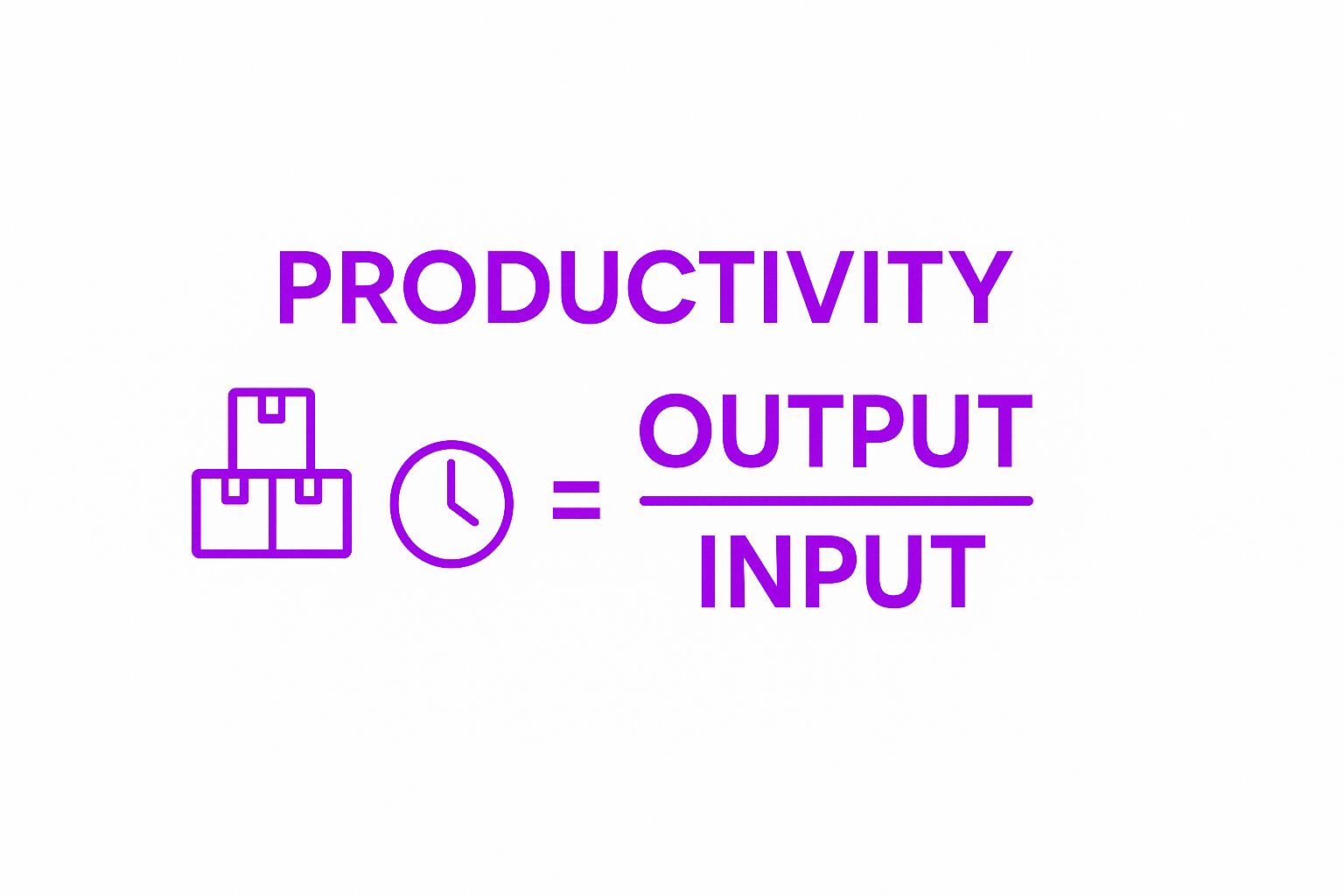
Employee productivity is a measure of how effectively a worker completes tasks in a given timeframe. To accurately calculate employee productivity, it is essential to use formulas and metrics that consider both output and input, providing a holistic view of performance. Businesses rely on productivity metrics to evaluate performance, allocate resources, and identify areas for improvement.
Unlike performance, which looks at overall job success, productivity focuses on efficiency. A highly productive employee gets more done with less wasted time, effort, and resources. This is critical in fast-paced environments where output directly impacts revenue and competitiveness.
Why Employee Productivity Matters
Every company, regardless of size or industry, depends on employee productivity to thrive. Emphasizing employee health through workplace health programs can significantly reduce illness and enhance overall employee wellbeing, leading to higher productivity. Higher productivity means more output, better customer service, and increased profits. On the flip side, low productivity leads to delays, wasted resources, and lost opportunities.
A productive workforce can drive innovation, keep customers happy, and create a more positive work environment. Companies with high productivity levels tend to have engaged employees who feel valued and motivated to contribute.
Factors That Affect Employee Productivity
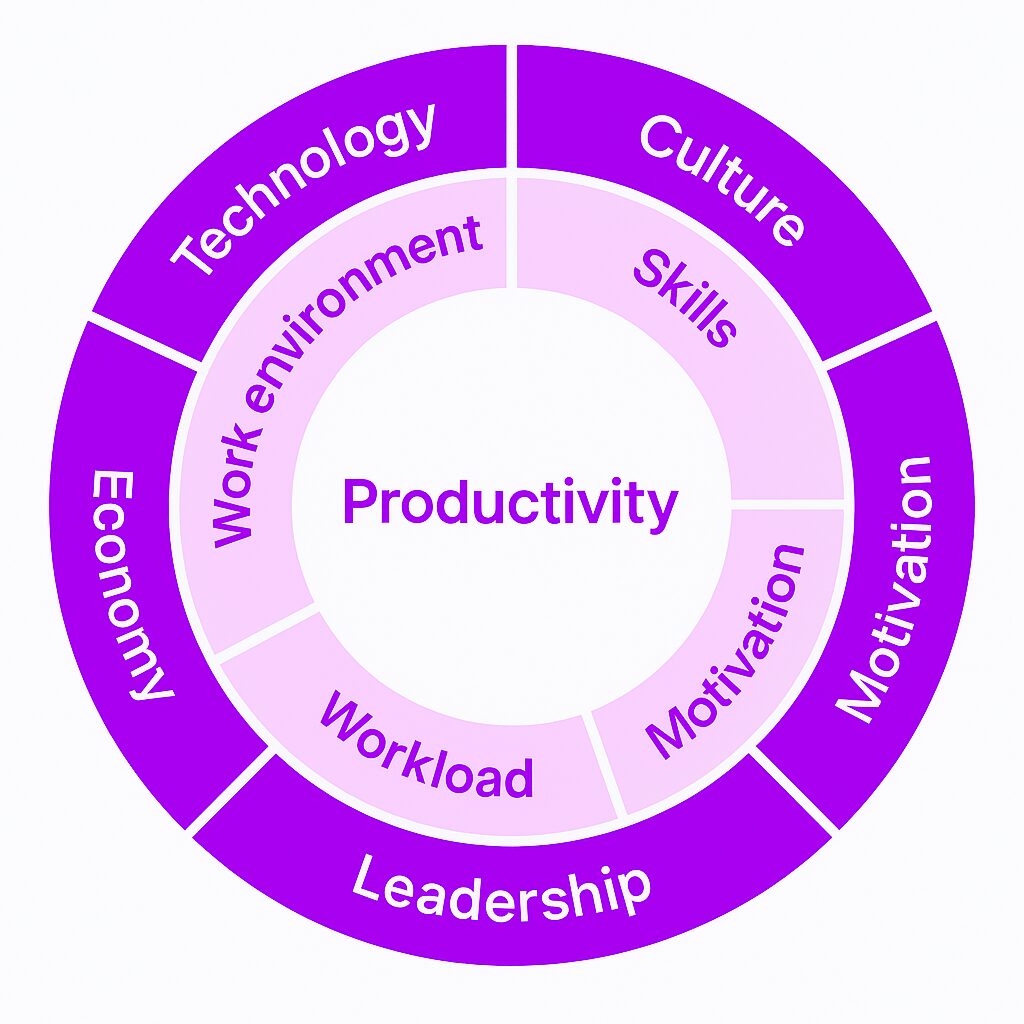
Many factors influence productivity, both positively and negatively. Some are within an employee’s control, while others depend on management, workplace culture, or external conditions. Automating data collection and analysis can significantly improve the measurement of employee productivity, providing more efficient and accurate insights through reliable employee productivity data.
Internal Factors:
-
Work environment: A cluttered, noisy, or uncomfortable workspace can reduce focus.
-
Skills and training: Employees who lack the right skills struggle to complete tasks efficiently.
-
Motivation: Recognition, career growth, and meaningful work contribute to engagement and enhance an employee’s productivity.
-
Workload: Too much or too little work can lead to stress or disengagement.
External Factors:
-
Technology: Outdated systems or slow software can hinder employees productivity by causing unnecessary delays and distractions.
-
Company culture: A toxic or poorly structured work environment discourages effort.
-
Leadership: Managers who set clear expectations and support their teams see higher productivity.
-
Economic conditions: Job market trends and industry shifts can affect morale and focus.
How to Measure Employee Productivity
Measuring employee productivity through various methods such as feedback, benchmarking, and key performance indicators (KPIs) helps businesses understand where improvements are needed. While output is a key factor, focusing solely on numbers can be misleading. Quality, engagement, and the ability to meet deadlines also play a role.
Common Productivity Metrics:
-
Output per employee – The amount of work completed in a given time.
-
Task completion rate – The percentage of tasks finished within deadlines.
-
Revenue per employee – The financial impact of each worker’s efforts.
-
Time tracking – Hours spent on tasks versus results achieved.
-
Customer satisfaction scores – How well employees meet client needs.
Companies should use a mix of these metrics rather than relying on just one. Context matters—high output with poor quality is not truly productive.
Key Strategies to Improve Productivity
Boosting employee productivity requires a mix of good leadership, smart processes, and the right tools. Here are some practical strategies:
Employee productivity improvement is essential for modern organizations, and various strategies and motivational tactics can be implemented to enhance it effectively.
1. Set Clear Goals
Employees work best when they know what’s expected. Setting specific, measurable goals can help increase employee productivity by providing clear direction and focus. Goals should be specific, measurable, and aligned with business objectives. Vague expectations lead to confusion and wasted effort.
2. Encourage Autonomy
Micromanagement slows things down. Giving employees control over how they complete tasks boosts motivation and efficiency. Trust them to make decisions and find the best ways to get things done.
3. Provide Training and Development
Workers who feel competent and skilled are more confident and productive. Regular training helps employees stay up to date and perform at their best.
4. Use the Right Tools
Invest in technology that simplifies tasks and removes bottlenecks. Using technology to collect and analyze employee productivity data can lead to more efficient and accurate insights. Project management software, automation tools, and collaboration platforms can reduce repetitive work and free up time for more important tasks.
5. Reduce Unnecessary Meetings
Meetings can be a major time drain. Only schedule them when necessary, keep them short, and ensure there’s a clear agenda. Asynchronous communication tools like email or project boards can replace many routine meetings.
6. Foster a Positive Work Environment
Happy employees are more productive. Promoting employee health through workplace wellness programs can significantly reduce illness and enhance overall employee wellbeing. A workplace that values respect, collaboration, and recognition encourages people to put in their best effort.
7. Encourage Breaks and Work-Life Balance
Burnout kills productivity. Encouraging regular breaks and respecting personal time helps employees stay focused and engaged.
The Role of Leadership in Employee Productivity
Leaders play a crucial role in driving employee productivity within an organization. Their actions, behaviors, and decisions have a significant impact on the work environment, employee engagement, and overall productivity.
Leaders as Role Models
Leaders must model the behavior they expect from their employees. This means demonstrating a strong work ethic, being transparent, and leading by example. When leaders prioritize productivity, employees are more likely to follow suit. Leaders can also encourage a culture of accountability by setting clear goals, expectations, and consequences.
Empowering Employees
Empowering employees is essential for improving productivity. Leaders can do this by providing autonomy, resources, and support. When employees feel trusted and valued, they are more likely to take ownership of their work and strive for excellence. Leaders can also encourage employee growth and development by providing opportunities for training, mentorship, and feedback.
Creating a Culture of Productivity
A culture of productivity is essential for driving employee engagement and overall productivity. This culture is built on a foundation of trust, respect, and open communication.
Reinforcing Vision and Goals
Reinforcing the organization’s vision and goals is critical for creating a culture of productivity. Leaders must communicate the organization’s purpose, mission, and objectives clearly and consistently. This helps employees understand how their work contributes to the organization’s success and motivates them to work towards common goals.
By creating a culture of productivity, leaders can foster an environment where employees feel motivated, engaged, and empowered to perform at their best. This, in turn, drives overall productivity, job satisfaction, and employee experience.
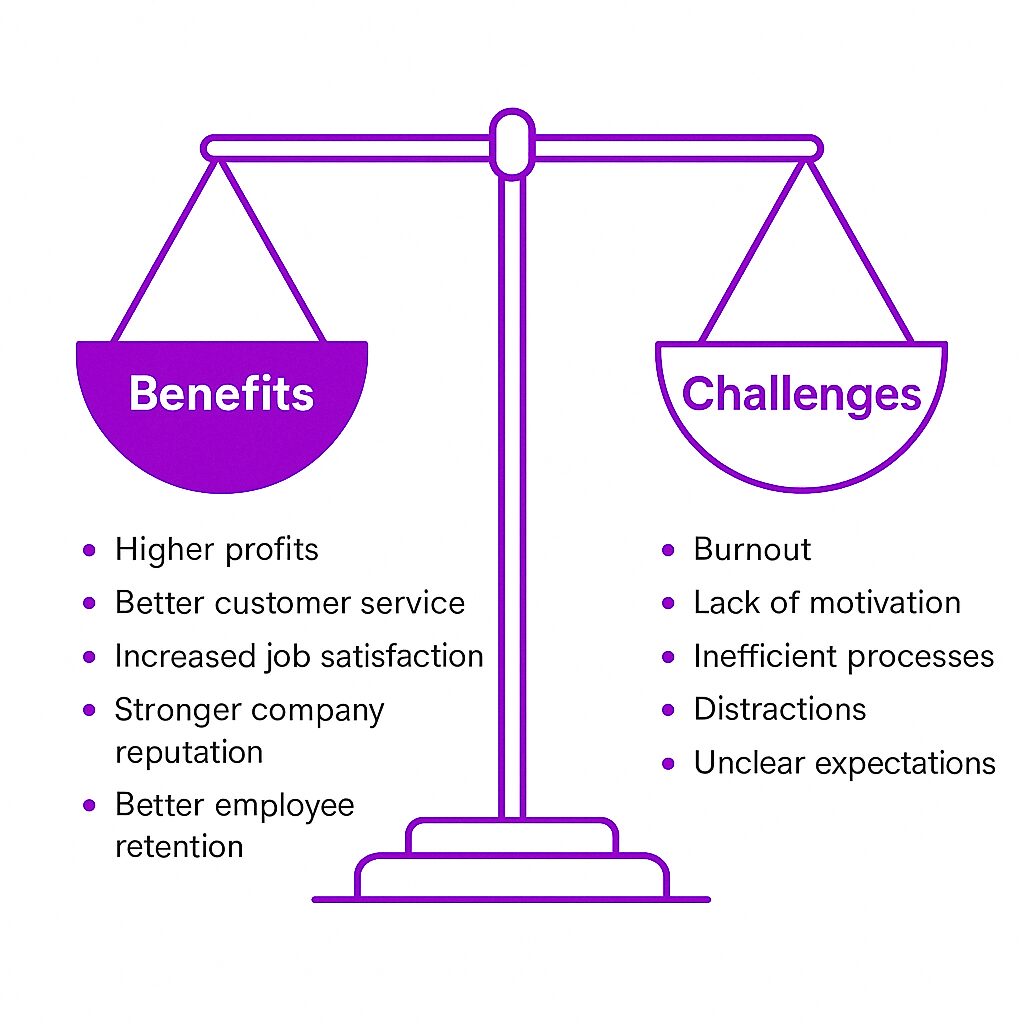
Benefits of High Employee Productivity
A productive workforce leads to several advantages: Productive employees are essential drivers of business success, enhancing profitability and customer service.
-
Higher profits: More output with the same resources improves the bottom line.
-
Better customer service: Employees who work efficiently can respond to customer needs faster.
-
Increased job satisfaction: Completing meaningful work keeps employees engaged.
-
Stronger company reputation: High productivity makes a business more competitive in its industry.
-
Better employee retention: Workers are more likely to stay at a company where they feel effective and valued.
Challenges That Can Hinder Productivity
Even with the best strategies, productivity can suffer due to common workplace issues. Higher labor productivity can significantly impact employee burnout and overall business performance, as factors like remote work and investments in technology influence productivity levels:
-
Burnout: Overworking employees reduces efficiency in the long run.
-
Lack of motivation:Without recognition or growth opportunities, employees may lose interest.
-
Inefficient processes: Poor workflows and redundant tasks slow down work.
-
Distractions: Emails, notifications, and office noise can disrupt focus.
-
Unclear expectations: Employees who don’t know what’s expected waste time figuring it out.
Related Concepts
Employee Engagement
Engaged employees are more productive because they feel connected to their work. Engagement goes beyond productivity by fostering loyalty and enthusiasm.
Time Management
Good time management helps employees prioritize tasks and avoid wasted effort. Productivity improves when workers focus on high-impact activities instead of low-value busywork.
Workplace Well-being
Physical and mental health affect an employee’s ability to perform well. Workforce productivity can be significantly enhanced by implementing strategies such as health programs, technology empowerment, and establishing benchmarks tailored to measure and manage productivity. A workplace that supports well-being leads to higher productivity and reduced absenteeism.
Remote Work Productivity
With more people working remotely, businesses must find ways to keep teams productive outside the office. Measuring workplace productivity through both quantitative and qualitative factors is crucial in remote work settings. Clear communication, reliable technology, and flexible policies can make remote work as effective as in-person work.
Real-World Examples
-
Google invests in employee well-being and flexible work policies, leading to high engagement and productivity. Google’s strategies to increase employee productivity through well-being and flexible work policies have led to high engagement and productivity.
-
Amazon uses automation to streamline tasks, improving efficiency in logistics and customer service.
-
A small marketing agency reduced meetings and switched to asynchronous communication, cutting wasted time and boosting output.
Final Thoughts
Employee productivity is about working smarter, not just harder. Businesses that support employees with clear goals, good tools, and a positive work culture see better results. Measuring productivity effectively and addressing common challenges can make a significant difference in overall performance. By focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can create a workforce that is both efficient and engaged.