What is Corporate Communications?
Corporate communications refers to the process of managing and guiding all internal and external messaging within a company. It ensures that the right information reaches employees, customers, investors, and the public. At its core, it is about maintaining transparency, protecting brand reputation, and fostering trust. It involves everything from internal memos and press releases to marketing campaigns and social media updates.
The corporate communications department is responsible for constructing a favorable brand image, maintaining uniform communication, supporting stakeholder engagement, and effectively managing crises to protect and enhance the company’s reputation.
Every company communicates, whether intentionally or not. Without a clear corporate communication strategy, messaging becomes inconsistent, leading to confusion and potential damage to reputation. By managing communications effectively, organizations ensure that their voice remains strong, unified, and aligned with business goals.
Why Corporate Communications Matters
Companies need to be heard. Employees must understand company objectives. Customers expect clear messaging. Investors require transparency. Poor communication leads to misunderstandings, decreased trust, and inefficiencies.
Corporate communication functions are essential tasks managed by the communications department to engage both internal and external audiences. These functions involve specialists working together to support the company’s overarching communication goals and strategies.
A strong corporate communication strategy helps organizations:
-
Maintain Reputation – Clear messaging fosters credibility.
-
Engage Employees – Informed employees perform better.
-
Strengthen Customer Trust – Transparent businesses retain customers.
-
Handle Crises – A prepared response limits damage.
-
Align Business Goals – Messaging remains consistent across departments.
Key Components of Corporate Communications
Internal Communication
Employees are the backbone of any business. Keeping them informed is critical. Effective employee communication ensures that employees understand company goals, policies, and changes. It also fosters a sense of belonging and engagement.
Common internal communication methods include:
-
Company Newsletters – Regular updates on company progress.
-
Internal Memos – Announcements and operational updates.
-
Town Hall Meetings – Leadership discussions with employees.
-
Collaboration Tools – Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and intranet systems facilitate communication.
-
Employee Surveys – Gathering feedback to improve engagement.
External Communication
How a company presents itself to the outside world affects its reputation. External communication involves interactions with customers, media, investors, and the public. It ensures messaging is clear, professional, and aligned with the brand.
Effective customer communications are crucial for engaging customers and enhancing loyalty, often involving collaboration between communication and marketing professionals to create targeted messaging and materials that meet customer needs.
Examples include:
-
Press Releases – Announcing major company news.
-
Public Relations (PR) – Managing relationships with media outlets.
-
Marketing Campaigns – Advertising and brand messaging.
-
Investor Communications – Keeping shareholders informed.
-
Crisis Management Statements – Handling negative press effectively.
Crisis Communication
No company is immune to challenges. How a business responds to crises determines its long-term success. Crisis communication involves planning, rapid response, and transparency to minimize damage.
Key steps in crisis communication:
-
Acknowledge the Issue – Delay worsens public perception.
-
Provide Facts – Misinformation spreads quickly. Offer clarity.
-
Take Responsibility – Admit mistakes when necessary.
-
Outline Action Plans – Show commitment to resolution.
-
Monitor Public Sentiment – Adjust messaging based on reactions.
Marketing and Brand Communication
Marketing and corporate communication often overlap. Marketing focuses on promoting products or services, while corporate communication manages brand perception. Both need to work together for consistency. Internal and external support play a crucial role in forming a comprehensive communication strategy, helping organizations promote their brand and minimize discrepancies.
Examples:
-
Social Media Messaging – Ensuring posts align with company values.
-
Advertising Strategies – Reinforcing brand identity.
-
Customer Communication – Handling inquiries and complaints professionally.
-
Content Marketing – Blogs, videos, and articles that reflect company values.
Leadership Communication
Executives and managers set the tone for corporate communication through effective management communication. Their ability to communicate clearly influences company culture and employee engagement.
Best practices for leadership communication:
-
Be transparent about company challenges and successes.
-
Encourage open dialogue with employees.
-
Use storytelling to make messages more relatable.
-
Provide clear direction and expectations.
Corporate Identity and Branding
Corporate identity and branding are pivotal elements of corporate communication, serving as the foundation for a company’s image and reputation in the market. A robust corporate identity is essential for building trust and credibility with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and investors. It involves creating a unique and consistent visual identity—comprising logos, color schemes, and typography—that reflects the company’s values and mission.
Effective corporate branding differentiates a company from its competitors and establishes a strong market presence. It is closely linked to corporate reputation, as a strong brand can help build a positive reputation and vice versa. Corporate communications professionals play a crucial role in developing and maintaining a company’s corporate identity and branding. They collaborate with marketing and design departments to ensure that all communication materials, including websites, social media, and advertising, are consistent with the company’s brand identity.
A well-developed corporate identity and branding strategy can drive business growth, increase customer engagement, and improve employee morale. By presenting a unified and professional image, companies can foster a sense of trust and loyalty among their stakeholders, ultimately contributing to long-term success.
Benefits of Corporate Communications
Improves Brand Reputation
A company’s image depends on how well it communicates. Positive, clear, and consistent messaging builds trust. A poorly managed message damages credibility.
Strengthens Employee Engagement
When employees understand company goals, they feel more connected. Strong internal communication leads to higher morale, productivity, and retention.
Enhances Crisis Management
Businesses face setbacks. A strong communication strategy ensures they respond swiftly and effectively, preventing long-term reputational damage.
Boosts Customer Trust
Customers expect clear and honest communication. Providing timely updates, responding to concerns, and maintaining transparency fosters loyalty.
Aligns Business Objectives
Every department must work towards the same goals. Corporate communication ensures that marketing, HR, leadership, and operations share a unified message.
Corporate Reputation and Responsibility
Corporate reputation and responsibility are critical components of corporate communication, shaping a company’s credibility and trustworthiness in the market. A company’s reputation is influenced by its actions, decisions, and communication, significantly impacting its bottom line. Corporate responsibility involves taking ownership of the social and environmental impacts of a company’s operations and activities.
Effective corporate responsibility strategies build trust and credibility with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and investors. Corporate communications professionals play a key role in developing and maintaining a company’s corporate reputation and responsibility. They work closely with departments such as sustainability and community relations to ensure that all communication materials, including reports and statements, are accurate and transparent.
A well-developed corporate reputation and responsibility strategy can drive business growth, increase customer engagement, and improve employee morale. These elements are closely linked to corporate identity and branding, as a strong brand can help build a positive reputation and vice versa. By demonstrating a commitment to ethical practices and transparent communication, companies can enhance their reputation and foster long-term success.
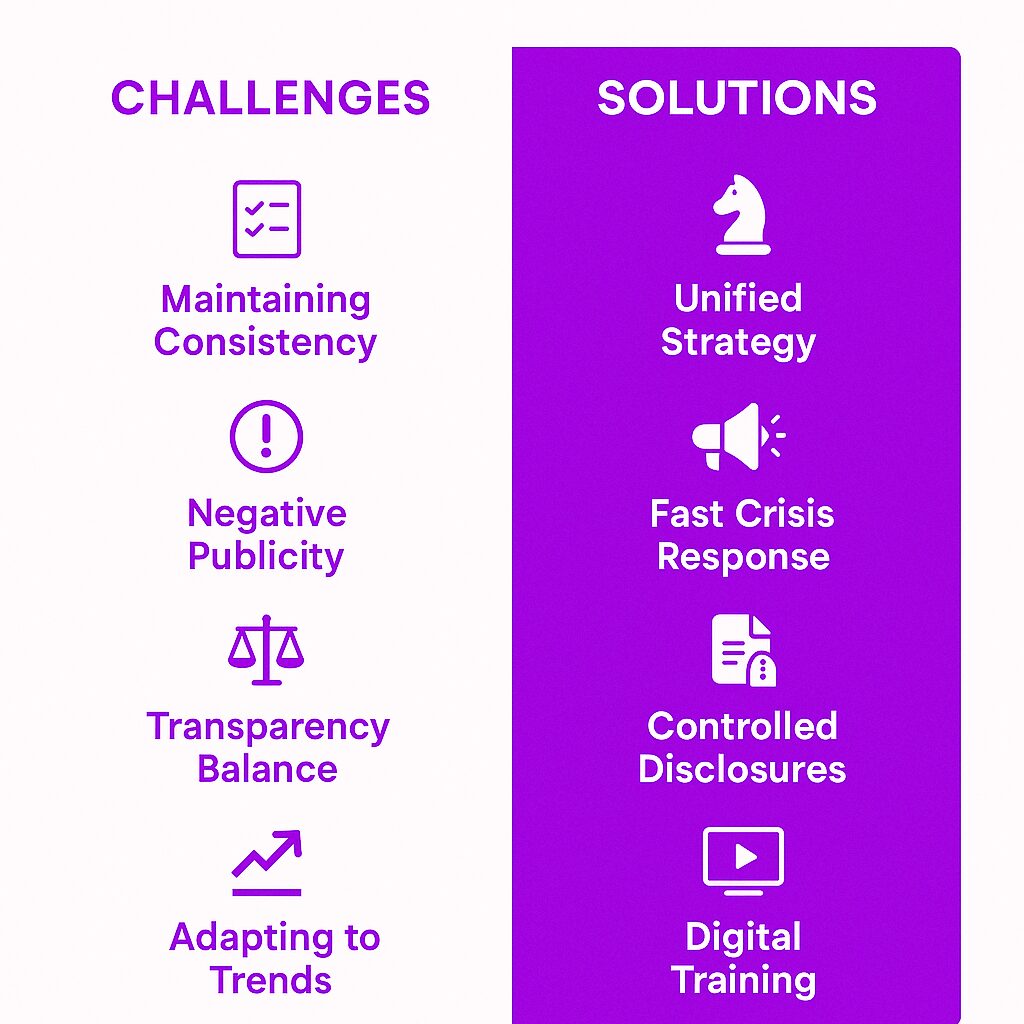
Challenges in Corporate Communications
Maintaining Consistency
Large organizations struggle to keep messaging uniform across teams, regions, and communication channels.
Handling Negative Publicity
Social media amplifies negative news. Companies must respond quickly, honestly, and strategically to minimize harm.
Balancing Transparency and Confidentiality
Some information must be shared, while other details remain confidential. Striking the right balance is crucial.
Adapting to Evolving Communication Trends
Digital platforms change how businesses communicate. Companies must stay ahead of trends, from video content to real-time engagement tools.
Practical Strategies for Effective Corporate Communications
Develop a Clear Communication Strategy
A structured approach ensures consistency. Identify key messages, target audiences, and the best communication channels for each situation.
A corporate communications team plays a pivotal role in achieving these communication goals by facilitating communication across all levels, engaging both internal and external audiences, and driving overall brand awareness and stakeholder interaction.
Use Multiple Communication Channels
Different audiences prefer different methods. A mix of email, video, social media, and face-to-face interactions maximizes reach.
Train Employees on Communication Best Practices
Employees are brand representatives. Providing media training, public speaking workshops, and writing guidelines improves company-wide messaging.
Implement Crisis Communication Plans
Preparation prevents panic. Define roles, create response templates, and rehearse scenarios to handle crises effectively.
Leverage Technology
Tools like intranet platforms, AI-driven chatbots, and automated email sequences improve communication efficiency and accessibility.
Careers in Corporate Communications
A career in corporate communications offers a wide range of opportunities for professionals to develop their skills and expertise in communication, marketing, and public relations. Corporate communications professionals play a critical role in shaping a company’s image and reputation, working across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and technology.
The role of a corporate communications professional typically involves developing and implementing communication strategies, creating content, and managing media relations. These professionals must have strong writing, speaking, and presentation skills, as well as the ability to work effectively in a team environment. A bachelor’s degree in communications, marketing, or a related field is typically required for a career in corporate communications. Many professionals also pursue advanced degrees, such as a master’s in business administration (MBA) or a master’s in communications.
The salary range for corporate communications professionals can vary widely depending on the industry, location, and level of experience. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for public relations specialists, which includes corporate communications professionals, was $62,810 in May 2020. This field offers a dynamic and rewarding career path for those interested in shaping corporate narratives and building strong relationships with internal and external audiences.
Real-World Examples of Corporate Communications
Crisis Communication: A Public Apology
A major airline faced backlash for mishandling a flight disruption. Instead of ignoring the issue, the CEO issued a public apology, provided refunds, and offered a clear plan to prevent future incidents. The response helped rebuild trust.
Internal Communication: Employee Engagement
A global tech company launched an internal newsletter featuring leadership insights, employee achievements, and upcoming initiatives. This increased employee engagement and alignment with company goals.
Marketing and Corporate Messaging Alignment
A retail brand ensured its sustainability messaging was reflected across PR statements, marketing campaigns, and executive speeches. This consistency reinforced its commitment to ethical business practices.
Stakeholder Communication: Investor Relations
A publicly traded company maintained credibility by sharing regular financial updates, holding transparent investor meetings, and responding promptly to shareholder concerns.
Related Concepts
Internal vs. External Communications
-
Internal Communication: Employee-focused messaging (e.g., HR updates, leadership emails).
-
External Communication: Customer, investor, and media engagement (e.g., press releases, public relations).
Crisis vs. Reputation Management
-
Crisis Communication: Handling immediate challenges.
-
Reputation Management: Long-term strategy to maintain a positive public image.
Digital Communication Trends
-
Social Media Strategy: Managing brand presence on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram.
-
AI-driven Communication: Using automation to improve customer interactions.
-
Video Communication: Increasing use of video content for storytelling and engagement.
Final Thoughts
Corporate communications shape how businesses interact with employees, customers, and the public. A strong communication strategy ensures clarity, trust, and consistency. Whether handling crises, engaging employees, or crafting a marketing message, effective communication is essential for business success.