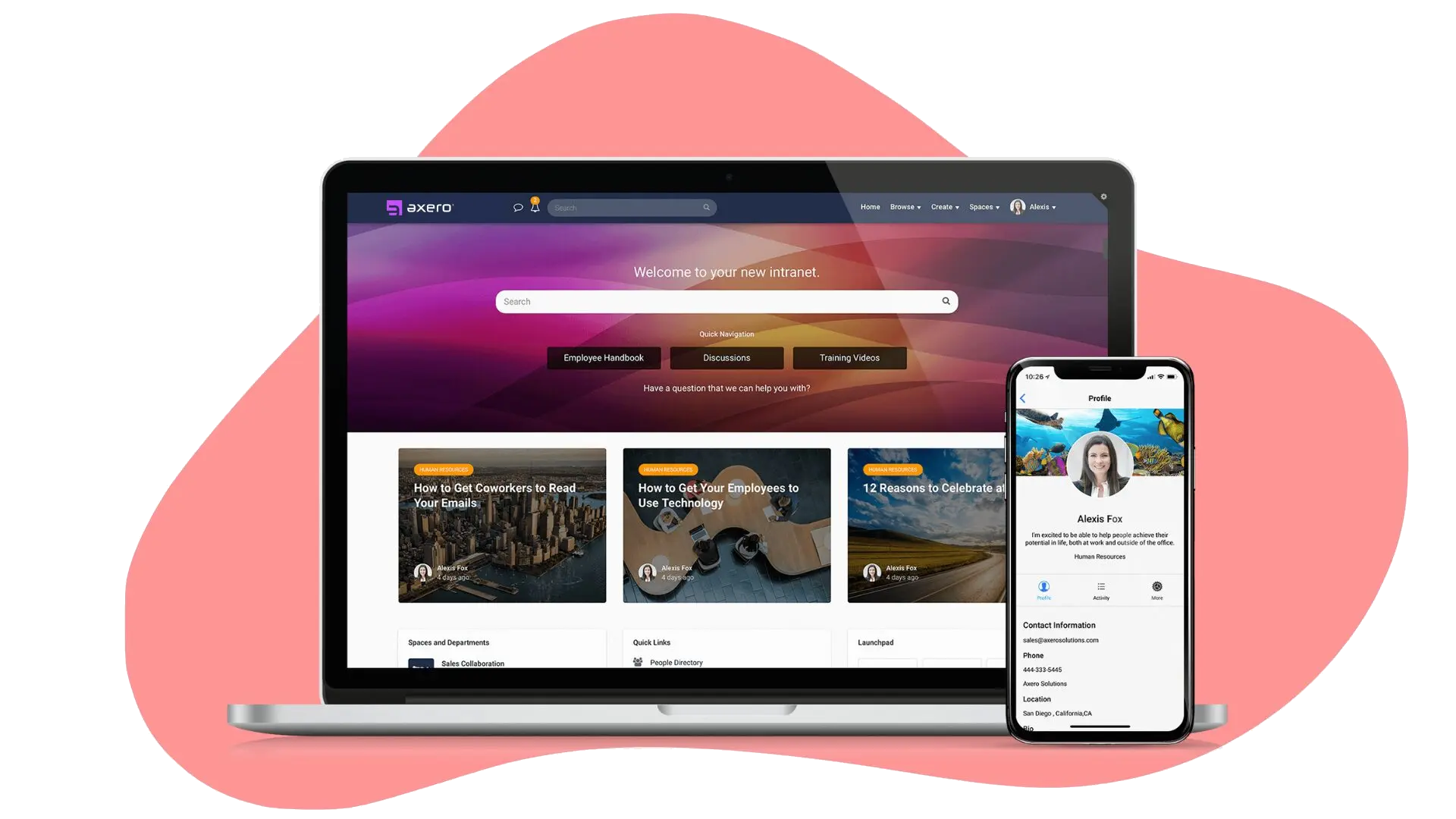
Despite how connected we are through technology, sometimes the modern workplace can really feel disconnected. Whether it’s departments operating in silos or new hires unclear about their onboarding, everything can sometimes seem unclear and disorganized.
How do we get the whole company working from the same page, especially in an era where 35% of US employees work remotely full-time? Can you achieve this with teams scattered across different time zones or even different countries? You certainly can! You just need the help of a CMS intranet. Our guide will break down how this and other tools can all work together to keep your organization on track.
What is a CMS intranet?
CMS stands for content management system. This piece of software allows its users to create and manage content without having to know detailed technical aspects such as coding. You have most likely heard of WordPress, as this is the most common, but it definitely isn’t the only CMS out there!
A company intranet is an internal and centralized hub that only employees can access. You need to have special permission to access an intranet, so it is perfect for internal communications and knowledge sharing for businesses.
So, an intranet content management system combines both. It is a private space for a company to use safely and securely, but it also comes with the ability to upload, alter, and modify any content that is placed into that space. For companies with teams stretched far and wide, it can provide a single place for everyone to gather together through one combined software platform.
Is an intranet the same as a CMS?
Similar to how people mix up an intranet and the internet all the time, at a quick glance, a content management system seems like the same thing as an intranet platform. Depending on the solution, they might not operate the same way. Because they can both be used to share information, you will often find many systems that combine both into one.
Many intranets don’t come with a CMS. If they don’t, typically IT staff have to help with managing the content. Anyone contributing to the content will need to have extensive training if they hope to be able to edit or change the content without the help of an IT pro.
Combining the two into one CMS intranet platform gives you the best of both worlds.
What are the benefits of a CMS intranet?
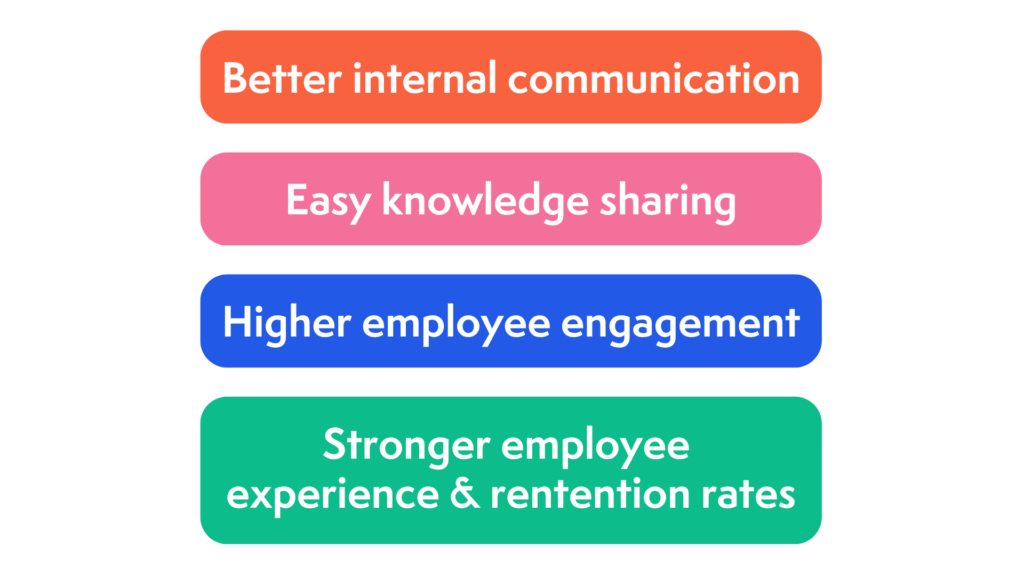
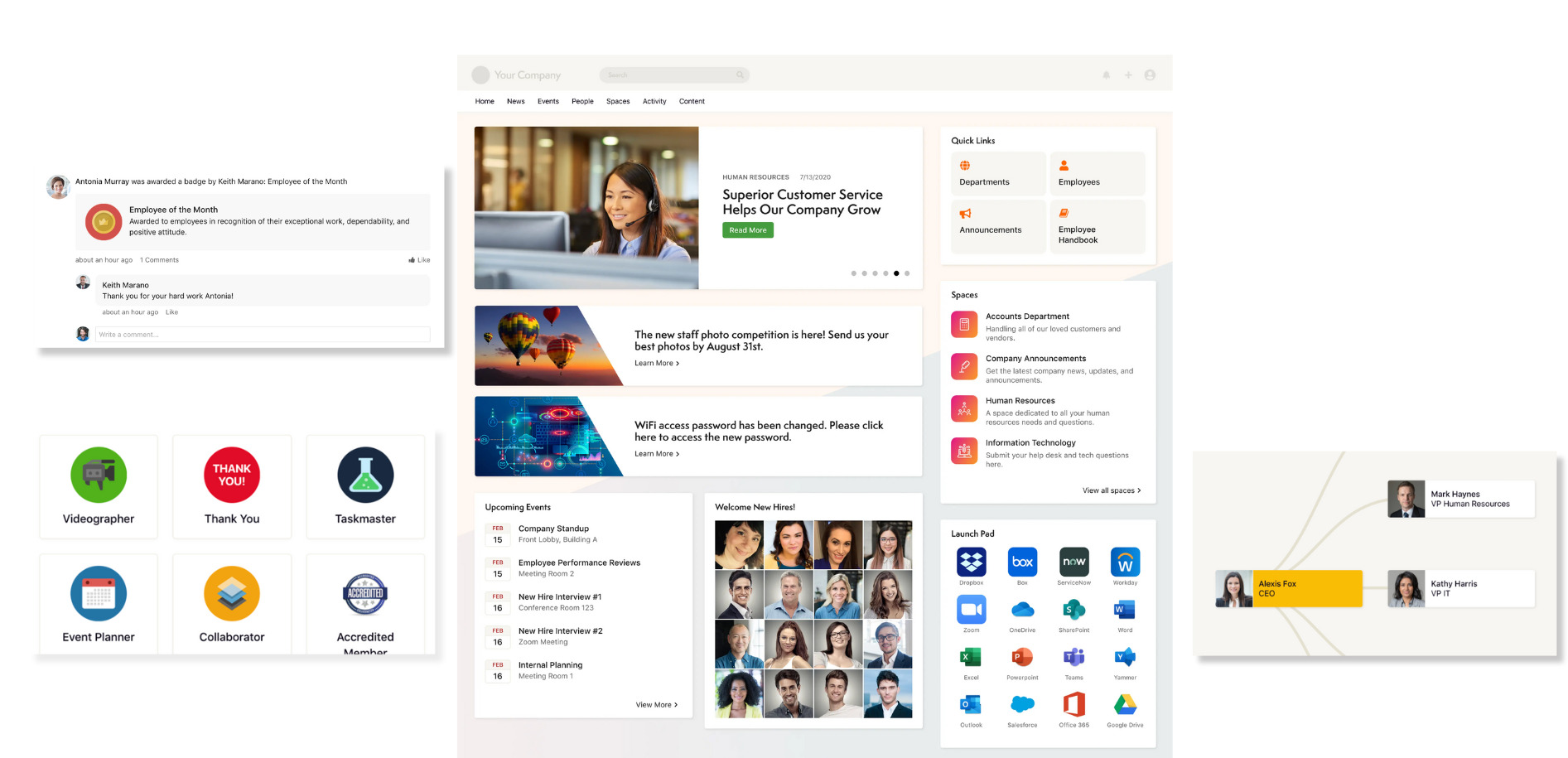
If you need a way to bring everyone in the company together, from new employees to senior leadership, you can’t go wrong with a company intranet with a built-in CMS. Having a CMS intranet means that an organization has one place where they can keep everyone together. Some of the benefits of a CMS intranet that we can typically see include:
1. Better internal communication
Internal communication can be a tricky business for many companies, even for small teams sitting side-by-side all day. 97% of workers believe that communication has an impact on how well they do on their daily tasks. A CMS intranet provides one platform that can be used for all aspects of company communication.
This can extend to both corporate communications and any company-wide notices. For example, when it comes to company updates and notices, these messages are usually sent through email. The problem is, though, that there’s no guarantee that employees are actually opening and reading these important messages. Placing these messages on a CMS intranet gives them a better chance of being seen by those who benefit most from them.
2. Easy knowledge sharing
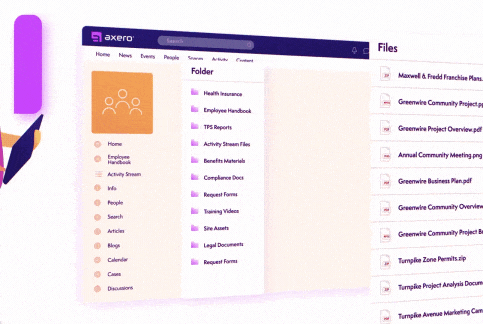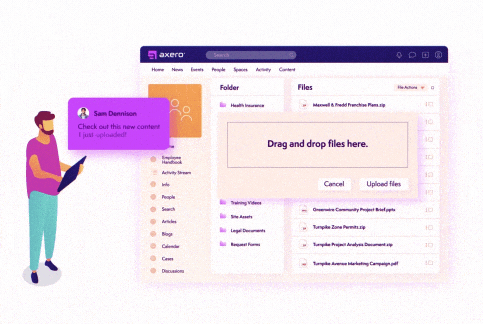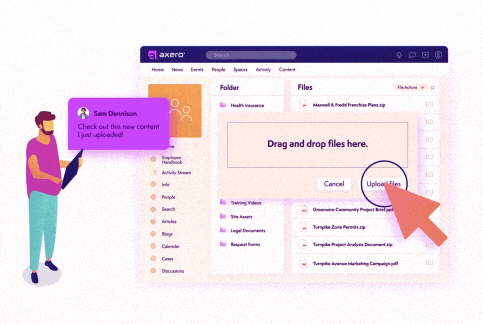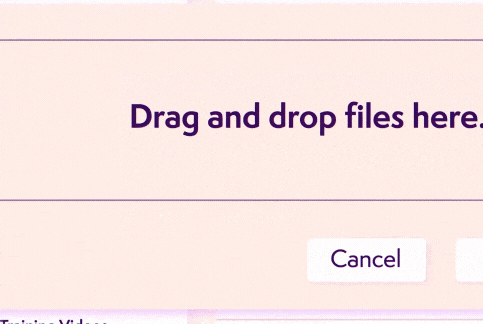
Emails are not the best way to share things. If you have important documents that need to be open and accessible to the right people at the right time, having to dig in a database and email the document can be time-consuming. Not to mention it’s also prone to accidents (i.e. CCing someone who shouldn’t see it, sending an email too soon, the list goes on!)
Having a content management system as part of your company intranet supports easy knowledge sharing and gives people a single source of truth. Since today’s intranets come with strong security protections, you can trust that all of your data and valuable information will be protected against potential attacks and breaches, while also allowing the right people to access important information when they need it.
3. Higher employee engagement
Providing employees with a CMS intranet gives them a place to connect with coworkers and stay informed about important information that they may need to know. Many CMS intranets come with some form of chat function and an array of employee engagement tools, so it is easier than ever to connect in any kind of environment.
Employees can also cut down on the time wasted on searching for relevant documents or information. Everything they need is just a search away on the intranet, improving productivity and boosting engagement.
4. Better employee experience and retention rates
People want to belong. When you take the time to improve your employee experience, you naturally unlock better retention rates too. Employees are more likely to be productive and deliver good levels of engagement when they have a better experience overall.
A big part of this people-centric culture involves offering the right tools to do the job. We all know that a modern job, regardless of industry or specialty, will make use of a wide variety of tools. A corporate intranet might be just one, and it might not even be the tool that an employee uses most each day, but its usability can have a big effect on the employee experience overall.
What are the essential features of a CMS intranet?
As with any tools designed for several uses, you must identify key features that will give your team the greatest level of success when managing their CMS intranet.
1. Easy to use
All CMS intranets should be easy to use. Employees will have different levels of technical understanding. While the IT team or an engineering department will be tech-savvy, it’s fair to say their level of knowledge might not be the same as everyone else’s.
A CMS intranet needs to be accessible to all, including frontline workers. It should feel intuitive to use, and people will hopefully need minimal training to get up to speed with the software. Though the user interface might seem a little intimidating at first, before long people will be navigating with ease.
2. Good security

This should be a given for any tools you bring into your company, but it is especially important when document management is involved. Sensitive materials are often stored on CMS intranets, and the average user might not be able to access every part of the system.
Nearly 73% of US small business owners reported a cyber attack last year. To protect company assets and data while also ensuring that they remain easily accessible to those who rightfully need them, businesses need to pick a CMS intranet with a good level of security.
3. Quick installation
No one wants to unnecessarily clog up employees’ time. IT shouldn’t be spending excessive hours setting up the software on every device. Though employee onboarding should include some discussion and a tour of tools frequently used by the company, hours should not be devoted to exploring and getting to know one tool.
Instead, choose software that can be loaded and set up in the blink of an eye. Though you might have to work behind the scenes to get the user interface ready, when it comes to actually rolling it out to users, everything should go as smoothly as possible. Many CMS intranets nowadays are actually cloud-based, so there is no need for a download and installation. All you need is an internet connection, and you are good to go!
4. Device compatibility
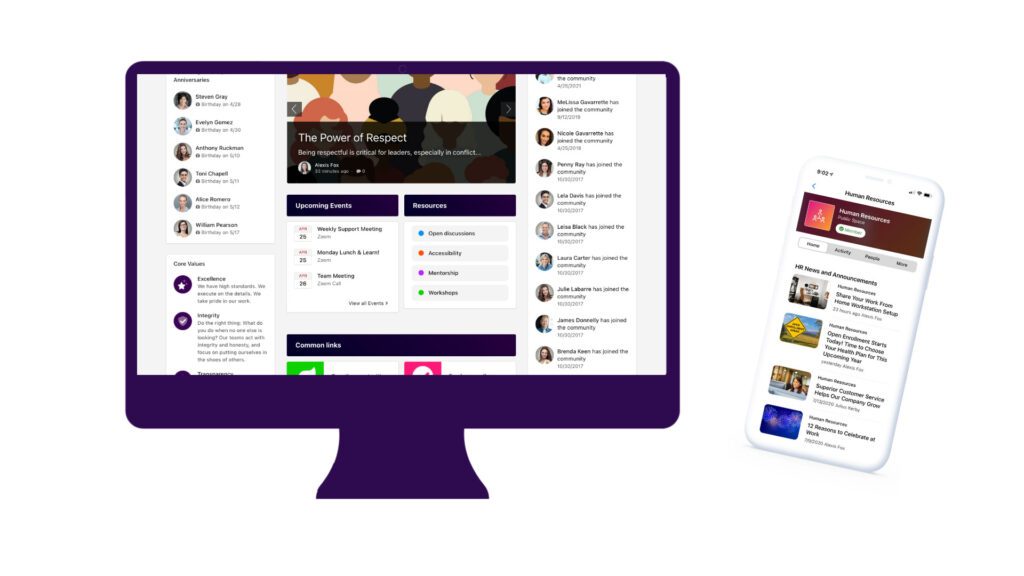
The vast majority of your employees will be accessing the CMS intranet via their work device – usually a laptop nowadays. However, that doesn’t mean that everyone will always be accessing the corporate intranet from this device. For intranets with CMS capabilities, a mobile intranet app can make the world of a difference.
A manager may want to throw out a quick post they come up with on their commute, or perhaps someone wants to check a document in a meeting. All they have to do is pull out their smartphone, and they can instantly access any part of the intranet they need.
5. Chat and social features
No CMS intranet should be all work and no fun. Many offer opportunities for employee engagement and improving company culture through the creation of a community hub. Here, users can come together to create a sense of community that isn’t necessarily related to business. Though the intranet is for the business first and foremost, it can also be used by employees to share, like, and comment on a variety of other content. Think of it like a social media network just for your company!
This can also be great for gauging how employees feel through the use of surveys, questions, and other forms of feedback. Placing it on the company intranet can be way less invasive than sending around email after email – and you might be more likely to actually get a reply.
6. AI-powered search functions
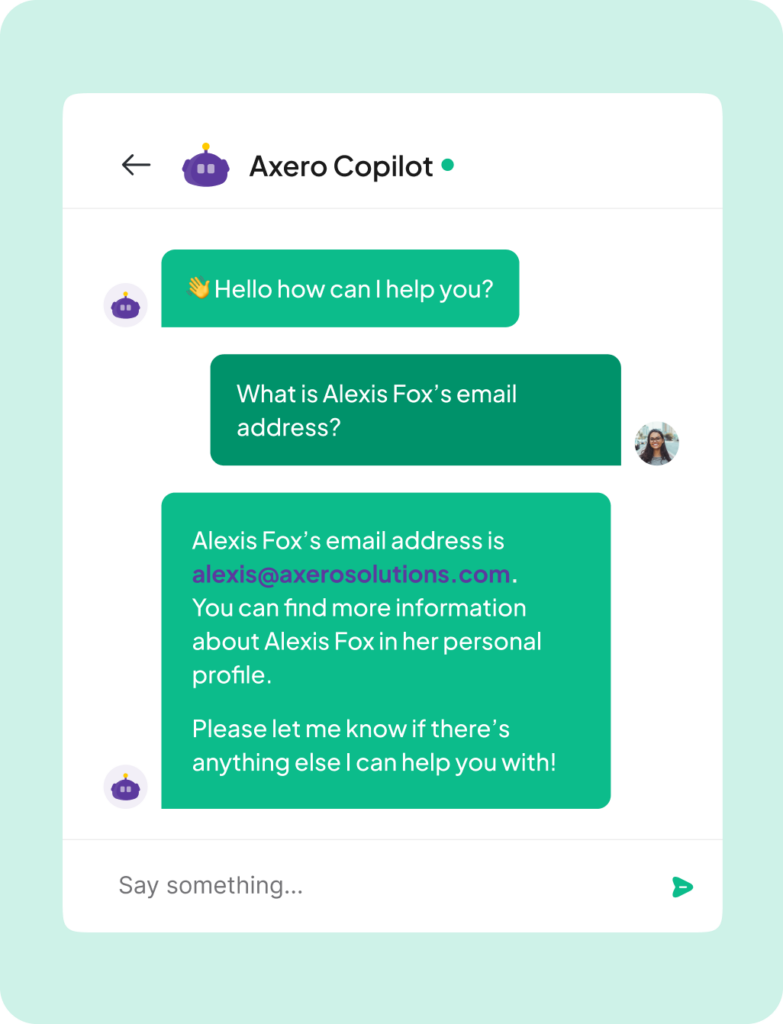
When you have your knowledge management system in place, documents can quickly become difficult to find! Even with the best organization in the world, a large database can be difficult to navigate.
An intranet that harnesses the power of artificial intelligence makes finding the right digital content a bit easier. You just have to ask the intranet for what you want, and then it digs the file out for you. Axero’s new feature Copilot (currently in beta!) is a bot that can do exactly that. Rather than waste time looking for specific important documents, you just have to ask the system for what you want!
7. Easy third-party integrations
While the right CMS intranet should be flexible enough to meet your needs and expectations, there will be some things that it can’t do. Having easy third-party integrations in place can help you streamline processes and ensure that no information is lost in transition.
For example, most people use Office 365 in their everyday work. Easy integration between the two makes document management easier, and employees can access the tools they need the most without ever having to leave the intranet.
8. Document management
Managing documents is never easy, but it is one of the primary uses of a CMS intranet. Anyone well-versed in content management knows that even the best-laid systems can end up with lost documents or maybe information spread across multiple entries that are impossible to track down.
If so, this is the time to take a step back and reassess. By placing all documents within the CMS intranet, they become much easier to find. Employees can hop on and perform a quick search or go to a designated knowledge base for precisely what they are searching for, without worrying that they are going to pull up either the wrong or an outdated piece of information.
9. Full customization
To make CMS intranets feel like just another part of the company, they have to be fully customizable. This goes beyond adding logos into the header and spreading your company colors across all the pages of your intranet portal.
A good CMS intranet will give you full control over every aspect of customization. You should be able to decide what widgets you want to appear on the homepage, have creative control over intranet templates, decide where they appear, and what tools all come together to create an intranet that is completely unique to your company alone. Choose the design and widgets that best suit your company’s brand and create a space that your employees are happy and proud to engage with.
10. Analytics
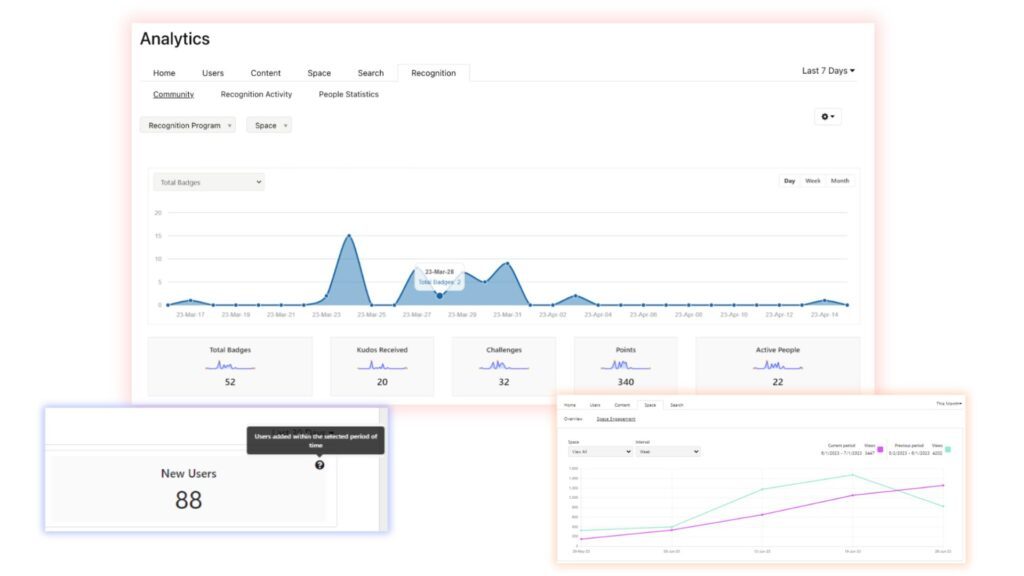
What would a tool be without analytics? You need to know which sections of the CMS intranet your employees are engaging in or with, and which are not getting the most traffic. Asking for feedback can only get you so far; sometimes, you have to look at the cold, hard data to see the bigger picture.
Don’t waste time trying to wrangle data or doing legwork. Any data should be collected, tabulated, and presented by the CMS intranet in an easily understandable format.
How to introduce a CMS intranet to your employees
So, you’ve found the perfect CMS intranet for your company to use, and you have put all the work in to optimize it and make it a great tool for collaboration amongst your team. How do you introduce it to your employees and make the transition as smooth as possible?
1. Define clear objectives
Why have you chosen to move to this particular platform over others? What benefits do you hope to gain from using this CMS intranet? You can’t expect to know if the transition to the new system will work if you don’t know what you want in the first place. Define clear objectives and identify a few metrics you can track so you can tell if this move has been a success.
2. Train everyone up
Though CMS intranets are supposed to be intuitive, we bet that the average user will feel a little overwhelmed when they encounter the interface for the first time. Train up a few employees to act as ambassadors and let them help roll out the software to wider teams. The initial launch might take some concentrated effort from all of you, but it can teach some valuable lessons for future onboarding!
3. Establish governance and rules
This is a piece of software that the whole company will have access to, even if some areas need certain clearances to gain entry to sensitive data. Establish clear rules for creating and publishing content and ensure that there is also a clear system for sanctions and reprimands if an employee breaks these rules.
4. Regularly update
You can’t just upload some helpful information and important documents and then leave them to rot in the system. An intranet should be the central point for a company and the best place to find out information. Without dedicating time and energy to maintaining and regularly updating your space, it will quickly become obsolete.
5. Gather feedback
Remember those metrics we set? Now is the time to put them to the test, and find out what your users think at the same time. What do they like, what do they not? Are you seeing a good ROI? Once you have established how the intranet is performing, you can make any required adjustments to make it even better.
Why choose Axero as your CMS intranet?
![<!--HubSpot Call-to-Action Code --><span class="hs-cta-wrapper" id="hs-cta-wrapper-de2f0cc3-a321-4658-9124-36ab91b4f3b6"><span class="hs-cta-node hs-cta-de2f0cc3-a321-4658-9124-36ab91b4f3b6" id="hs-cta-de2f0cc3-a321-4658-9124-36ab91b4f3b6"><!--[if lte IE 8]><div id="hs-cta-ie-element"></div><![endif]--><a href="https://cta-redirect.hubspot.com/cta/redirect/347412/de2f0cc3-a321-4658-9124-36ab91b4f3b6" ><img class="hs-cta-img" id="hs-cta-img-de2f0cc3-a321-4658-9124-36ab91b4f3b6" style="border-width:0px;" src="https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/347412/de2f0cc3-a321-4658-9124-36ab91b4f3b6.png" alt="best intranet software platforms"/></a></span><script charset="utf-8" src="https://js.hscta.net/cta/current.js"></script><script type="text/javascript"> hbspt.cta.load(347412, 'de2f0cc3-a321-4658-9124-36ab91b4f3b6', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); </script></span><!-- end HubSpot Call-to-Action Code -->](https://axerosolutions.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/wiki-1024x1009.jpg)
When deciding what you want in a CMS intranet, you can often end up with a list as long as your arm. How can you possibly find one tool that meets everything on your wishlist?
Luckily for you, it exists in Axero! Our platform supports smooth collaboration and communication and we can help you tailor and shape it to whatever you want to be. Secure? You bet. Easy to use? We got you. Fun and flexible? Of course!
Want to see what Axero can do for you? Get in touch today and get ready to see how the power of an intranet can bring your company together under one neat umbrella.