What is Employee Well-Being?
Employee wellbeing refers to the overall state of an employee’s mental, physical, and emotional health in the workplace, highlighting its multi-faceted nature. It goes beyond basic job satisfaction and looks at how work affects a person’s quality of life. A well-structured employee well-being strategy ensures that employees feel supported, valued, and motivated in their roles.
Organizations that prioritize employee well-being see improvements in engagement, productivity, and retention. When employees feel their needs are met, they contribute more effectively to business success.
Definition and Importance of Employee Well-Being
Employee well-being is a crucial aspect of an organization’s success, encompassing the physical, emotional, and mental health of its employees. It is essential for companies to prioritize employee well-being, as it directly impacts productivity, retention, and overall job satisfaction. When employees feel supported and valued, they are more likely to be engaged, motivated, and committed to their work. In contrast, neglecting employee well-being can lead to burnout, absenteeism, and turnover, ultimately affecting the organization’s bottom line.
By fostering a culture that promotes mental health and overall well-being, companies can create a more positive and productive work environment. This holistic approach not only benefits employees but also drives business success, making employee well-being a vital component of any effective business strategy.
The 5 Pillars of Employee Well-Being

The five pillars of employee well-being are essential for creating a supportive and thriving workplace. These pillars include:
-
Career Well-being: Employees feel engaged and satisfied with their work, utilizing their strengths and skills to contribute to the organization’s success. Providing opportunities for career growth and development is key to maintaining high levels of career well-being.
-
Social Well-being: Employees have positive relationships with their colleagues, feel supported, and are part of a cohesive team. Encouraging team-building activities and fostering an inclusive culture can enhance social well-being.
-
Financial Well-being: Employees feel secure in their financial situation, with access to fair compensation, benefits, and opportunities for growth. Offering financial literacy programs and competitive salaries can help support financial well-being.
-
Physical Well-being: Employees prioritize their physical health, with access to wellness programs, healthy work environments, and opportunities for self-care. Providing ergonomic office furniture and promoting regular movement can improve physical well-being.
-
Emotional Well-being: Employees feel supported in their mental health, with access to resources, tools, and a culture that promotes emotional intelligence and resilience. Offering counseling services and encouraging open conversations about mental health can enhance emotional well-being.
By addressing these five pillars, organizations can create a comprehensive well-being program that supports all aspects of employee health and satisfaction.
Why Employee Well-Being Matters
Employee well-being is essential for both individuals and organizations. When employees feel physically and mentally healthy, they perform better, collaborate more effectively, and remain loyal to their companies. Conversely, when well-being is neglected, businesses experience higher turnover, lower productivity, and increased absenteeism.
Organizations can take specific steps to improve employee wellbeing, such as enhancing mental health services and implementing effective management practices.
The Impact of Poor Well-Being
-
Increased stress and burnout
-
Higher turnover rates
-
Lower engagement and motivation
-
Reduced job performance
-
Increased health-related absences
Companies that fail to address well-being may struggle with a disengaged workforce and a damaged employer reputation. On the other hand, businesses that invest in well-being initiatives create environments where employees can thrive.
Increases Employee Retention and Reduces Turnover
Investing in employee well-being is crucial for reducing turnover and increasing retention. When employees feel valued and supported, they are more likely to stay with the organization, reducing the costs associated with recruitment and training. A study by Gallup found that employees who are engaged and thriving are 32% less likely to be watching for or actively seeking another job.
By implementing well-being initiatives that address the diverse needs of employees, companies can foster a loyal and committed workforce. This not only enhances employee well-being but also contributes to long-term business success by maintaining a stable and experienced team.
Key Components of Employee Well-Being
Physical Well-Being
Physical well-being includes overall health, fitness, and workplace ergonomics. Employees need access to a safe, comfortable work environment and resources to maintain their physical health. Improving workplace conditions and addressing occupational health can enhance employee morale and productivity.
Ways to support physical well-being:
-
Providing ergonomic office furniture
-
Encouraging regular movement and breaks
-
Offering wellness programs and gym memberships
-
Supporting access to healthcare services
Mental and Emotional Well-Being
Mental and emotional well-being focuses on managing stress, anxiety, and psychological safety in the workplace. Employees who feel emotionally secure and supported are more likely to be engaged and productive.
Workplace conditions significantly impact mental health, with many workers experiencing at least one mental health challenge due to factors like the pandemic and increased workload.
Ways to support mental and emotional well-being:
-
Providing access to counseling or mental health services
-
Encouraging open conversations about mental health
-
Reducing workplace stress through reasonable workloads
-
Offering mindfulness or resilience training programs
Social Well-Being
Social well-being includes workplace relationships, team dynamics, and overall company culture. Employees thrive in workplaces where they feel connected and supported. A supportive environment fosters employee engagement and productivity, addressing both work-related and personal challenges to support employee wellbeing.
Ways to support social well-being:
-
Encouraging team-building activities
-
Fostering an inclusive and diverse culture
-
Providing mentorship programs
-
Creating spaces for informal interactions
Financial Well-Being
Financial well-being relates to an employee’s ability to manage financial stress and plan for the future. Employees who feel financially stable are less likely to experience anxiety and distraction at work.
Ways to support financial well-being:
-
Offering competitive salaries and benefits
-
Providing financial literacy programs
-
Assisting with retirement planning and savings options
-
Supporting employees with emergency financial assistance programs
Professional Well-Being
Professional well-being focuses on career growth, job satisfaction, and skill development. Employees who see opportunities for advancement and skill-building are more likely to stay engaged.
Ways to support professional well-being:
-
Offering career development programs
-
Providing regular feedback and coaching
-
Encouraging internal mobility and promotions
-
Supporting continued education and certifications
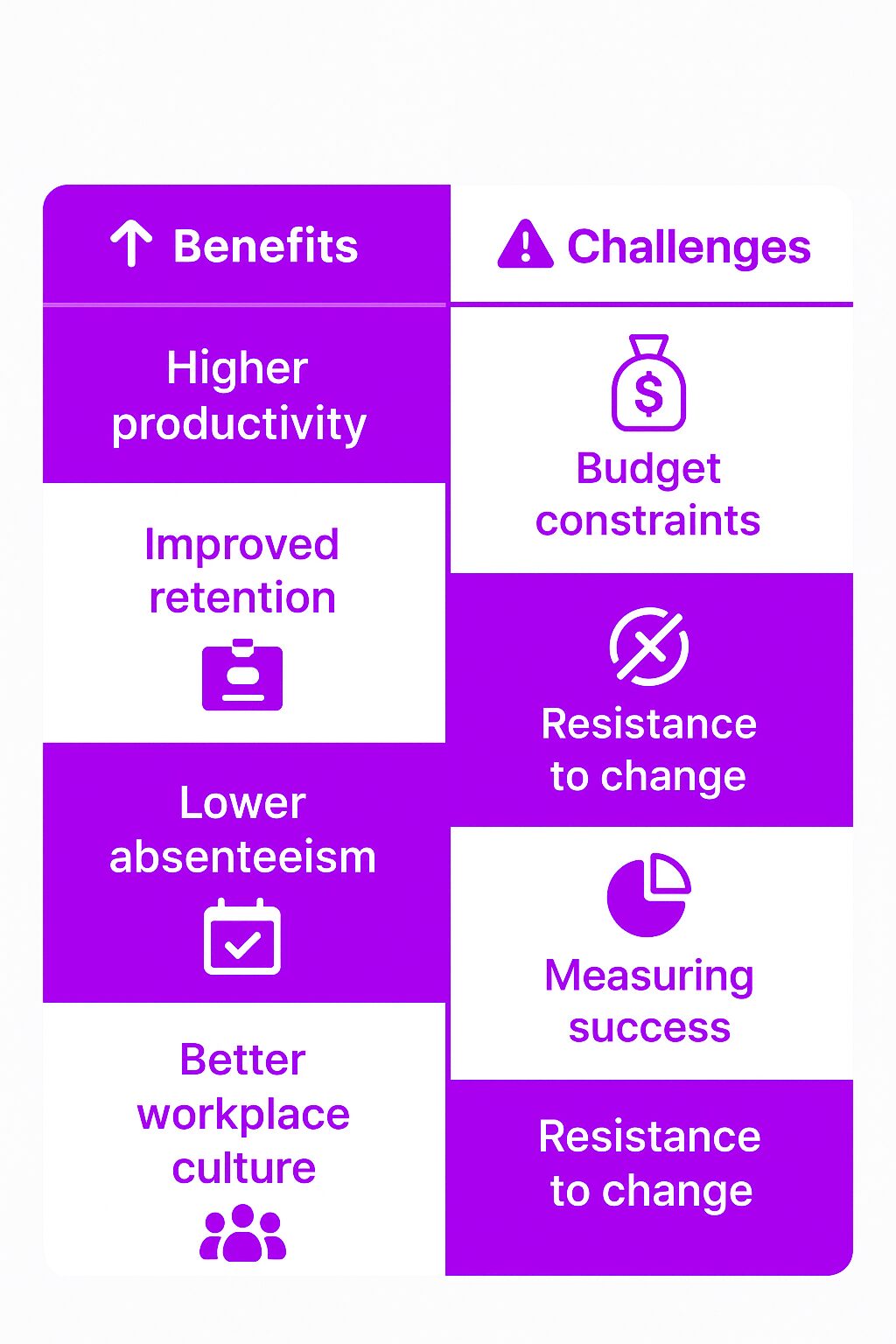
Benefits of Employee Well-Being Initiatives
Organizations that invest in employee well-being experience significant benefits:
-
Higher Productivity – Employees perform better when they feel healthy and supported.
-
Improved Retention – Workers are more likely to stay with companies that care about their well-being.
-
Lower Absenteeism – Healthier employees take fewer sick days.
-
Better Workplace Culture – Well-being programs create a more positive, engaged workforce.
-
Stronger Employer Brand – Companies with strong well-being initiatives attract top talent.
Implementing a wellness program is crucial as it enhances employee health and morale, leading to reduced absenteeism and healthcare costs.
Reduces Absenteeism and Healthcare Expenses
Investing in employee well-being can also reduce absenteeism and healthcare expenses. When employees prioritize their physical and mental health, they are less likely to take sick days or require medical attention. A study by the American Psychological Association found that employees who prioritize their well-being are 25% less likely to experience chronic stress, which can lead to absenteeism and healthcare expenses.
By promoting a culture of health and well-being, organizations can minimize the financial impact of health-related absences and medical costs. This proactive approach not only benefits employees but also supports the overall financial health of the company.
Less Burnout and Improved Employee Engagement
Employee well-being is also crucial for reducing burnout and improving employee engagement. When employees feel supported and valued, they are less likely to experience burnout and more likely to be engaged and motivated. A study by Gallup found that employees who are engaged and thriving are 43% more likely to report high levels of well-being, which is linked to improved employee engagement and reduced burnout.
By implementing strategies that support employee well-being, companies can create a more resilient and motivated workforce. This not only enhances employee satisfaction but also drives higher levels of productivity and engagement, contributing to the overall success of the organization.
Challenges in Implementing Employee Well-Being Programs
Budget Constraints
Some organizations struggle with allocating resources to well-being initiatives. However, investing in employee well-being leads to long-term cost savings through increased productivity and retention.
Developing an employee wellbeing strategy is crucial to prioritize necessary interventions and leverage advanced research and insights.
Resistance to Change
Employees or management may resist new well-being initiatives, especially if they require adjustments to existing work habits.
Measuring Success
Unlike traditional business metrics, well-being is difficult to quantify. Organizations must find effective ways to track progress, such as employee surveys and well-being assessments.
Best Practices for Employee Well-Being
Promote a Healthy Work-Life Balance
Companies should encourage employees to disconnect from work and prioritize their personal lives. This can include:
-
Flexible work arrangements
-
Encouraging employees to use their paid time off
-
Setting clear boundaries for after-hours work communication
Encourage Open Conversations About Well-Being
Creating a culture where employees feel comfortable discussing their well-being is essential. Leadership should:
-
Regularly check in with employees
-
Provide mental health resources
-
Lead by example in prioritizing well-being
Implement a Holistic Well-Being Program
A strong well-being program should cover all aspects of employee well-being, including physical, mental, social, financial, and professional well-being.
Managers play a crucial role in supporting employee wellbeing, and effective management can greatly influence an employee’s decision to stay with the organization.
Use Technology to Support Well-Being
Digital tools can make well-being programs more accessible. Examples include:
-
Employee wellness apps
-
Virtual fitness programs
-
AI-driven mental health support
-
Online learning platforms for career development
Recognize and Reward Employees
Recognition plays a vital role in well-being. Employees feel valued when their contributions are acknowledged. Companies should:
-
Provide regular feedback and praise
-
Offer meaningful rewards and incentives
-
Celebrate employee milestones and achievements
Related Sub-Concepts
Employee Engagement vs. Employee Well-Being
Employee engagement focuses on motivation and commitment, while well-being covers the holistic health of employees. High well-being leads to better engagement.
Workplace Wellness Programs
These are structured initiatives designed to promote health and well-being, including fitness challenges, stress management workshops, and mental health support.
Burnout Prevention
Burnout occurs when employees experience prolonged stress. Preventing burnout requires workload management, mental health support, and flexible work arrangements.
Work-Life Integration vs. Work-Life Balance
Work-life balance separates personal and work life, while work-life integration blends the two. Both approaches aim to reduce stress and improve well-being.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Google provides extensive employee well-being programs, including on-site fitness centers, wellness coaching, and mindfulness training.
Salesforce
Salesforce offers mental health days and employee assistance programs to support emotional well-being.
Patagonia
Patagonia promotes work-life balance by offering on-site childcare, flexible schedules, and outdoor wellness activities.
The Future of Employee Well-Being
As the workplace evolves, employee well-being strategies must adapt. Companies will need to:
-
Address remote work challenges by ensuring employees feel connected and supported.
-
Integrate AI-driven well-being tools for personalized employee support.
-
Expand mental health initiatives to meet growing employee needs.
Developing an evolving employee wellbeing strategy is crucial to address remote work challenges, integrate AI-driven tools, and expand mental health initiatives.
Organizations that prioritize well-being will create healthier, more engaged, and more productive workplaces. By focusing on holistic well-being strategies, companies can enhance employee satisfaction and long-term business success.