, and developing loyalty programs.
-
Finance: A CXO in finance can focus on improving customer engagement, streamlining account opening processes, and enhancing online banking experiences.
-
Technology: A CXO in technology can focus on improving user experiences, developing intuitive product interfaces, and enhancing customer support.
-
Hospitality: A CXO in hospitality can focus on improving guest experiences, streamlining check-in processes, and enhancing loyalty programs.
In each of these sectors, a CXO can play a critical role in driving business growth, improving customer satisfaction, and creating a competitive advantage. By understanding the unique challenges and opportunities in each sector, a CXO can develop targeted strategies to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
In addition to these sectors, other industries that can benefit from a CXO include:
-
Education: Improving student experiences, streamlining enrollment processes, and enhancing online learning platforms.
-
Government: Improving citizen experiences, streamlining service delivery, and enhancing online engagement platforms.
-
Non-Profit: Improving donor experiences, streamlining fundraising processes, and enhancing online engagement platforms.
Ultimately, any organization that interacts with customers or stakeholders can benefit from a CXO. By prioritizing customer experience, organizations can drive business growth, improve customer satisfaction, and create a competitive advantage.
Best Practices for CXOs
-
Understand Your Audience: Regularly gather feedback through surveys, social listening, and data analysis.
-
Create a Unified Experience Strategy: Align all departments to maintain a consistent approach to customer and employee experience.
-
Invest in Technology: Use AI, automation, and data analytics to improve personalization and efficiency.
-
Measure Success: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track improvements in experience management.
-
Foster a Customer-Centric Culture: Train employees to prioritize experience in their daily interactions.
The Future of the CXO Role
As experience becomes a competitive differentiator, the CXO role will continue to evolve. Companies will invest more in AI-driven personalization, predictive analytics, and omnichannel experiences. The demand for experience-focused leadership will grow, making CXOs a critical part of the executive team.
Real-World Examples
-
Amazon: Uses AI to personalize recommendations, ensuring a seamless shopping experience.
-
Apple: Creates a premium in-store and online experience, reinforcing its brand value.
-
Google: Focuses on employee experience, offering perks that enhance job satisfaction and productivity.
Conclusion
The Chief Experience Officer plays a vital role in shaping how customers, employees, and stakeholders interact with a company. By focusing on a holistic approach to experience management, businesses can drive growth, enhance brand loyalty, and improve overall satisfaction. The CXO role is not just a trend—it’s a necessary evolution in modern business strategy.